- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Streptavidin-Horseradish Peroxidase, SAv-HRP
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 405210 | 1 mL | 104€ | ||||
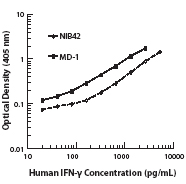
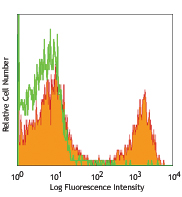
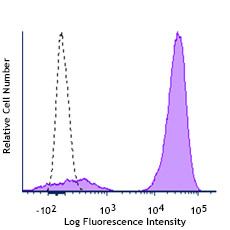
Streptavidin binds to biotin with high affinity. Streptavidin-HRP is useful for detecting biotinylated antibodies, e.g., in ELISA, ELISPOT, IHC or Western blotting. For ELISA applications, HRP will act on soluble substrates, such as ABTS or TMB, to yield a colorimetric reaction. For ELISPOT or Western blotting applications, HRP will act on precipitating substrates, such as 4CN, to yield a colorimetric reaction.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat, All Species
- Formulation
- Buffered solution containing bovine protein and preservatives (methylisothiazolone, bromonitrodioxane, and other active isothiazolones).
- Preparation
- Streptavidin is conjugated with horseradish peroxidase under optimal conditions.
- Storage & Handling
-
The streptavidin-HRP solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C. Avoid exposure to sodium azide.To obtain lot-specific expiration date, please enter the lot number in our Concentration and Expiration Lookup or Certificate of Analysis online tools.)
This product has a shelf-life of 12 months or less. Please use our Expiration Lookup Tool to verify the expiration date of your lot of product - Application
-
ELISA - Quality tested
ELISPOT, WB, IHC - Reported in the literature, not verified in house - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this Streptavidin-HRP is quality control tested by ELISA assay. For ELISA or Western blot analysis, the reagent should be titrated between 1:1000 - 1:3000 to determine optimal conditions. For ELISPOT analysis, the reagent should be titrated between 1:500 - 1:1500 to determine optimal conditions. Avoid using biotin-containing solutions as diluents and solutions containing sodium azide. Sodium azide is an inhibitor of horseradish peroxidase. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
Streptavidin-HRP is useful as a second step reagent for indirect enzymatic labelling, in conjunction with biotinylated primary antibodies. Sav-HRP is recommended for ELISA, ELISPOT and Western blotting, when used with the relevant substrate system.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Li KJ, et al. 2006. J. Leukoc. Biol. doi:10.1189/jlb.1105668.PubMed
- Weldon S, et al. 2009. J. Immunol. 183:8148. PubMed
- Basnayake K, et al. 2010. J Am Soc Naphrol. 21:1165. PubMed
- Marder W, et al. 2011. Ann Rheum Dis. PubMed
- Cheng J, et al. 2012. Mol Biol Cell. 23:2891. PubMed
- Vishwakarma V, et al. 2012. Infect Immun. 80:3236. PubMed
- Sun X, et al. 2013. J. Immunol. 190:2536. PubMed
- Van Phan T, et al. 2013. Biochem Pharmacol. 85:1145. PubMed
- Ranganathan P, et al. 2013. J Rhematol. 40:129. PubMed
- Din Su, et al. 2013. Occup Med. PubMed
- Bulut GB, et al. 2013. Blood. 122:3964. PubMed
- Chia YL, et al. 2013. Antiviral Res. 3542:354. PubMed
- Ahn JM, et al. 2014. Mol Cell Proteomics. 13:30. PubMed
- Din SU, et al. 2014. Occup Med. 64:39. PubMed
- Balmer ML, et al. 2014. Sci Transl Med. 21:237. PubMed
- Klehmet J, et al. 2014. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. PubMed
- Wu CC, et al. 2014. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 23:1569. PubMed
- Peng JG, et al. 2014. J Virol. 88:8386. PubMed
- Chlon TM, et al. 2014. J Virol. 88:11315. PubMed
- Sadovskaya I, et al. 2014. Carbohydr Poly. 111:139. PubMed
- Liu T, et al. 2015. Infect Immun. 83:2011. PubMed
- Himmelein S, et al. 2015. J Virol. 89:5747. PubMed
- Dinter J, et al. 2015. J Mol Endocrinol. 54:205. PubMed
- Yang L, et al. 2015. J Immunol. 194:5635. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Gene ID
- NA
- UniProt
- View information about Biotin on UniProt.org
 Login / Register
Login / Register 








Follow Us