- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Vascular permeability factor (VPF), VEGF164, VEGF-A
-
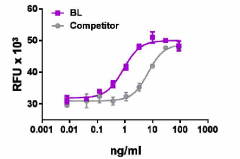
Recombinant rat VEGF-A induces the proliferation of HUVEC cells in a dose dependent manner. BioLegend’s protein was compared side-by-side to the leading competitor’s equivalent product.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 556804 | 25 µg | $411.00 | |||
| 556806 | 100 µg | $879.00 | |||
| 556808 | 500 µg | $2332.00 | |||
Select size of product is eligible for a 40% discount! Promotion valid until December 31, 2024. Exclusions apply. To view full promotion terms and conditions or to contact your local BioLegend representative to receive a quote, visit our webpage.
The VEGF family includes VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, and placental growth factor (PlGF). VEGF-A is generated as multiple isoforms by alternative splicing. These isoforms are generically identified as VEGFxxx where xxx refers to the number of amino acids. Rat isoforms include VEGF-120, VEGF-164, and VEGF-188. The VEGF gene is highly conserved among human, dog, cow, mouse, rat, pig, and chicken. VEGF164 plays a critical role in new blood vessel formation in vivo. VEGF164 induces angiogenesis on different levels. It acts as mitogen especially on endothelial cells, raises the vessel permeability and dilatation by releasing NO, and has chemotactic impact on monocytes/macrophages which plays a crucial role in inducing inflammatory neovascularization. Angiogenic activities of VEGFs are mediated primarily through the two receptors VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2. VEGFR-2 signaling is enhanced by interactions with co-receptors such as heparin/heparan sulfate and Neuropilin 1. VEGF induces osteoclast migration and activation. In addition, it supports the survival of mature osteoclasts. These processes play a key role in repairing and remodeling during bone development.
Product Details
- Source
- Rat VEGF-A, amino acids (Ala27-Arg190) (Accession# AY033506), was expressed in 293E cells.
- Molecular Mass
- The 164 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 19.2 kD. The protein migrates approximately at 25 kD in DTT-reducing conditions and at approximately 50 kD in non-reducing conditions by SDS-PAGE. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Ala.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in 5 mM citric acid, 5 mM NaH2PO4, 0.15 M NaCl, pH 4.0.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 ng per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 10 and 25 µg sizes are bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- ED50 = 0.6 - 3.6 ng/mL, corresponding to a specific activity of 0.27 - 1.67 x 106 units/mg, as determined by induction of HUVEC cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
- Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Disulphide-linked homodimer
- Distribution
-
VEGF-164 is expressed in most tissues and is released by many cells, including endothelial cells. Although it is a diffusible protein, a significant fraction remains cell- and extracellular-matrix associated.
- Function
- VEGF-164 acts on endothelial cells, induces angiogenesis, vasculogenesis, cell growth, cell migration, and inhibits apoptosis. It increases vascular permeability. VEGF is upregulated by hypoxia, and CXCL8/IL-8 stimulates VEGF expression and VEGFR2 activation in endothelial cells.
- Interaction
- Endothelial cells, bone marrow-derived pericytes, vascular smooth muscle cells, monocytes, macrophages, and mesenchymal stem cells.
- Ligand/Receptor
- VEGFR-1 (fms-like tyrosine kinase 1) and VEGFR-2 (kinase domain receptor, and fetal liver kinase 1).
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Neural Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Angiogenesis, Cell Biology, Neuroscience, Stem Cells, Synaptic Biology
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines, Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
1. Sulpice E, et al. 2004. Eur. J. Biochem. 271:3310.
2. Cursiefen C, et al. 2004. J. Clin. Invest 113:1040.
3. Voelkel NF, et al. 2006. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 290:L209.
4. Rennel E, et al. 2008. Br. J. of Cancer 98:1250.
5. Reddy K, et al. 2008. Angiogenesis 11:257.
6. Martin D, et al. 2008. J. Biol. Chem. 284:6038.
7. Muthusamy A, et al. 2010. BMC Biochemistry 11:43. - Gene ID
- 83785 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about VEGF-A on UniProt.org
