- Clone
- 53-6.7 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- T8, Lyt2, Ly-2
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-

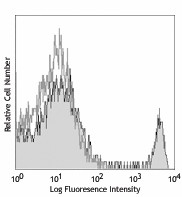
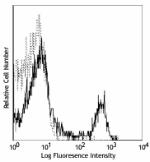
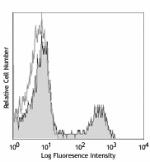
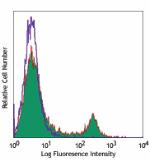
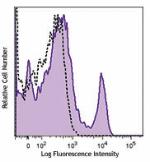
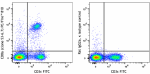
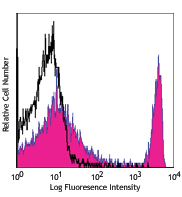
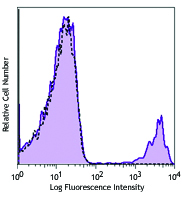
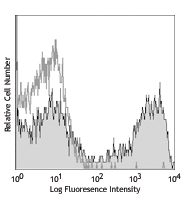
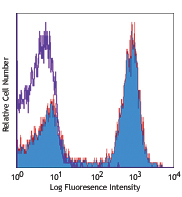
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with biotinylated CD8 (clone 53-6.7) (filled histogram) or rat IgG2a, κ isotype control (open histogram), followed by Sav-PE.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100703 | 50 µg | 34€ | ||||
| 100704 | 500 µg | 71€ | ||||
CD8, also known as Lyt-2, Ly-2, or T8, consists of disulfide-linked α and β chains that form the α(CD8a)/β(CD8b) heterodimer and α/α homodimer. CD8a is a 34 kD protein that belongs to the immunoglobulin family. The CD8 α/β heterodimer is expressed on the surface of most thymocytes and a subset of mature TCR α/β T cells. CD8 expression on mature T cells is non-overlapping with CD4. The CD8 α/α homodimer is expressed on a subset of γ/δ TCR-bearing T cells, NK cells, intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes, and lymphoid dendritic cells. CD8 is an antigen co-receptor on T cells that interacts with MHC class I on antigen-presenting cells or epithelial cells. CD8 promotes T cell activation through its association with the TCR complex and protein tyrosine kinase lck.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- Mouse thymus or spleen
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with biotin under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
IHC - Reported in the literature, not verified in house - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤ 0.25 µg per 106 cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
Clone 53-6.7 antibody competes with clone 5H10-1 antibody for binding to thymocytes3. The 53-6.7 antibody has been reported to block antigen presentation via MHC class I and inhibit T cell responses to IL-2. This antibody has also been used for depletion of CD8a+ cells. Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunoprecipitation1,3, in vivo and in vitro cell depletion2,10,15, inhibition of CD8 T cell proliferation3, blocking of cytotoxicity3,4, immunohistochemical staining5,6 of acetone-fixed frozen sections and zinc-fixed paraffin-embedded sections, and spatial biology (IBEX)29,30. Clone 53-6.7 is not recommended for immunohistochemistry of formalin-fixed paraffin sections. The Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin < 0.01 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for functional assays or in vivo studies (Cat No. 100746).
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Ledbetter JA, et al. 1979. Immunol. Rev. 47:63. (IHC, IP)
- Hathcock KS. 1991. Current Protocols in Immunology. 3.4.1. (Deplete)
- Takahashi K, et al. 1992. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:5557. (Block, IP)
- Ledbetter JA, et al. 1981. J. Exp. Med. 153:1503. (Block)
- Hata H, et al. 2004. J. Clin. Invest. 114:582. (IHC)
- Fan WY, et al. 2001. Exp. Biol. Med. 226:1045. (IHC)
- Shih FF, et al. 2006. J. Immunol. 176:3438. (FC)
- Kamimura D, et al. 2006. J. Immunol. 177:306.
- Bouwer HGA, et al. 2006. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:5102. (FC, Deplete)
- Kao C, et al. 2005. Int. Immunol. 17:1607. PubMed
- Ko SY, et al. 2005. J. Immunol. 175:3309. (FC) PubMed
- Rasmussen JW, et al. 2006. Infect. Immun. 74:6590. PubMed
- Lee CH, et al. 2009. Clin. Cancer Res. PubMed
- Geiben-Lynn R, et al. 2008. Blood 112:4585. (Deplete) PubMed
- Kingeter LM, et al. 2008. J. Immunol. 181:6244. PubMed
- Guo Y, et al. 2008. Blood 112:480. PubMed
- Andrews DM, et al. 2008. J. Virol. 82:4931. PubMed
- Britschqui MR, et al. 2008. J. Immunol. 181:7681. PubMed
- Kenna TJ, et al. 2008. Blood 111:2091. PubMed
- Jordan JM, et al. 2008. Infect. Immun. 76:3717. PubMed
- Todd DJ, et al. 2009. J. Exp. Med. 206:2151. PubMed
- Bankoti J, et al. 2010. Toxicol. Sci. 115:422. (FC) PubMed
- Medyouf H, et al. 2010. Blood 115:1175. PubMed
- Riedl P, et al. 2009. J. Immunol. 183:370. PubMed
- Apte SH, et al. 2010. J. Immunol. 185:998. PubMed
- Bankoti J, et al. 2010. Toxicol. Sci. 115:422. (FC) PubMed
- del Rio ML, et al. 2011. Transpl. Int. 24:501. (FC) PubMed
- Cui L, et al. 2015. J Control Release. 206:220. PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2020. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117:33455-65. (SB) PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2022. Nat Protoc. 17:378-401. (SB) PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_312742 (BioLegend Cat. No. 100703)
AB_312742 (BioLegend Cat. No. 100704)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Ig superfamily, CD8α chain, 34 kD
- Distribution
-
Most thymocytes, T cell subset, some NK cells, lymphoid dendritic cells
- Function
- Co-receptor for TCR
- Ligand/Receptor
- MHC class I molecule
- Antigen References
-
1. Barclay A, et al. 1997. The Leukocyte Antigen FactsBook Academic Press.
2. Zamoyska R. 1994. Immunity 1:243.
3. Ellmeier W, et al. 1999. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17:523. - Gene ID
- 12525 View all products for this Gene ID
- Specificity (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- CD8alpha
- Specificity Alt (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- CD8a
- App Abbreviation (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- FC,IHC
- UniProt
- View information about CD8alpha on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
- How many biotin molecules are per antibody structure?
- We don't routinely measure the number of biotins with our antibody products but the number of biotin molecules range from 3-6 molecules per antibody.
Other Formats
View All CD8a Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
APC anti-mouse CD8a
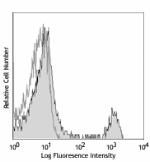
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD8 (clone 53-6.... -
Biotin anti-mouse CD8a
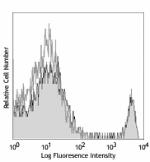
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with biotinylated CD8... -
FITC anti-mouse CD8a
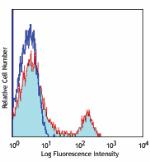
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD8 (clone 53-6.... -
PE anti-mouse CD8a
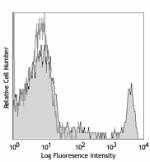
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD8 (clone 53-6.... 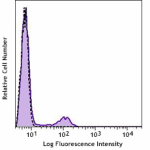
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD8a (clone 53-6... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse CD8a

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3&e... -
Purified anti-mouse CD8a
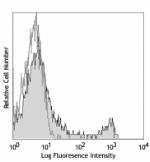
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with purified CD8 (cl... 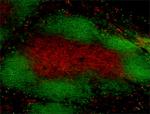
C57BL/6 frozen mouse spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... 
Fresh, frozen mouse spleen was stained with purified CD8a cl... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD8a

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3ε ... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD8a
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 FITC and CD8... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD8a
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD8 (clone 53-6.... 
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (1%), 500 µm-thick mouse thymus secti... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD8a
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD8 (clone 53-6.... 
C57BL/6 mouse frozen lymph node section was fixed with 4% pa... 
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (1%), 500 μm-thick mouse spleen secti... 
Confocal image of C57BL/6 mouse lung sample acquired using t... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse CD8a
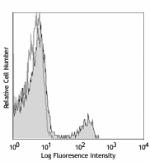
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD8 (clone 53-6.... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse CD8a
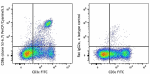
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with CD8 (clone 53-6.7) Al... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD8a
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3ε FIT... -
PerCP anti-mouse CD8a
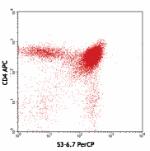
C57BL/6 thymocytes were stained with CD8 (clone 53-6.7) PerC... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse CD8a

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3ε FITC and CD... 
BL6 mouse lymph nodes, fixed O/N in PLP, blocked with 10% ra... 
Confocal image of C57BL/6 mouse spleen sample acquired using... 
Confocal image of C57BL/6 mouse thymus sample acquired using... 
Confocal image of C57BL/6 mouse small intestine sample acqui... 
Confocal image of C57BL/6 mouse liver sample acquired using ... -
Brilliant Violet 570™ anti-mouse CD8a
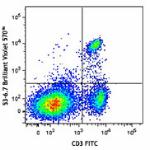
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 FITC and CD8... 
-
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse CD8a

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 PE and CD8a ... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse CD8a
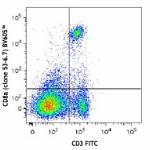
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 FITC and CD8... -
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse CD8a
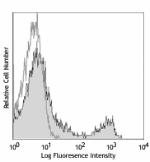
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with LEAF™ purified C... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse CD8a

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 PE and CD8a ... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse CD8a

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 PE and CD8a ... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse CD8a

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 APC and CD8a... -
Purified anti-mouse CD8a (Maxpar® Ready)
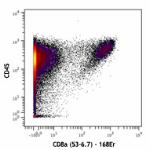
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 147Sm-anti-CD45 (30-F... -
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-mouse CD8a
C57BL/6 mouse frozen lymph node section was fixed with 4% pa... 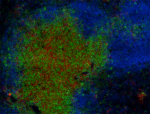
C57BL/6 mouse frozen lymph node section was fixed with 4% pa... 
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (1%), 500 µm-thick mouse thymus secti... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD8a

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3ε FITC and C... 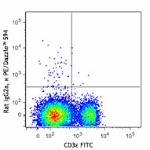
-
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse CD8a

C57BL/6 thymocytes were stained with CD4 PE and CD8a (clone ... 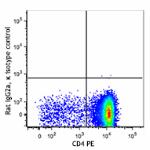
-
GoInVivo™ Purified anti-mouse CD8a
-
TotalSeq™-A0002 anti-mouse CD8a
-
Spark Blue™ 550 anti-mouse CD8a
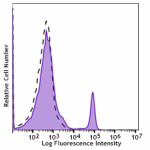
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD8 (clone 53-6.... -
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-mouse CD8a
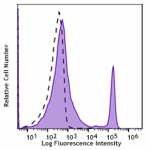
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD8a (clone 53-6... -
TotalSeq™-C0002 anti-mouse CD8a
-
TotalSeq™-B0002 anti-mouse CD8a
-
Spark YG™ 570 anti-mouse CD8a
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... -
PE/Fire™ 640 anti-mouse CD8a
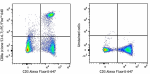
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 Alexa Fluor®... -
PE/Fire™ 700 anti-mouse CD8a
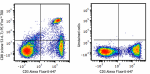
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3 A... -
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-mouse CD8a Antibody
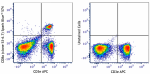
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3e APC an... -
Spark Violet™ 423 anti-mouse CD8a Antibody
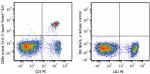
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3 PE and ... -
Spark UV™ 387 anti-mouse CD8a
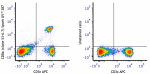
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3ε ... -
Spark Blue™ 515 anti-mouse CD8a
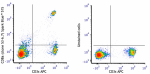
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3ε ... -
APC/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse CD8a
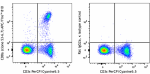
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3&e... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-mouse CD8a (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
PE/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse CD8a
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3ε ... -
Spark PLUS UV395™ anti-mouse CD8a

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3ε ... -
PerCP/Fire™ 780 anti-mouse CD8a

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3ε ...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 










Follow Us