- Other Names
- VEGFA165, MVCD1, VEGF, Vascular permeability factor (VPF)
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
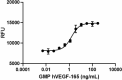
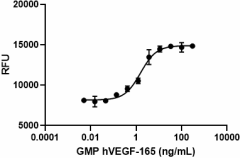
GMP recombinant human VEGF-165 induces dose-dependent proliferation of HUVEC cells. Deep Blue Cell Viability™ Kit (Cat. No. 424701) is used to measure the proliferation. The ED50 range for this effect is 1 - 6 ng/mL.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 583714 | 25 µg | 352€ | ||||
| 583716 | 100 µg | 934€ | ||||
VEGF (known also as VEGFA) was initially identified in conditioned medium from bovine pituitary follicular cells. VEGFA belongs to the VEGF family, which has the following members: VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C (VEGF-2), VEGF-D, and PlGF (placental growth factor). In addition, viral VEGF homologs (collectively called VEGF-E) and snake venom VEGFs, such as T.f. (Trimeresurus flavoviridis) and svVEGF (called VEGF-F), have been described. VEGFA is alternatively spliced to generate variants with different numbers of amino acids, such as VEGFA121, VEGFA145, VEGFA165, and VEGFA189. VEGFA165 is predominant and responsible for VEGFA biological potency.
While VEGF121 is freely diffusible and does not bind to neuropilins (NRPs) or heparan sulphate (HS), VEGF165 and VEGF189 bind to both, resulting in retention on the cell surface or in the extracellular matrix. NRP1 lacks a typical kinase domain and acts as a co-receptor, and in response to VEGF165, NRP1 couples with VEGF-Rs to signal in endothelial cells. In addition, it has been suggested that bone marrow cells that are recruited to Ewing’s tumors are differentiated into vascular smooth muscle cells, and VEGF165 is responsible for this differentiation.
VEGFA is highly expressed in most of the solid tumors generated in breast, lung, renal, colorectal, and liver tissues. VEGFA has strong vascular permeability activity, and significantly contributes to the formation of ascites tumors. VEGFA can act as a direct proinflammatory mediator during the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and protect rheumatoid synoviocytes from apoptosis, which contributes to synovial hyperplasia. VEGFA is expressed in synovial macrophages and synovial fibroblasts in RA patients. Also, VEGFA is associated to age-related macular degeneration (AMD). AMD is due to neovascularization that originates from endothelial cells in the choroid that grow into neurosensory retina as choroidal neovascularization (CNV).
Product Details
- Source
- Human VEGF-165, amino acids Ala27-Arg191 (Accession# AAM03108) was expressed in 293E cells.
- Molecular Mass
- The 165 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 19 kD. The DTT-reduced protein migrates at approximately 20-28 kD and non-reduced protein migrates at 50 kD by SDS-PAGE. The N-terminal amino acid is Alanine.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.1 µm filtered protein solution is in 5 mM citric acid, 5 mM Na2HPO4, 0.15 M NaCl pH 4.0.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.1 EU per µg protein as determined by the LAL method
- Concentration
- 500 µg/mL
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% endotoxin-free BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week or stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
- ED50 = 1 - 6 ng/mL as determined by the dose-dependent stimulation of HUVEC cell proliferation. Deep Blue Cell Viability™ Kit (Cat. No. 424701) is used to measure the proliferation.
- Application
-
Bioassay
Cell Culture - Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are validated in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
- Disclaimer
-
GMP Recombinant Proteins. BioLegend GMP recombinant proteins are manufactured in a dedicated GMP facility and compliant with ISO 13485:2016. For research or ex vivo cell processing use. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Our processes include:
- Batch-to-batch consistency
- Material traceability
- Documented procedures
- Documented employee training
- Equipment maintenance and monitoring records
- Lot-specific certificates of analysis
- Quality audits per ISO 13485:2016
- QA review of released products
BioLegend GMP recombinant proteins are manufactured and tested in accordance with USP Chapter 1043, Ancillary Materials for Cell, Gene and Tissue-Engineered Products and Ph. Eur. Chapter 5.2.12.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Homodimer
- Distribution
-
Widely expressed
- Function
-
VEGFA is a key player in vasculogenesis, the formation of blood vessels from progenitor cells, as well as angiogenesis. The expression of the VEGFA gene is upregulated via hypoxia, estrogen, and NF-κB pathways. In addition, VEGFA is upregulated by PDGF-BB, P1GF, TGFβ1, IGF1, FGFs, HGF, TNFα, and IL-1. VEGFA induces proliferation and cell migration in endothelial cells, and plays important roles during wound healing. Also, VEGFA regulates haematopoietic stem cell survival.
VEGFA interacts with vascular endothelial cells and monocytes/macrophages, which express VEGFR1. This interaction induces proliferation of endothelial cells and stimulates migration of monocytes/macrophages. VEGFR2 is expressed in endothelial cells and VEGFR2-signaling is essential for the development of vascular systems in the embryo. - Interaction
- Embryonic Stem Cells, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Neural Stem Cells
- Ligand/Receptor
- VEGFR1 (Flt-1), VEGFR2 (KDR/Flk-1)
- Bioactivity
- Measured by its ability to induce proliferation of HUVEC.
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells, Mesenchymal cells, Neural Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Angiogenesis, Cell Biology, Neuroscience, Stem Cells, Synaptic Biology
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines, Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
- Conn G, et al. 1990. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 87:1323-7.
- Gerber HP, et al. 2002. Nature. 417:954-8.
- Shibuya M. 2006. J Biochem Mol Biol. 39:469-78.
- Reddy K, et al. 2008. Angiogenesis. 11:257-67.
- Shibuya M. 2008. BMB Rep. 41:278-86.
- Monaghan-Benson E, et al. 2010. Am J Pathol. 177:2091-102.
- Koch S & Claesson-Welsh L. 2012. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2:a006502.
- Gene ID
- 7422 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about VEGF-165 on UniProt.org

 Login / Register
Login / Register 














Follow Us