- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP1), Monocyte chemoattractant and activating factor (MCAF), JE, Small inducible cytokine A2 (SCYA2), HC-11 (HC11), P6, Smooth muscle cell chemotactic factor (SMC-CF, SMCCF), CCL2, MCP-1, MCP1,CCL-2, MCP-1/CCL2
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 565001 | 4 pack | 94 CHF | ||||
CCL2, also known as MCP-1, is a member of the CC ß chemokine family. It is widely expressed in endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells and monocytes in response to several atherogenic stimulants such as CD40 ligand, platelet derived growth factor (PDGF), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and oxidized low density lipoprotein. Several recent in vivo studies have disclosed critical roles of MCP1 in atherosclerosis. In addition, MCP-1 has been implicated in monocytic infiltration of tissues during several inflammatory diseases, and has been implicated in macrophage-mediated tumor growth suppression in mice. CCL2 has been shown to have direct effects on tumor cells in an autocrine and paracrine fashion in multiple cancers, including breast, lung, cervix, ovary, sarcoma, and prostate. In addition, MCP-1 plays a key role in the regulation of MMPs during transmigration. MCP-1/CCl2 has been described as a new diagnostic marker and therapeutic target for progressive renal injury in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney epithelial cells, including glomerular podocytes and tubular cells express MCP-1 in response to high glucose and advanced glycation end products. MCP-1 promotes inflammation and progressive injury in diabetic kidneys. The importance of MCP-1 in the early development of diabetic nephropathy has been determined in animal models incorporating genetically deficient mice or therapeutic blockade of the MCP-1 receptor (CCR2).
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Source
- Human MCP1, (amino acids Gln24-Thr99, NM_002982) was expressed in E. coli.
- Molecular Mass
- The 76 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 8,685 Da. The DTT-reduced protein migrates at approximately 8kDa and non-reduced protein migrates at approximately 13kDa by SDS-PAGE. The N-terminal amino acid is Glycine.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE
- Formulation
- Lyophilized in sterile-filtered PBS, pH 7.2, containing 1% BSA, 0.09% sodium azide, and protease inhibitors.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vials can be stored between 2°C and 8°C until the expiration date. Prior to use, reconstitute the lyophilized powder with 0.2 mL of PBS containing a carrier protein (e.g., 1% BSA, protease free), pH7.4. Re-cap vial, vortex. Allow the reconstituted standard to sit at room temperature for 15 minutes, vortex again to mix completely. The reconstituted standard stock solution can be aliquoted into polypropylene vials and stored at -70°C for up to one month. Do not re-use diluted standards. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Application
-
ELISA - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
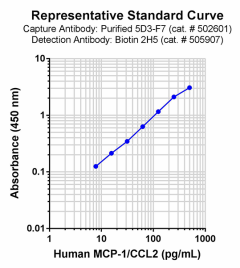
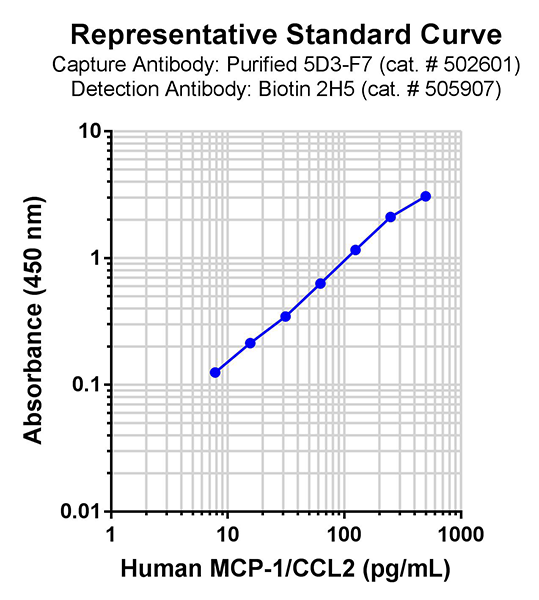
Each lot of this protein is quality control tested by ELISA. For use as an ELISA standard with the 5D3-F7 and 2H5 antibody pair, a standard curve comprised of doubling dilutions from 500 pg/mL to 7.81 pg/mL is suggested. For use as an ELISA standard with the Poly5360 antibody pair, a standard curve comprised of doubling dilutions ranging from 1000 to 15.6 pg/mL is suggested. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance.
- Application Notes
-
This MCP-1/CCL2 protein is useful as a standard for a human MCP-1/CCL2 sandwich ELISA when used with one of the following antibody pairs: Pair 1 (capture: purified 5D3-F7 antibody; detection: biotinylated 2H5 antibody), or Pair 2 (capture: purified Poly5360; detection: biotinylated Poly 5360).
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Chemokine
- Distribution
-
MCP-1 (CCL2) is secreted by fibroblast, endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, tumor cells, phytohemaglutinin stimulated mononuclear cells.
- Function
- MCP-1 induces migration of monocytes, memory/activated T cells, NK cells, myeloid dendritic cells, neutrophils, astrocytes, mesangial cells, and bone marrow endothelial cells. MCP-1 is induced by IL-1b, TNF, IFNg, PDGF, IL-4, MIF, and IL-17.
- Ligand/Receptor
- MCP-1 mediates its cellular effects primarily through CCR2 receptor
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Neuroinflammation, Neuroscience
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
1. Loberg RD, et al. 2007. Cancer Research. 67:9417-9424.
2. Gregory JL, et al. 2006. J. Immunol. 177:8072-8079.
3. Qui Z, et al. 2009. Immunology. 214:835-842.
4. Reichel CA, et al. 2009. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29(11):1787-93.
5. McQuibban GA, et al. 2002. Blood 100:1160-1167.
6. Tesh GH, et al. 2008. Amm. J. Physiol Renal Physiol. 294:F697-F701. - Gene ID
- 6347 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about MCP-1 on UniProt.org
 Login / Register
Login / Register 

















Follow Us