- Clone
- A16088B (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Vaspin, Visceral adipose tissue-derived serine protease inhibitor, Visceral adipose-specific serpin, OL-64
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG2b, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
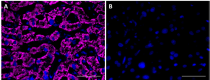
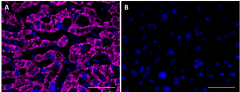
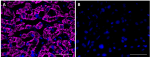
IHC staining purified anti-Serpin A12 (clone A16088B) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human liver tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Tris-EDTA (10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA, pH 9.0), the tissue was incubated with (panel A) and without (panel B) 10 µg/mL of purified anti-Serpin A12 (clone A16088B) followed by incubation with Alexa Fluor® 647 Goat anti-mouse IgG (Cat. No. 405322) for 1 hour at room temperature. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (Cat. No. 422801). Images were with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm -

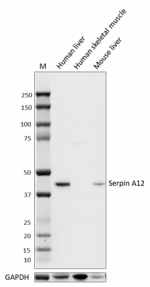
Whole cell extracts (15 µg total protein) from indicated tissues were resolved by 4-12% Bis-Tris gel electrophoresis, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and probed with 0.1 µg/mL of purified anti-Serpin A12 (clone A16088B) overnight at 4°C. Proteins were visualized by chemiluminescence detection using HRP Goat anti-mouse IgG (Cat. No. 405306). Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-GAPDH (Cat. No. 607903) was used as a loading control at a 1:50000 dilution. Western-Ready™ ECL Substrate Premium Kit (Cat. No. 426319) was used as a detection agent. Lane M: Molecular weight marker -
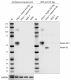
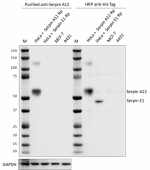
Whole cell extracts (15 µg total protein) spiked with 20 ng Recombinant Human Serpin A12 (Cat. No. 756806) or Serpin E1 (Cat. No. 753804) from indicated cell lines were resolved by 4-12% Bis-Tris gel electrophoresis, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and probed with 0.1 µg/mL of purified anti-Serpin A12 (clone A16088B) overnight at 4°C. Proteins were visualized by chemiluminescence detection using HRP Goat anti-mouse IgG (Cat. No. 405306). Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-GAPDH (Cat. No. 607903) was used as a loading control at a 1:50000 dilution. Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-His Tag (Cat. No. 362614) was used as spiked recombinant protein control at a 1:500 dilution. Western-Ready™ ECL Substrate Premium Kit (Cat. No. 426319) was used as a detection agent. Lane M: Molecular weight marker
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 624651 | 25 µg | 150 CHF | ||||
| 624652 | 100 µg | 350 CHF | ||||
Human Serpin A12, also known as Vaspin, is a secreted adipokine that is found in visceral adipose tissue. It belongs to the serpin superfamily, class A. It's known protease target is KLK7, a member of the kallikrein family. In humans, Serpin A12 expression may increase at the onset of diabetes and decrease when the disease aggravates. The administration of recombinant Serpin A12 in a diet-induced mouse obesity model suggests that it may represent an insulin-sensitizing adipokine. Low serum concentration of Serpin A12 may be a risk factor for the progression of type-2 diabetes mellitus. Although its mechanism of action is not fully understood, KLK7 inhibition seems to be the most likely underlying physiological mechanism for the compensatory effects on obesity-induced insulin resistance. In addition to its relation to diabetes, Serpin A12 exerts protective effects on heart disease. Its low concentrations correlate with coronary artery diseases’ severity and unstable angina pectoris. Serpin A12 may inhibit endothelial cell apoptosis, attenuate high glucose stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, and chemokinesis. It also acts as a ligand for the cell surface GRP78/voltage dependent anion channel complex in endothelial cells and promotes proliferation, inhibits apoptosis, and protects against diabetes mellitus associated vascular injuries.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Recombinant fragment of human Serpin A12
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
IHC-P - Quality tested
WB - Verified - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded immunohistochemical staining. For immunohistochemistry, a concentration range of 1.0 - 10.0 µg/mL is suggested. For western blotting, the suggested use of this reagent is 0.1 - 1.0 µg/mL. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
For immunohistochemistry, Citrate buffer, 10X (Cat. No. 420902) or Tris-EDTA pH 9.0 is recommended.
- RRID
-
AB_3083413 (BioLegend Cat. No. 624651)
AB_3083413 (BioLegend Cat. No. 624652)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Monomer
- Distribution
-
Expressed in visceral adipose tissues and liver. Possibly present in adipocytes. Present in the plasma and serum
- Function
- Adipokines that modulate insulin action by specifically inhibiting target protease KLK7 in white adipose tissues
- Interaction
- KLK7, GRP78/VDAC complex
- Biology Area
- Cardiovascular Biology, Signal Transduction
- Antigen References
-
- Li HL, et al. 2011. Clin Chem Lab Med. 49:1547-54.
- Jung CH, et al. 2011. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 413:264-9.
- Li H, et al. 2013. Atherosclerosis. 228:61-8.
- Nakatsuka A, et al. 2012. Diabetes. 61:2823-32.
- Heiker JT, et al. 2013. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 70:2569-83.
- Hida K, et al. 2005. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 30:10610.
- Jian W, et al. 2014. PLoS One. 9:e94763.
- Gene ID
- 145264 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Serpin A12 on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Other Formats
View All Serpin A12 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-Serpin A12 | A16088B | IHC-P,WB |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us