- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- IL7, Interleukine 7, Interleukin-7, Lymphopoietin-1, PBGF
-
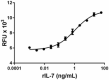
Recombinant rat IL-7 induces the proliferation of PHA activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes. -
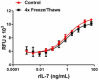
Stability testing for recombinant rat IL-7. Recombinant rat IL-7 was aliquoted in DPBS at 0.2 mg/mL and one aliquot was kept at 4°C (control) and another was frozen and thawed four times (4X Freeze/Thaws). After this procedure, the samples were tested by the induction of proliferation of PHA activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 777702 | 10 µg | $206.00 | |||
| 777704 | 25 µg | $382.00 | |||
Select size of product is eligible for a 40% discount! Promotion valid until December 31, 2024. Exclusions apply. To view full promotion terms and conditions or to contact your local BioLegend representative to receive a quote, visit our webpage.
IL-7 was initially described as a stromal derived factor which is capable of inducing the growth of pre-B cells in vitro. IL-7 acts on a variety of cells through its receptor (IL-7R), a heterodimer consisting of IL-7Rα (CD127) and a common γc chain (CD132) shared by other cytokine (IL-2, IL-4, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21) receptors. In addition, IL-7Rα is shared with TSLP. The generation of IL-7-deficient and IL-7Rα-deficient mice and monoclonal antibody blocking experiments confirmed the requirement of IL-7 for B-cell development in mice. Mutations in IL-7Rα observed in patients with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) also underlies the importance of IL-7 signaling in T-cell development in humans. However, the presence of B cells in these individuals suggests important differences between the role of IL-7 in murine and human lymphocyte development. Thus, although human B-cell development does not appear to require IL-7, immature human B cells do proliferate in response to IL-7. Nevertheless, most recent information suggests that IL-7 dependence in human lymphopoiesis increases during development in cord blood and bone marrow. The amino acid sequence of rat IL-7 possesses approximately 89 % and 70 % identity with mouse and human, respectively. Microarray data identified IL-7 transcripts in preovulatory follicles in rats, while IL-7Rα (CD127) and γc chain (CD132) were detected in granulosa cells and preovulatory oocytes. In vitro studies showed that IL-7 induces oocyte maturation and inhibits apoptosis in granulosa cells.
Product Details
- Source
- Rat IL-7, amino acids Asp26 – Ile154 (Accession # P56478) was expressed in CHO cells. The amino-terminal contains 8His-2(GGGS) IEGR tag.
- Molecular Mass
- The 149 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 16.9 kD. The DTT-reduced and non reduced protein migrates at approximately at 20 – 25 and 17 kD respectively by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is His.
- Purity
- >95 %, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in DPBS, pH 7.2
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.1 EU per µg protein as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
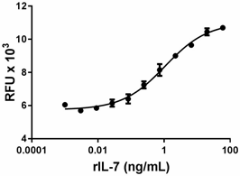
- Recombinant rat IL-7 induces the proliferation of PHA activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes. The ED50 = 0.3 – 1.5 ng/mL.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Cytokine
- Distribution
-
IL-7 is produced by epithelial cells in thymus, bone marrow, and intestine. Additional sites of IL-7 production include epithelial goblet cells, keratinocytes, fetal liver, adult liver, dendritic cells, skeletal muscle cells, fibroblastic reticular cells, and follicular dendritic cells.
- Function
- IL-7 induces proliferation of human immature B cells, and it is critical for T-cell development and peripheral T-cell homeostasis.
- Interaction
- Immature B cells, T cells, naïve and memory CD4 and CD8 cells, dendritic cells.
- Ligand/Receptor
- IL-7Rα (CD127), common gamma chain (γc or CD132).
- Bioactivity
- Rat IL-7 induces the proliferation of PHA activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes.
- Cell Type
- Hematopoietic stem and progenitors
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines, Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
- Park LS, et al. 1990. J Exp Med. 171:1073.
- Fry TJ and Mackall CL, 2002. Blood. 99:3892.
- Lai L, et al. 2006. Blood. 107:1776.
- Link A, et al. 2007. Nat Immunol. 8:1255.
- Wofford J, et al. 2008. Blood 111:2101.
- Parrish YK, et al. 2009. J Immunol. 182:4255.
- Saini M, et al. 2009. Blood. 113:5793.
- Guimond M, et al. 2009. Nat Immunol. 10:149.
- Cheng Y, et al. 2011. Biol Reprod. 84:707.
- Gene ID
- 25647 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about IL-7 on UniProt.org
