- Clone
- 4B12 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- C-C chemokine receptor type 7 (CCR7), MIP-3 beta receptor, EBV-induced G protein coupled receptor 1, EBI-1, CD197
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
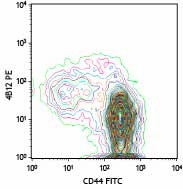
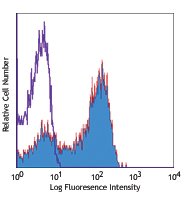
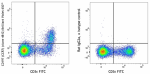
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with CCR7-PE (clone 4B12) and CD44-FITC (gated on CD3+ cell population) -
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with CCR7-PE (clone 4B12) and CD44-FITC (gated on CD3+ cell population)
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120105 | 50 µg | 147€ | ||||
| 120106 | 200 µg | 341€ | ||||
CD197 is also known as C-C chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7) or EBI-1. CCR7 is a G-coupled rhodopsin-like member of the GPCR superfamily with a predicted molecular weight of 43 kD that is expressed on hematopoietic stem cells, most naive T cells, some memory T cells, B subset, and mature dendritic cells. CCR7 is a receptor for the chemokines CCL19 (MIP3 beta) and SLC (6CKine, Exodus-2, TCA-4, CCL21) that plays a role in thymocytes development, T cell adhesion at intestinal sites, the homeostatic recirculation of memory T cells, and chemotaxis.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- Mouse CCR7 transfected RBL-2H3 cells
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with PE under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤ 2.0 µg per 106cells in 100 µl staining volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
The 4B12 antibody does not inhibit binding of ligand to receptor. Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunoprecipitation. To reduce non-specific binding to cells bearing Fc-receptors, pre-incubation of cells with anti-mouse CD16/CD32, clone 93 (Cat. No. 101301/101302) is recommended prior to immunofluorescent staining.
Staining with clone 4B12 is recommended at 37°C (see supplemental data of PE staining at differing temperatures). -
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Ohl L, et al. 2004. Immunity 21:279.
- Ritter U, et al. 2004. J. Leukocyte Biol. 76:472.
- Lan YY, et al. 2005. Am. J. Transplant. 5:2649. (FC)
- Lee JH, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:301. (FC) PubMed
- Kurooka M and Kaneda Y. 2007. Cancer Res. 67:227. (FC) PubMed
- Thompson BD. 2007. J. Biol. Chem. 282:9547. (FC)
- Sakai N, et al. 2006. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:14098. (FC)
- Turnquist HR, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:7018. (FC)
- Hwang IY, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:439. (FC) PubMed
- Kang SG, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:3724.
- Mao A et al. 2005. J. Immunol. 175:5146. PubMed
- Allende ML, et al. 2008. FASEB J. 22:307. PubMed
- Kang SG, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:3724. PubMed
- Chen H, et al. 2005. J. Immunol. 175:591. PubMed
- Florido M, et al. 2009. Immunobiology. 214:643. PubMed
- Bankoti J, et al. 2010. Toxicol. Sci. 115:422. (FC) PubMed
- del Rio ML, et al. 2011. Transpl. Int. 24:501. (FC) PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_389357 (BioLegend Cat. No. 120105)
AB_389357 (BioLegend Cat. No. 120106)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Rhodopsin-like GPCR superfamily, G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, integral membrane protein, predicted molecular weight 43 kD
- Distribution
-
Hematopoietic stem cells, T subsets, mature dendritic cells
- Function
- Homozygous mutation. Receptor for MIP-3 beta and SLC chemokines. Probable mediator of EBV effects on B lymphocytes. Plays a role in T cell adhesion at intestinal sites; may also play a role in the homeostatic recirculation of memory T cells and chemotaxis.
- Ligand/Receptor
- MIP3 beta, SLC (6CKine, Exodus-2, TCA-4)
- Cell Type
- Hematopoietic stem and progenitors, T cells, Dendritic cells, Tregs
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules, Cytokine/Chemokine Receptors, GPCR
- Antigen References
-
1. Schweickart VL, et al. 1994. Genomics 23:643.
2. Yoshida R, et al. 1998. J. Biol. Chem. 273:7118.
3. Campbell JJ, et al. 1998. J. Cell Biol. 141:1053.
4. Willimann K, et al. 1998. Eur. J. Immunol. 28:2025. - Gene ID
- 12775 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD197 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- What type of PE do you use in your conjugates?
- We use R-PE in our conjugates.
- Does staining at room temperature or even at 37°C help for checking chemokine receptors expression?
-
Due to continuous recycling of many chemokine receptors, it may be worthwhile to consider staining at room temperature or at 37°C if the staining at lower temperature (which can potentially reduce receptor turnover) is not optimal.
Other Formats
View All CD197 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | FC,IP |
| Biotin anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | FC |
| PE anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | FC |
| APC anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | FC |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | FC |
| Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | FC |
| PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | FC |
| PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | FC |
| Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | FC |
| PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | FC |
| PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | FC |
| Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | FC |
| Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | FC |
| TotalSeq™-A0377 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | PG |
| TotalSeq™-C0377 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | PG |
| TotalSeq™-B0377 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | PG |
| APC/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) Antibody | 4B12 | FC |
| Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) | 4B12 | FC |
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)
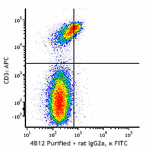
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with CD197 (clone 4B12) purified... 
Peyer’s patches of a CX3CR1-GFP -/+ mouse were fi... -
Biotin anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with CD3 FITC and biotinyl... 
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with CD3 FITC and biotinyl... -
PE anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)
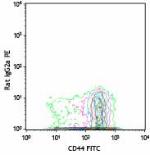
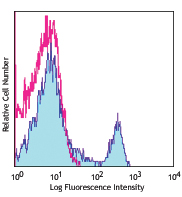
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with CCR7-PE (clone 4B12) and CD... 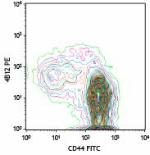
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with CCR7-PE (clone 4B12) and CD... -
APC anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)

C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with 4B12 APC and 145-2C11 (CD3)... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)
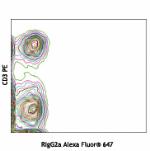
C57BL/6 Splenocytes stained with RIgG2a, κ Alexa Fluor... 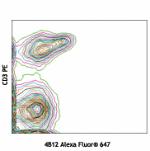
C57BL/6 Splenocytes stained with RIgG2a, κ Alexa Fluor... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)
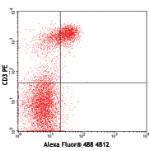
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with 4B12 Alexa Fluor® 488 a... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3ε ... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)
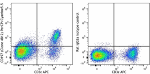
C57B/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e APC and CD19... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)

C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD3 FITC and CD197 (cl... 
-
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)

C57BL/6 mouse lymphocytes were stained with CD3 Alexa Fluor&... 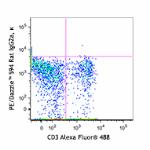
-
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)
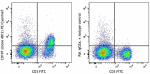
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD3 FITC and CD197 (cl... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)

Mouse splenocytes stained with FITC CD3 and CD197 (clone 4B1... 
-
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)

Mouse splenocytes stained with FITC CD3 and CD197 (clone 4B1... 
-
TotalSeq™-A0377 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)
-
TotalSeq™-C0377 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)
-
TotalSeq™-B0377 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)
-
APC/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7) Antibody
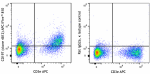
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3e APC an... -
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse CD197 (CCR7)
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3ε FITC a...

 Login / Register
Login / Register 














Follow Us