- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- CSF1, CSF-1, MCSF
-
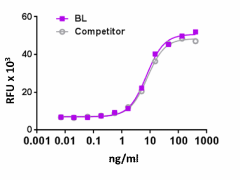
Recombinant rat M-CSF induces the proliferation of M-NFS-60 cells in a dose dependent manner. BioLegend’s protein was compared side-by-side to the leading competitor’s equivalent product.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 556902 | 10 µg | $223.00 | |||
| 556904 | 25 µg | $422.00 | |||
| 556906 | 100 µg | $1160.00 | |||
M-CSF was first characterized as a glycoprotein that induces monocyte and macrophage colony formation from precursors in murine bone marrow cultures. M-CSF is constitutively present at biologically active concentrations in human serum, and binds CD14+ monocytes, and promotes the survival and proliferation of peripheral blood monocytes. In addition, M-CSF enhances monocyte functions such asphagocytic activity, microbial killing, and tumor cell cytotoxicity. It also induces the synthesis of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1-β, TNF-α, and INF-γ in monocytes. M-CSF induces RANKL in mature osteoclasts, and is consequently a potent stimulator of mature osteoclast resorbing activity. Also, M-CSF induces VEGF in monocytes in human tumors. High levels of M-CSF, mononuclear phagocytes, and VEGF are associated with poor prognosis in patients with cancer. High levels of M-CSF have also been correlated to other pathologies such as pulmonary fibrosis and atherosclerosis. M-CSF binds to its receptor M-CSFR, and this receptor is shared with another ligand, IL-34. Human M-CSF and IL-34 exhibit cross-species specificity by both binding to the human and mouse M-CSF receptors. Respectively, rat M-CSF has 80% and 77% identity with mouse and human M-CSF.
Product Details
- Source
- Rat M-CSF, amino acids (Glu33-Pro186) (Accession# NM_023981), was expressed in 293E cells.
- Molecular Mass
- The 154 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 20.1 kD. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced protein migrate at approximately 25 - 35 kD and 55 - 70 kD by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Glu.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in PBS, pH 7.2.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 ng per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- ED50 = 2.5 - 12.5 ng/mL, corresponding to a specific activity of 0.8 - 4.0 x 105 units/mg, as determined by induction of N-MSF-60 mouse myelogenous leukemia lymphoblast cell proliferation.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
- Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Disulfide-linked glycosilated homodimer
- Distribution
-
M-CSF is broadly expressed. It is released by fibroblasts, breast cancer cell lines, alveolar macrophages, stromal bone marrow cells, endothelial cells, and mesenchymal cells.
- Function
- M-CSF is the key regulator of the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes and also plays a central role in the regulation of osteoclastogenesis. M-CSF also regulates the development of Paneth cells, Langerhans cells, lamina propria dendritic cells, and microglia.
- Interaction
- Monocytes, macrophages, mononuclear phagocyte precursors, microglia, proliferating smooth muscle cells, umbilical vein endothelial cells, and breast cancer cell lines.
- Ligand/Receptor
- M-CSFR or CSF1R (CD115).
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells, Hematopoietic stem and progenitors
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Cell Proliferation and Viability, Immunology, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines, Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
1. Kawasaki ES, et al. 1985. Science 230:291.
2. Wei S, et al. 2010. J. Leuko. Biol. 88:495.
3. Hodge JM, et al. 2011. PLos One 6:e21462.
4. Morandi A, et al. 2011. PLos One 6:e27450.
5. Erblich B, et al. 2011. PLos One 6:e26317.
6. MacDonald KP, et al. 2010. Blood 116:3955.
7. Nakanishi A, et al. 2013. Int. J. Mol. Med. 31:874. - Gene ID
- 78965 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about M-CSF on UniProt.org
