- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Coronavirus spike Protein RBD, S1 RBD, Spike Protein RBD
-
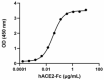
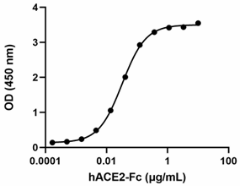
When recombinant SARS-CoV-2 S1 Protein RBD (V483A) is immobilized at 2 µg/mL, recombinant human ACE2-Fc (Cat. No. 793202) binds in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is 10 - 50 ng/mL. HRP Protein A (Cat. No. 689202) was used to detect the binding. -
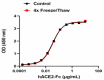
Stability Testing for Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 S protein RBD (V483A). Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 S protein RBD (V483A) was aliquoted in PBS at 0.2 mg/mL. One aliquot was frozen and thawed four times (4x Freeze/Thaw), and compared to a control kept at 4°C (Control). The samples were tested by their ability to bind recombinant human ACE2-Fc chimera in a dose dependent-manner. The ED50 for this effect is 10 – 50 ng/mL.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 560004 | 25 µg | $215.00 | |||
| 560006 | 100 µg | $510.00 | |||
SARS-CoV-2 is a respiratory virus which causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The coronavirus spike (S) glycoprotein is a class I viral fusion protein on the outer envelope of the virion that plays a critical role in viral infection by recognizing host cell receptors and mediating fusion of the viral and cellular membranes. The S glycoprotein is synthesized as a precursor protein consisting of ~1,300 amino acids that is then cleaved into an amino (N)-terminal S1 subunit (~700 amino acids) and a carboxyl (C)-terminal S2 subunit (~600 amino acids). Three S1/S2 heterodimers assemble to form a trimer spike protruding from the viral envelope. The S1 subunit contains a receptor-binding domain (RBD) that can specifically bind to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), the receptor on target cells. Triggered by receptor binding, proteolytic processing and/or acidic pH in the cellular compartments, the class I viral fusion protein undergoes a transition from a metastable pre-fusion state to a stable post-fusion state during infection, in which the receptor-binding subunit is cleaved, and the fusion subunit undergoes large-scale conformational rearrangements to expose the hydrophobic fusion peptide, induce the formation of a six-helix bundle, and bring the viral and cellular membranes close for fusion. The trimeric SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) S glycoprotein consisting of three S1-S2 heterodimers binds the cellular receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and mediates fusion of the viral and cellular membranes through a pre- to post-fusion conformation transition. SARS-CoV-2 S1 with a mutation at the position 483, where the Val has changed to Ala, appeared initially in North America. This mutation is located in the S1 protein RBD; nevertheless, Val483 is not directly involved in the contact with ACE2, but it might affect the binding energy and subsequently favor the mutant to bind stronger to ACE2.
Product Details
- Source
- SARS-CoV-2 S Protein RBD (V483A) amino acid Arg319-Phe541 (Accession # QHD43416.1), with a C-terminal 8His tag was expressed in 293E cells.
- Molecular Mass
- The 234 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 26.3 kD. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced proteins migrate at approximately 35 kD and 30 kD by SDS-PAGE, respectively. The predicted N-terminal amino acid is Arg.
- Purity
- > 95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in PBS, pH 7.2
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.1 EU per µg protein as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 25 µg size is bottled at 200 µg/mL. 100 µg size and larger sizes are lot-specific and bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C to 8°C up to 2 weeks, at -20°C up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- When recombinant SARS-CoV-2 S1 Protein RBD (V483A) is immobilized at 2 µg/mL recombinant human ACE2-Fc (Cat. No. 793202) binds in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is 10 - 50 ng/mL. HRP Protein A (Cat. No. 689202) was used to detect the binding.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are validated in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Monomer
- Distribution
-
SARS-CoV-2
- Function
- Attaches the virion to the cell membrane by interacting with host receptor (ACE2) initiating the infection
- Interaction
- Ciliated cells in nasal mucosa and bronchus, pneumocytes
- Ligand/Receptor
- ACE2
- Bioactivity
- Measured by its ability to bind to recombinant human ACE2-Fc
- Cell Type
- Endothelial cells, Macrophages, NK cells, T cells
- Biology Area
- Adaptive Immunity, Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Antigen References
-
- Lu R, et al. 2020. Lancet. S0140-6736(20)30251-8.
- Li F. 2016. Annu Rev Virol. 3:237-261.
- Belouzard S, et al. 2012. Viruses. 4:1011-33.
- Song W, et al. 2018. PLoS Pathog. 14:e1007236
- Li F, et al. 2020. Nature. 221-224.
- Mlcochova P, et al. 2021. Nature. 559:114-119.
- Ashwaq O, et al. 2021. Future Virol. 10.2217/fvl-2020-0384.
- Gene ID
- 43740568 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about S Protein RBD on UniProt.org
