- Clone
- A16145B (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Beta-Nerve growth factor, Nerve Growth Factor, NGFB
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG2a, κ
-
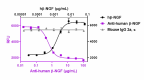
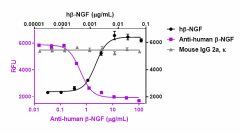
Recombinant human β-NGF (Black Circles, Cat. No. 762206) induces the proliferation of human erythroleukemia TF-1 cells. Anti-human β-NGF antibody (clone A16145B , Purple Squares) neutralizes the proliferation function of recombinant human β-NGF at 0.08 µg/mL in TF-1 cells in a dose-dependent manner while the isotype control (Cat. No. 400264, Green Triangles) does not have the effect. The ND50 = 0.1-0.8 µg/mL. -
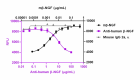
Recombinant Mouse β-NGF (Black Circles, Cat. No. 598104) induces the proliferation of human erythroleukemia TF-1 cells. Anti-human β-NGF antibody (clone A16145B , Purple Squares) neutralizes the proliferation function of recombinant mouse β-NGF at 0.005 µg/mL in TF-1 cells in a dose-dependent manner while the isotype control (Cat. No. 400264, Green Triangles) does not have the effect. The ND50 = 5-20 µg/mL.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 617903 | 100 µg | $270.00 | |||
| 617904 | 1 mg | $715.00 | |||
Select size of product is eligible for a 40% discount! Promotion valid until December 31, 2024. Exclusions apply. To view full promotion terms and conditions or to contact your local BioLegend representative to receive a quote, visit our webpage.
Neurotrophins are growth factors that modulate growth, differentiation, and survival of neurons. These structurally related proteins include nerve growth factor (NGF/β-NGF), brain-derived neurogenic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin-3, and neurotrophin-4/5. They are highly homologous and share a similar structure of a tertiary folded, cysteine rich "knot". Neurotrophins are critical to the development of the central and peripheral nervous systems, and they play important roles in injury-induced neuronal regeneration. β-NGF is a member of the neurotrophin family which controls growth, survival, and maturation of neurons. In peripheral and central neurons, neurotrophins are important regulators for survival, differentiation, and maintenance of nerve cells. They are detectable throughout embryogenesis and into the adult stage in the central and peripheral nervous systems. In animal models, β-NGF prevents neuronal degeneration and has become a therapeutical target in neuron regeneration studies. β-NGF is also critical for the survival and maintenance of sympathetic and sensory neurons. It is the main neurotrophin that maintains homeostasis of neurogenesis. It prevents neurons from undergoing apoptosis and promotes maturation while supporting axonal branching. Two receptors are known to interact with NGF, p75NTR and TrkA. The NGF-TrkA signaling pathway induces two pathways through activation of PI3K-Akt or Ras-MAPK. Either one of the pathways leads to CREB phosphorylation and increases expression of anti-apoptosis genes to keep neurons alive. Animal models of neurodegenerative diseases suggest that NGF can promote myelin repair of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. Clinical studies indicate that dysregulation of NGF signaling is related to Alzheimer's disease.
Product Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Recombinant Human β-NGF
- Formulation
- 0.2 µm filtered in phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing no preservative.
- Preparation
- The Ultra-LEAF™ (Low Endotoxin, Azide-Free) antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- The antibody is bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial, typically between 2 mg/mL and 3 mg/mL. Older lots may have also been bottled at 1 mg/mL. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C. This Ultra-LEAF™ solution contains no preservative; handle under aseptic conditions.
- Application
-
Neut - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by neutralization of the proliferation induced by recombinant human β-NGF (0.08 µg/mL) on TF-1 human erythroleukemia cells. ND50 range: 0.1 - 0.8 µg/mL. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_2814462 (BioLegend Cat. No. 617903)
AB_2814462 (BioLegend Cat. No. 617904)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Dimer
- Distribution
-
Hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid gland, testes, epididymis, vascular smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, mast cells, eosinophils.
- Function
- β-NGF is important for maintaining neuron homeostasis.
- Interaction
- Neurons, astrocytes, eosinophils, B, T, and mast cells.
- Ligand/Receptor
- Low-affinity NGF receptor (p75NTR); high-affinity NGF receptor (TrkA).
- Cell Type
- B cells, Eosinophils, Fibroblasts, Mast cells, Mature Neurons, Neural Stem Cells, Neurons, T cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Cell Proliferation and Viability, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience, Synaptic Biology
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines, Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
- Ullrich A, et al. 1983. Nature. 303:821.
- Klein R, et al. 1991. Cell. 65:189.
- Welker P, et al. 2000. Immunology 99:418.
- Fahnestock M, et al. 2004. Prog. Brain Res. 146:101.
- Bruno MA. Cuello AC. 2006. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:6735.
- Aloe L, et al. 2015. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 13:294.
- Gene ID
- 4803 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about beta-NGF on UniProt.org
Other Formats
View All β-NGF Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-human β-NGF | A16145B | Neut |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-human β-NGF
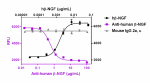
Recombinant human β-NGF (Black Circles, Cat. No. 762206) in... 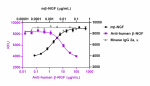
Recombinant Mouse β-NGF (Black Circles, Cat. No. 598104) ind...
