- Clone
- 3H4 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor, HB-EGF-like growth factor
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications

-

NUGC-3 cells (human gastric cancer cells) were stained with anti-human HB-EGF (clone 3H4) APC (filled histogram) or mouse IgG1, κ APC isotype control (open histogram).
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 383705 | 25 tests | 196 CHF | ||||
| 383706 | 100 tests | 409 CHF | ||||
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) is a member of the EGF family of growth factors. Human HB-EGF was initially identified as a protein of 22 kD secreted by macrophage-like U937 cells. It belongs to the EGF family of proteins that includes EGF, TGF-α, HB-EGF, epigen, epiregulin, betacellulin, neuroregulin, and tomoregulin. All the EGF family members are synthesized as type I membrane protein precursors, which can undergo proteolytic cleavage at the plasma membrane to release a mature soluble ectodomain. It has been suggested that various metalloproteinases participate in the shedding of HB-EGF, such as MMP-3, MMP-7, ADAM9, ADAM10, ADAM12, and ADAM17. The ectodomain shedding is stimulated by phorbol esters, calcium ionophore, lysophosphatidic acid, and IL-1β. In addition, nardilysin, a metalloendopeptidase of the M16 family, binds HB-EGF and enhances its shedding through activation of TACE (ADAM17). The membrane-anchored HB-EGF acts in cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix interactions. In addition, the membrane HB-EGF is the receptor for diphtheria toxin that can be internalized and induce apoptotic death. HB-EGF plays a crucial role in cardiac valvulogenesis. Newborn knockout mice have malformed semilunar and atrioventricular heart valves and poorly differentiated lungs. HB-EGF is overexpressed in several types of cancer such as pancreatic carcinoma, ovarian cancer, and gastric carcinoma. HB-EGF is also involved in cancer metastasis and invasion of ovarian cancer, head and neck cancer, and thyroid carcinoma cells.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Human HB-EGF, extracellular domain (recombinant)
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA)
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with APC under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µL per million cells in 100 µL staining volume or 5 µL per 100 µL of whole blood. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Hamaoka M, et al. 2010. J Biochem. 148:55.
- RRID
-
AB_3106177 (BioLegend Cat. No. 383705)
AB_3106177 (BioLegend Cat. No. 383706)
Antigen Details
- Distribution
-
Monocytes, macrophages, T cells, neutrophils, eosinophils, myeloid leukemia blasts, myeloma cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, and normal or neoplastic epithelial cells
- Function
- HB-EGF is associated with proliferation and differentiation of stromal cells, apoptosis, and morphogenesis. It participates in inflammation, wound healing, atherosclerotic plaque progression, and cardiac valvulogenesis. TNF-α and IL-1β induces HB-EGF in endothelial cells.
- Interaction
- Fibroblast, smooth muscle cells, monocytes/macrophages, endothelial cells, astrocytes, keratinocytes, normal and neoplastic epithelial cells
- Ligand/Receptor
- EGFR (ErbB1) and ErbB4; also binds to heparan-sulphate proteoglycans
- Cell Type
- Epithelial cells, Macrophages, T cells
- Biology Area
- Angiogenesis, Cancer Biomarkers
- Molecular Family
- Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
- Higashiyama S, et al. 1991. Science. 251:936.
- Hirata M, et al. 2001. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 283:915.
- Jackson LF, et al. 2003. EMBO J. 22:2704.
- Nishi E, et al. 2006. J. Biol. Chem. 281:31164.
- Yotsumoto F, et al. 2008. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 365:555.
- Ota I, et al. 2013. Oncol Rep. 30:1593.
- Gene ID
- 1839 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about HB-EGF on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All HB-EGF Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-human HB-EGF | 3H4 | FC,ICC,WB,IP |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-human HB-EGF | 3H4 | FC |
| APC anti-human HB-EGF | 3H4 | FC |
| PE anti-human HB-EGF | 3H4 | FC |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-human HB-EGF
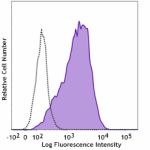
NUGC-3 cells (human gastric cancer cells) were stained with ... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-human HB-EGF
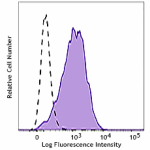
NUGC-3 cells (human gastric cancer cells) were stained with ... -
APC anti-human HB-EGF

NUGC-3 cells (human gastric cancer cells) were stained with ... -
PE anti-human HB-EGF

NUGC-3 cells (human gastric cancer cells) were stained with ...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 












Follow Us