- Clone
- RA3-6B2 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- B220
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
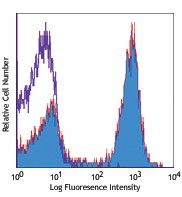
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with biotinylated RA3-6B2, followed by Sav-PE -
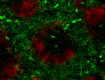
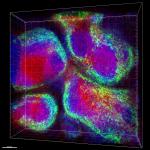
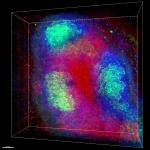
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10 minutes at room temperature and blocked with 5% FBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Then the section was stained with 10 µg/ml of biotin anti-mouse B220 (clone RA3-6B2) and Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD29 (clone HMβ1-1) (green) overnight at 4°C, followed by 2.5 µg/ml of Spark YG™ 570 Streptavidin (red) for 2 hours at room temperature. The image was captured by 10X objective.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 103203 | 50 µg | 20€ | ||||
| 103204 | 500 µg | 76€ | ||||
CD45R, also known as B220, is an isoform of CD45. It is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family with a molecular weight of approximately 180-240 kD. CD45R is expressed on B cells (at all developmental stages from pro-B cells through mature B cells), activated B cells, and subsets of T and NK cells. CD45R (B220) is also expressed on a subset of abnormal T cells involved in the pathogenesis of systemic autoimmunity in MRL-Faslpr and MRL-Fasgld mice. It plays a critical role in TCR and BCR signaling. The primary ligands for CD45 are galectin-1, CD2, CD3, and CD4. CD45R is commonly used as a pan-B cell marker; however, CD19 may be more appropriate for B cell specificity.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse, Human
- Reported Reactivity
- Cat
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- Abelson murine leukemia virus-induced pre-B tumor cells
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with biotin under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
IHC-F - Verified - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤ 0.25 µg per 106 cells in 100 µl volume. For immunohistochemistry, a concentration range of 5.0 - 10 µg/mL is suggested. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
Clone RA3-6B2 has been described to react with an epitope on the extracellular domain of the transmembrane CD45 glycoprotein which is dependent upon the expression of exon A and specific carbohydrate residues. Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunoprecipitation1, in vitro and in vivo modulation of B cell responses2-4, immunohistochemistry of acetone-fixed frozen sections and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections5,6, and spatial biology (IBEX)14,15.
- Application References
-
- Coffman RL. 1982. Immunol. Rev. 69:5. (IP)
- George A, et al. 1994. J. Immunol. 152:1014. (Activ)
- Asensi V, et al. 1989. Immunology 68:204. (Activ)
- Domiati-Saad R, et al. 1993. J. Immunol. 151:5936. (Activ)
- Hata H, et al. 2004. J. Clin. Invest. 114:582. (IHC)
- Monteith CE, et al. 1996. Can. J. Vet. Res. 60:193. (IHC)
- Shih FF, et al. 2006. J. Immunol. 176:3438. (FC)
- Chang C L-T, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:6984.
- Fazilleau N, et al. 2007. Nature Immunol. 8:753.
- Lang GL, et al. 2008. Blood 111:2158. PubMed
- Charles N, et al. 2010. Nat. Med. 16:701. (FC) PubMed
- del Rio ML, et al. 2011. Transpl. Int. 24:501. (FC) PubMed
- Murakami R, et al. 2013. PLoS One. 8:73270. PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2020. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117:33455-65. (SB) PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2022. Nat Protoc. 17:378-401. (SB) PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_312988 (BioLegend Cat. No. 103203)
AB_312988 (BioLegend Cat. No. 103204)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family, 180-240 kD
- Distribution
-
B cells, T cell subset, NK cell subset
- Function
- Phosphatase, T and B cell activation
- Ligand/Receptor
- Galectin-1, CD2, CD3, CD4
- Cell Type
- B cells, NK cells, T cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Immunology, Inhibitory Molecules, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Barclay A, et al. 1997. The Leukocyte Antigen FactsBook Academic Press.
2. Trowbridge IS, et al. 1993. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 12:85.
3. Kishihara K, et al. 1993. Cell 74:143.
4. Pulido R, et al. 1988. J. Immunol. 140:3851. - Gene ID
- 19264 View all products for this Gene ID 5788 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD45R on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- How many biotin molecules are per antibody structure?
- We don't routinely measure the number of biotins with our antibody products but the number of biotin molecules range from 3-6 molecules per antibody.
Other Formats
View All CD45R/B220 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
C57BL/6 mouse frozen lymph node section was fixed with 4% pa... 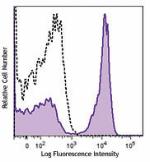
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 (clon... Formalin-fixed, 300 micron-thick mouse spleen section was bl... 
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (4%), 500 μm-thick mouse spleen secti... -
APC anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
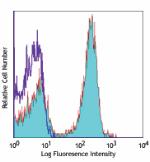
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with RA3-6B2 APC -
Biotin anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
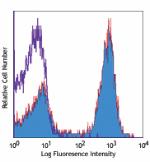
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with biotinylated RA3-6B2,... 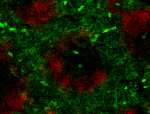
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... -
FITC anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
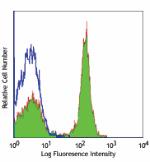
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with RA3-6B2 FITC -
PE anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
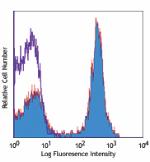
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with RA3-6B2 PE 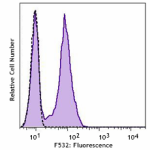
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 (clon... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
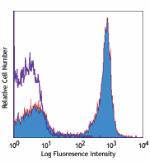
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with RA3-6B2 PE/Cyanine5 -
Purified anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
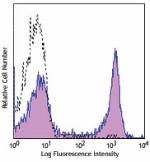
C57BL/6 mouse slenocytes were stained with purified B220 (cl... 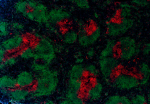
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... 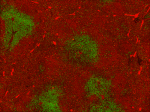
Fresh, frozen mouse spleen was stained with purified CD45R/B... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with RA3-6B2 PE/Cyanine7 -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with RA3-6B2 APC/Cyanine7 -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with RA3-6B2 Alexa Fluor® ... 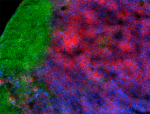
C57BL/6 mouse frozen lymph node section was fixed with 4% pa... 
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (4%), 500 µm-thick mouse spleen secti... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
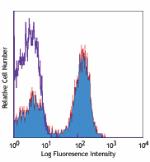
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with RA3-6B2 Alexa Fluor® ... 
C57BL/6 mouse frozen lymph node sections were fixed with 4% ... Formalin-fixed, 300 micron-thick mouse spleen section was bl... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
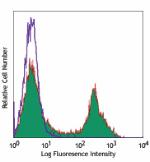
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with Pacific Blue™ R... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
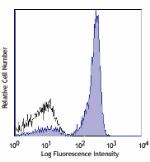
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with RA3-6B2 Alexa Fluor&r... -
PerCP anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
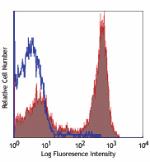
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with RA3-6B2 PerCP -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with CD3 APC and CD45R/B22... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
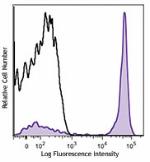
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 (clon... 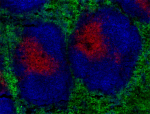
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen sections were fixed with 4% para... -
Brilliant Violet 570™ anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220

57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 FITC and CD45... 
-
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
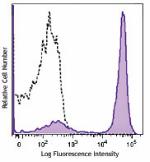
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 (clon... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
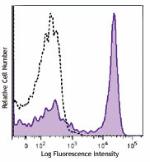
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 (clon... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
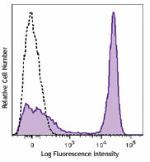
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 (clon... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
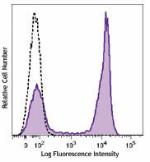
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 (clon... 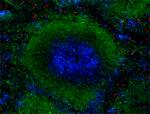
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... 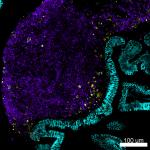
Confocal image of C57BL/6 mouse small intestine sample acqui... -
Purified anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220 (Maxpar® Ready)

Mouse splenocytes stained with 143Nd-anti-TCRb (H57-597) and... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
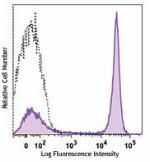
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 (clon... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
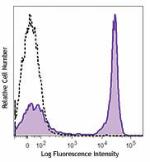
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 (clon... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 PE and B220 ... 
-
Brilliant Violet 750™ anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
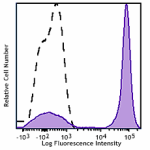
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45/B220 (clone... -
TotalSeq™-A0103 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
-
Spark Blue™ 550 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
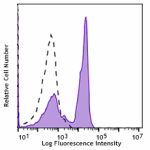
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 (clon... -
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
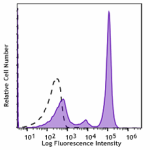
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 (clon... -
TotalSeq™-B0103 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
-
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
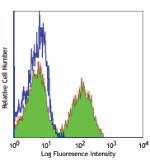
BALB/c mouse splenocytes stained with Ultra-LEAF™ purified R... -
TotalSeq™-C0103 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
-
PE/Fire™ 640 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
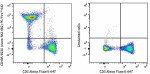
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 Alexa Fluor®... -
APC/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
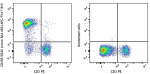
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 PE and CD45R... -
PE/Fire™ 700 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
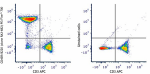
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 APC and CD45... -
Spark Violet™ 538 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
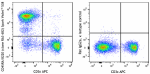
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with CD3ε APC and CD45R/B2... -
Spark YG™ 581 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
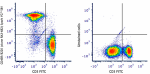
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3 F... -
Spark YG™ 570 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
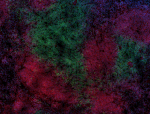
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... -
PE/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
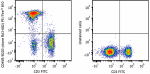
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with anti-mouse CD3 FITC a... -
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220 Antibody
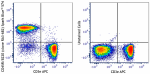
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3e APC an... -
Spark Violet™ 423 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220 Antibody
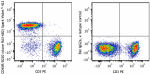
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3 PE and ... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
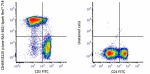
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3 F... -
Spark UV™ 387 anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220
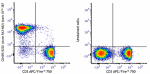
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with anti-mouse CD3 APC/Fi... -
Spark PLUS UV395™ anti-mouse/human CD45R/B220

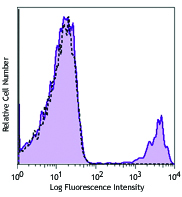
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3ε ...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 













Follow Us