- Clone
- mAb 33 (33) (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- KIR2DL4, 2DL4, p49, KIR103
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-

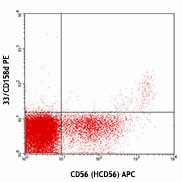
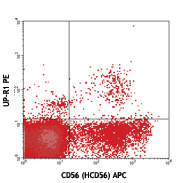
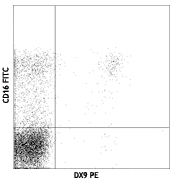
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were cultured 16 hrs with IL-2, then stained with CD56 (clone HCD56) APC and CD158d (clone 33) PE (top) or mouse IgG1, κ PE isotype control (bottom). -

| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 347005 | 25 tests | 123€ | ||||
| 347006 | 100 tests | 288€ | ||||
CD158 molecules, also known as KIRs (killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors), are a family of transmembrane proteins with either two (KIR2D) or three (KIR3D) Ig-like extracellular domains. Some KIRs, with long cytoplasmic domains, contain ITIMs and possess inhibitory functions and others, with short cytoplasmic regions, lack ITIM and have activation functions. Fourteen polymorphic KIR genes have been reported in humans. KIR2DL4 (CD158d) is a unique receptor which has an ITIM in its cytoplasmic domain and a charged residue in the transmembrane domain. It possesses both inhibitory and activation functions. Two common alleles (10A and 9A) of KIR2DL4 have been reported. The 10A allele (with 10 adenines at the end of the transmembrane exon) receptor is expressed on CD56high NK subset, whereas its expression on CD56dim NK cells is inducible upon culture. The major 9A allele receptor is a secreted form. HLA-G is the ligand of CD158d.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- NK3.3 cells and KIR2DL4-Ig fusion protein
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA)
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with PE under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
KIR2DL4 expression in NK cells is highly localized to the endosomes3. mAb 33 can be internalized by NK cells by endocytosis at 37°C3, and induces NK cell cytotoxicity1,2. Based on in-house observations, we suggest incubating for 45 - 60 minutes at room temperature with clone mAb 33 to observe better CD158d staining.
This clone has been tested in-house and determined to not be suitable for applications in immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded tissue sections (IHC-P). -
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Rajagopalan S, et al. 2001. J. Immunol. 167:1877. (FC)
- Goodridge JP, et al. 2003. J. Immunol. 171:1768. (FC)
- Rajagopalan S, et al. 2006. PLoS Biol. 4:e9.
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_2028416 (BioLegend Cat. No. 347005)
AB_2130692 (BioLegend Cat. No. 347006)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Contains two Ig-like extracellular domains, 45-50 kD
- Distribution
-
On CD56high NK cells and cultured CD56dim NK cells
- Ligand/Receptor
- HLA-G
- Cell Type
- NK cells
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Rajagopalan S, et al. 2006. PLoS Biol. 4:e9.
2. Goodridge JP, et al. 2007. Eur. J. Immunol. 37:199. - Gene ID
- 3805 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD158d on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
- What type of PE do you use in your conjugates?
- We use R-PE in our conjugates.
Other Formats
View All CD158d Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| PE anti-human CD158d (KIR2DL4) | mAb 33 (33) | FC |
| APC anti-human CD158d (KIR2DL4) | mAb 33 (33) | FC |
| TotalSeq™-A0913 anti-human CD158d (KIR2DL4) | mAb 33 (33) | PG |
| Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-human CD158d (KIR2DL4) | mAb 33 (33) | FC,Activ |
| TotalSeq™-B0913 anti-human CD158d (KIR2DL4) | mAb 33 (33) | PG |
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
PE anti-human CD158d (KIR2DL4)
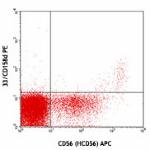
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were cultured 16 hrs with... 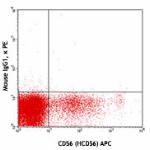
-
APC anti-human CD158d (KIR2DL4)
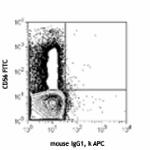
IL-2 stimulated (18hrs) human peripheral blood lymphocytes s... 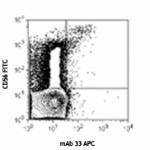
IL-2 stimulated (18hrs) human peripheral blood lymphocytes s... -
TotalSeq™-A0913 anti-human CD158d (KIR2DL4)
-
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-human CD158d (KIR2DL4)

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were cultured 16 hrs with... 
-
TotalSeq™-B0913 anti-human CD158d (KIR2DL4)
 Login / Register
Login / Register 













Follow Us