- Clone
- O91F4 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- GLUL, Glutamine Synthetase
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
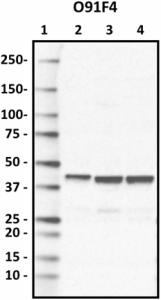
Western blot of purified anti-Glutamine synthetase antibody (clone O91F4). Lane 1: Molecular weight marker; Lane 2: 10 µg of human brain lysate; Lane 3: 10 µg of mouse brain lysate; Lane 4: 10 µg of rat brain lysate. The blot was incubated with 1 µg/mL of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C, followed by incubation with HRP-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG (Cat. No. 405306). Enhanced chemiluminescence was used as the detection system. -
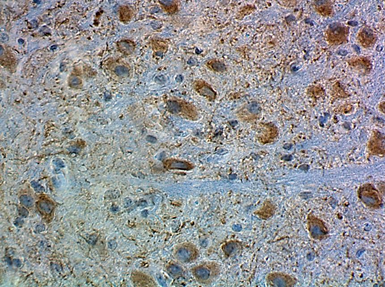
IHC staining of purified anti-Glutamine synthetase antibody (clone O91F4) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded mouse brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Sodium Citrate H.I.E.R (Cat. No. 928502), the tissue was incubated with 0.5 µg/ml of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C. BioLegend’s Ultra Streptavidin (USA) HRP Detection Kit (Multi-Species, DAB, Cat. No. 929901) was used for detection followed by hematoxylin counterstaining, according to the protocol provided. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale Bar: 50 µm -
IHC staining of purified anti-Glutamine synthetase antibody (clone O91F4) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Sodium Citrate H.I.E.R (Cat. No. 928502), the tissue was incubated with 10 µg/ml of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C. BioLegend’s Ultra Streptavidin (USA) HRP Detection Kit (Multi-Species, DAB, Cat. No. 929901) was used for detection followed by hematoxylin counterstaining, according to the protocol provided. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale Bar: 50 µm -
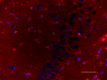
IHC staining of purified anti-Glutamine synthetase antibody (clone O91F4) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded mouse brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Sodium Citrate H.I.E.R. (Cat. No. 928502), the tissue was incubated with 0.5 µg/mL of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C, followed by incubation with 2.5 µg/mL of Alexa Fluor® 594 goat anti-mouse IgG for one hour at room temperature. The slide was mounted with fluoromount G with DAPI. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm -
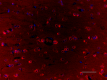
IHC staining of purified anti-Glutamine synthetase antibody (clone O91F4) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded rat brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Sodium Citrate H.I.E.R. (Cat. No. 928502), the tissue was incubated with 0.5 µg/mL of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C, followed by incubation with 2.5 µg/mL of Alexa Fluor® 594 goat anti-mouse IgG for one hour at room temperature. The slide was mounted with fluoromount G with DAPI. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm -
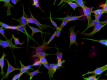
ICC staining of purified anti-Glutamine synthetase antibody (clone O91F4) on SH-SY5Y cell. The cells were fixed with 4% PFA, permeabilized with a buffer containing 0.1% Triton X-100 and 0.25% BSA, and blocked with 2% normal goat serum and 0.02% BSA. The cells were then incubated with 2 µg/mL of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C, followed by incubation with 2.5 µg/mL of Alexa Fluor® 594 goat anti-mouse IgG for one hour at room temperature. The cells were co-stained with Flash Phalloidin™ Green 488 (Cat. No. 424201). The slide was mounted with fluoromount G with DAPI. The image was captured with a 60X objective. Scale bar: 20 µm
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 856201 | 25 µg | 85€ | ||||
| 856202 | 100 µg | 221€ | ||||
Glutamine Synthase (GLUL) is primarily expressed in astrocytes in the brain. The main function of GLUL is to catalyze the condensation of glutamate and ammonia to form glutamine. GLUL plays an important role in the metabolic regulation of glutamate, detoxification of brain ammonia, as well as recycling of neurotransmitters. GLUL expression in endothelial cells may be involved in cell migration during pathological angiogenesis. Upregulation of astrocytic GLUL to uptake excess ammonia and glutamate may play a neuroprotective role during neuroinflammation.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Recombinant human GLUL protein expressed in HEK293T cell
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
WB - Quality tested
IHC-P, ICC - Verified - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by Western blotting. For Western blotting, the suggested use of this reagent is 1.0 - 10 µg per mL. For immunohistochemistry on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections, a concentration range of 0.5 - 10 µg/mL for chromogenic staining and 0.5 - 5.0 µg/mL for fluorescent staining is suggested. For immunocytochemistry, a concentration range of 2.0 - 10 μg/mL is recommended. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application References
-
- Shajahan-Haq AN, et al. 2014. Mol Cancer. 13:239. (WB)
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_2783452 (BioLegend Cat. No. 856201)
AB_2783452 (BioLegend Cat. No. 856202)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- GLUL is a 373 amino acid protein with an apparent molecular mass of ~ 42 kD.
- Distribution
-
Tissue Distribution: Predominantly expressed in brain, kidney, and liver.
Cellular Distribution: Extracellular, cytosol, nucleus, and mitochondrion. - Interaction
- Forms homooctamer and homotetramer.
- Cell Type
- Astrocytes
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Mitochondrial Function, Neuroinflammation, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers, Synaptic Biology
- Molecular Family
- Postsynaptic proteins, Presynaptic proteins
- Antigen References
-
- Eelen G, et al. 2018. Nature. (7721):63-69
- Spodenkiewicz M, et al. 2016. Biology (Basel). 5(4)
- Fan S, et al. 2018. J Cell Biochem. 119(7):6008
- Gene ID
- 2752 View all products for this Gene ID 14645 View all products for this Gene ID 24957 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Glutamine synthetase on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All Glutamine synthetase Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-Glutamine synthetase | O91F4 | WB,IHC-P,ICC |
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-Glutamine synthetase
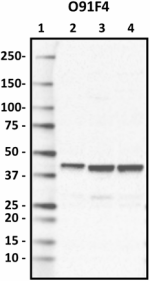
Western blot of purified anti-Glutamine synthetase antibody ... 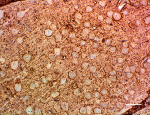
IHC staining of purified anti-Glutamine synthetase antibody ... 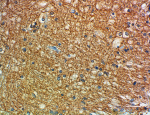
IHC staining of purified anti-Glutamine synthetase antibody ... 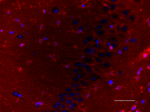
IHC staining of purified anti-Glutamine synthetase antibody ... 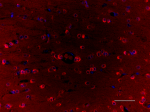
IHC staining of purified anti-Glutamine synthetase antibody ... 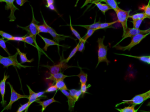
ICC staining of purified anti-Glutamine synthetase antibody ...

 Login / Register
Login / Register 









Follow Us