 |
| BioLegend provides an array of reagents for Siglec study and detection. Siglecs mainly recognize sialylated glycans and gangliosides. Typically, in their basal state, Siglecs are bound with ligands on the same cell (cis), preventing them from acting. However, sialylated (trans) glycan ligands (present on glycoproteins and glycolipids) can outcompete cis ligands due to their high affinity. Siglecs generally are associated with the prevention of excessive innate and adaptive immune responses. Cognasse et al. investigated the roles of Siglecs in the control of platelet-induced inflammation. |
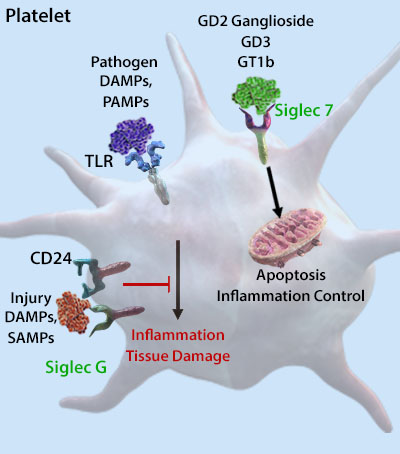 |
| Adapted from Cognasse, F. et al. 2015. Front. Immunol. 6:83 PubMed |
| Pathogen recognition receptors (like TLRs) can induce inflammation upon the binding of their targets. However, certain Siglecs are able to limit inflammation even after TLR engagement. Upon the binding of some DAMPs (damage associated molecular patterns) or SAMPs (self-associated molecular patterns), CD24 and human Siglec-10/mouse Siglec-G inhibit ITIM motifs, limiting TLR activation. Siglec-7 is capable of inducing platelet apoptosis via intrinsic and extra-mitochondrial pathways. These mechanisms help control tissue damage, platelet inflammatory responses, and excessive inflammatory reactions. |


 Login / Register
Login / Register 






Follow Us