- Clone
- A18228E (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- HPCA, Neuron-specific calcium-binding protein hippocalcin, Calcium-Binding Protein BDR-2, BDR-2
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG2b, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-

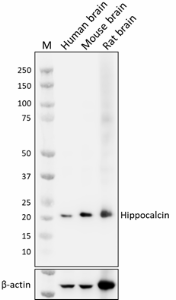
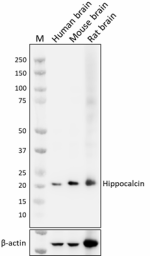
Whole cell extracts (15 µg total protein) from indicated tissues were resolved by 4-12% Bis-Tris gel electrophoresis, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and probed with 1.0 µg/mL of purified anti-hippocalcin (clone A18228E) overnight at 4°C. Proteins were visualized by chemiluminescence detection using HRP goat anti-mouse IgG (Cat. No. 405306). Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-β-actin (Cat. No. 664804) was used as a loading control at a 1:50000 dilution. Western-Ready™ ECL Substrate Premium Kit (Cat. No. 426319) was used as a detection agent. Lane M: Molecular weight marker -
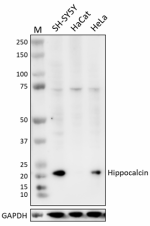
Whole cell extracts (15 µg total protein) from indicated cell lines were resolved by 4-12% Bis-Tris gel electrophoresis, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and probed with 0.5 µg/mL of purified anti-hippocalcin (clone A18228E) overnight at 4°C. Proteins were visualized by chemiluminescence detection using HRP goat anti-mouse IgG (Cat. No. 405306). Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-GAPDH (Cat. No. 607904) was used as a loading control at a 1:50000 dilution. Western-Ready™ ECL Substrate Premium Kit (Cat. No. 426319) was used as a detection agent. Lane M: Molecular weight marker
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 619251 | 25 µg | 166 CHF | ||||
| 619252 | 100 µg | 415 CHF | ||||
|
Hippocalcin, a member of the neuronal calcium (Ca2+) sensor family, is a Ca2+-binding protein that translocates between membrane and cytosol through its Ca2+/myristoyl switch. Its structural composition consists of 191 amino acids, forming a compact protein with a molecular weight of approximately 21 kD. The protein is characterized by the presence of four EF-hand motifs, each containing a helix-loop-helix structure, facilitating high-affinity Ca2+ binding. Through its Ca2+-sensing capabilities, hippocalcin modulates various crucial cellular functions and signaling pathways. It participates in the regulation of intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and influences Ca2+-dependent signaling cascades. The protein's interactions with key proteins and enzymes enables it to contribute to processes such as neurotransmitter release, synaptic plasticity, and neuronal excitability. Hippocalcin’s involvement in human diseases has been observed in several conditions. In neurological disorders like epilepsy, dysregulation of hippocalcin disrupts Ca2+ signaling, leading to neuronal hyperexcitability and the manifestation of seizures. Additionally, alterations in hippocalcin expression and function have been linked to neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, suggesting its potential role in disease progression. Furthermore, elevated levels of hippocalcin have been associated with certain cancers, such as breast and lung cancer, indicating its involvement in tumor progression and metastasis. |
Product Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Recombinant fragment of Hippocalcin
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
WB - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by western blotting. For western blotting, the suggested use of this reagent is 0.125 - 1.0 µg/mL. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
This product is not suitable for immunocytochemistry (ICC) and immunohistochemistry (IHC-P).
- RRID
-
AB_3068101 (BioLegend Cat. No. 619251)
AB_3068101 (BioLegend Cat. No. 619252)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Ca2+ -dependent oligomerization
- Distribution
-
Abundant in brain and hippocampus; membrane/cytoplasmic translocation
- Function
- Bind to Ca2+ to regulate neuronal activity
- Interaction
- β2-adaptin subunit of the AP2 adaptor complex, PSD95
- Ligand/Receptor
- Ca2+
- Cell Type
- Mature Neurons, Neural Stem Cells, Neurons
- Biology Area
- Neuroscience, Signal Transduction
- Molecular Family
- Postsynaptic proteins, Synaptic Vesicle Trafficking/Endocytosis
- Antigen References
-
- O'Callaghan DW, et al. 2003. J Cell Biol. 163:715-21.
- Palmer CL, et al. 2005. Neuron. 47:487-94.
- Kobayashi M, et al. 2005. Neuroscience. 133:471-84.
- Kerrigan TL, et al. 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 5:57.
- Park S-Y, et al. 2017. Stem Cell Reports. 8:95-111.
- Gene ID
- 3208 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Hippocalcin on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All Hippocalcin Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-Hippocalcin | A18228E | WB |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us