- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Interleukin 5, Eosinophil Differentiation Factor (EDF), T-Cell Replacing Factor (TRF), Colony-Stimulating Factor (Eosinophil), B-Cell Differentiation Factor II (BCDF-II), Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte inducer.
-
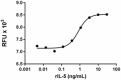
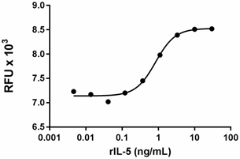
Rat IL-5 induces the proliferation of TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells in a dose dependent manner. EC50 for this effect is 0.5 – 2.5 ng/mL. -
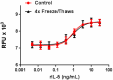
Stability testing for rat IL-5. Recombinant rat IL-5 was aliquoted in PBS, pH 7.2 at 0.2 mg/mL and one aliquot was kept at 4°C (control), and another was frozen and thawed four times (4x freeze/thaws). After this procedure, the samples were tested for their ability to induce TF-1 cell proliferation.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 778502 | 10 µg | $218.00 | |||
| 778504 | 25 µg | $364.00 | |||
| 778506 | 100 µg | $1113.00 | |||
| 778508 | 500 µg | $2929.00 | |||
Select size of product is eligible for a 40% discount! Promotion valid until December 31, 2024. Exclusions apply. To view full promotion terms and conditions or to contact your local BioLegend representative to receive a quote, visit our webpage.
IL-5 is a homodimeric glycoprotein that was initially identified by its ability to support the in vitro growth and differentiation of mouse B cells and eosinophils. IL-5 induces eosinophil progenitor cell proliferation, terminal differentiation, and activation. In animal models of allergic diseases or helminth infection, IL-5 induces a massive proliferation of eosinophil progenitors in the bone marrow, promotes eosinophil recruitment with eotaxins, and prolongs eosinophil survival in local tissues. IL-5 regulates genes involved in B cell terminal differentiation. Thus, IL-5 induces CD38-activated splenic B cells to differentiate into immunoglobulin M-secreting cells and go through m to g1 class switch recombination at the DNA level, resulting in immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) production. IL-5 binds the IL-5R complex, which consists of an IL-5Rα chain specific for IL-5 and a common β-chain that is shared by the receptors for IL-3 and GM-CSF. The alpha subunit is required for ligand-specific binding whereas association with the beta subunit results in increased binding affinity. IL-5 plays important roles in the pathogenesis of asthma, hypereosinophilic syndromes, and eosinophil-dependent inflammatory disease.
Product Details
- Source
- Rat IL-5, amino acids (Met20 - Val132) (Accession # Q08125 ) was expressed in 293E cells. The amino-terminal contains 8His-GGGSIEGR tag
- Molecular Mass
- The 133 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 15.1kD. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced protein migrate at approximately 20 -28kD and 45 - 50kD respectively by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is His.
- Purity
- > 95% by SDS-PAGE gel as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in PBS pH 7.2.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.1 EU per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- Rat IL-5 induces the proliferation of TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells in a dose dependent manner. The proliferation was measured using Deep Blue Cell Viability™ Kit (Cat. No. 424701). The ED50 = 0.5 - 2.5 ng/mL.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Dimer
- Distribution
-
Activated Th2 cells, mast cells, eosinophils, and basophils. In addition, newly identified IL-5 producing cells are: natural helper cells or nuocytes (lately identified as type II innate lymphoid cells), MPPtype2, and Ih2 cells.
- Function
- IL-5 regulates the production of eosinophils from purified hematopoieitic progenitors and regulates genes involved in B cell terminal differentiation. IL-25 and IL-33 induce Th2 cytokines, among them IL-5.
- Interaction
- Eosinophils, B cells, basophils, and activated T cells.
- Ligand/Receptor
- Heterodimer IL-5Rα (CD125); β-subunit (CDw131). The β-subunit is shared with IL-3R and GM-CSFR.
- Bioactivity
- Induces the proliferation of TF-1 cells.
- Cell Type
- Hematopoietic stem and progenitors, Embryonic Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
- Lopez AF, et al. 1988. J Exp Med. 167:219.
- Horikawa K and Takatsu K, 2006. Immunology. 118:497.
- Moro K, et al. 2010. Nature. 463:540.
- Neill DR, et al. 2010. Nature. 464:1367.
- Saenz SA, et al. 2010. Nature. 464:1362.
- Ikutai M, et al. 2012. J Immunol. 188:703.
- Yazuda K, et al. 2012. P Nat Acad Sci USA. 109:3451.
- Gene ID
- 24497 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about IL-5 on UniProt.org
