- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- KIT-ligand, Kitl, KL-1, mast cell grow factor (MGF), steel factor (SF), FPH2, SHEP7
-
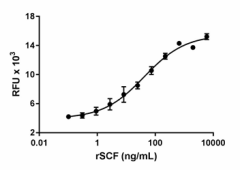
Recombinant rat SCF induces the proliferation of human TF-1 cells. The ED50 for this effect is 20 – 60 ng/mL.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 782301 | 2 µg | $89.00 | |||
| 782302 | 10 µg | $223.00 | |||
This product is not available for shipping outside of the United States.
Select size of product is eligible for a 40% discount! Promotion valid until December 31, 2024. Exclusions apply. To view full promotion terms and conditions or to contact your local BioLegend representative to receive a quote, visit our webpage.
Rat SCF was identified and purified from buffalo rat liver-conditioned medium. It is synthesized as a membrane-bound form of 273 amino acids. The protein contains a proteolytic cleavage site that is cleaved from the cell to release an active soluble protein. The soluble SCF is glycosylated at both N-linked and O-linked sites. MMP-9 plays a physiological role in SCF release from the membrane, and this action has a significant part in differentiating and mobilizing stem and progenitors cells from the bone marrow. SCF increases the proliferation of myeloid and lymphoid hematopoietic progenitors in bone marrow cultures. SCF/c-kit interaction in mast cells results in mast cell degranulation and liberation of mediators, such as histamine, inflammatory cytokines, and chemokines. Also, activation of c-kit in dendritic cells regulates T helper cell differentiation and allergic asthma. In addition, SCF plays an important role in revascularization of ischemic limbs. Ischemia induces plasma elevation of SCF and thrombopoietin (TPO) and lower levels of GM-CSF and erythropoietin (EPO). SCF and TPO induce the release of CXCL12 from platelets thereby increasing CXCL12 levels in plasma. This results in an extensive mobilization of CXCR4+VEGFR1+ cells (hemangiocytes) accelerating revascularization of the ischemic limbs. SCF and its receptor (c-kit) drive the recruitment and expansion of different stem cell types, including hematopoietic, neuronal, germ, and cardiac. SCF gene transfer promotes cardiac repair after myocardial infarction via in situ recruitment and expansion of c-kit+ cells. Also, c-kit signaling plays a key role in the pancreas, including islet morphogenesis, islet vascularization, and beta cell survival and function.
Product Details
- Source
- Rat SCF, amino acid Met - (Gln26– Ala189) (Accession # NP_068615.1) was expressed in E.coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 165 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 18.4 kD. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Met.
- Purity
- ≥ 98% by SDS-PAGE gel and HPLC analyses.
- Formulation
- Lyophilize from sterile 0.22 μm filtered protein solution is in PBS pH7.2.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.1 EU per μg protein as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- Lyophilized recombinant protein is at 2 and 10 μg total protein
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for one month, at -20°C for six months, or at -70°C for one year. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. Reconstitute the protein in sterile water at 0.1 mg/ml. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C to -70°C. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in sterile buffer (PBS, HPBS, DPBS, or EBSS) containing carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA and stored in working aliquots at -20°C to -70°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- Recombinant rat SCF induces the proliferation of human TF-1 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The proliferation was measured using the Deep Blue Cell Viability™ Kit (Cat. No. 424701). The ED50 for this effect is 20 – 60 ng/mL.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in lliophylized format are shipped on blue ice.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Homodimer
- Distribution
-
Fibroblast, keratinocytes, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells.
- Function
- SCF promotes growth, differentiation, and activation of mast cells, takes part in early stages of hematopoiesis, erythropoiesis, development of melanocytes, gametogenesis, and the survival of Cajal cells from the intestine.
- Interaction
- Mast cells, natural killer cells, dendritic cells, eosinophils, epithelial, endothelial, melanocytes, germen cells, cholangiocytes, platelets, myeloid leukaemia cells, and intestinal cells of Cajal.
- Ligand/Receptor
- c-kit (CD117)
- Bioactivity
- Rat SCF induces the proliferation of human TF-1 cells.
- Cell Type
- Hematopoietic stem and progenitors, Embryonic Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Angiogenesis, Cell Biology, Immunology, Signal Transduction, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines, Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
- Zsebo KM, et al. 1990. Cell. 63(1):195-201
- Lu HS, et al. 1996. J Biol Chem. 271:11309.
- Heissig B, et al. 2002. Cell. 109:625.
- Jin DK, et al. 2006. Nat Med. 12:557.
- Krishnamoorthy N, et al. 2008. Nat Med. 14:565.
- Ray P, et al. 2010. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1183:104.
- Yaniz-Galende E, et al. 2012. Circ Res. 111:1434.
- Feng ZC, et al. 2015. Diabetologia. 58:654.
- Gene ID
- 60427 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about SCF on UniProt.org
