- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily, member 11 (TNFSF11), Osteoprotegerin ligand (OPGL), Receptor activator of NF-kappa-B ligand (RANKL), TNF-related activation-induced cytokine (Trance), Osteoclast differentiation factor (ODF), CD254
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 577102 | 10 µg | 188€ | ||||
RANKL gene encodes a type II membrane protein of 316 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 35 kD. RANKL is cleaved to produce a soluble form with biological activity. The shedding of membrane-bound RANKL appears to be mediated by expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 14 and ADAM10. Suppression of MMP14 in primary osteoblasts increases membrane-bound RANKL and promotes osteoclastogenesis in cocultures with macrophages. Therefore, RANKL shedding seems to be an important process that down-regulates local osteoclastogenesis. Alternatively, an increased production of RANKL by osteoblastic cells leads to osteoclast differentiation, activation, and survival, which results in increased bone resorption. Binding of RANKL to its receptor RANK activates TNF receptor- associated factor 6 (TRAF6), which is linked to downstream pathways including NF-kB, c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) or Src. TRAF6 has been shown to be necessary for the differentiation of osteoclastic cells by enhancing Src kinase, essential for osteoclast function.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Source
- Mouse TRANCE, amino acids Lys158-Asp316 (Accession # NM_011613.3) was expressed in insect cells, with an N-terminal 9-His tag and IEGR-Xa sequence.
- Molecular Mass
- The 178 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 20 kD. The DTT-reduced protein migrates at approximately 20 kD by SDS-PAGE.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- 0.22 µm filtered protein solution is in PBS
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 ng per µg cytokine as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/mL
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at -20°C for up to six months, or at -70°C or colder until the expiration date. For maximum results, quick spin vial prior to opening. The protein can be aliquoted and stored at -20°C or colder. Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
- Activity
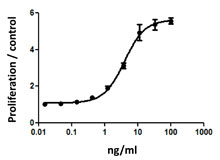
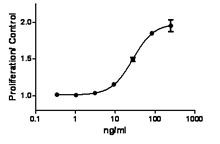
- Bioactivity was measured by its property to induce osteoclast differentiation in RAW264.7 cells in the absence of any cross-linking. The bioactivity is equivalent to competitor cytokines.
- Application
-
Bioassay - Quality tested
- Application Notes
-
BioLegend carrier-free recombinant proteins provided in liquid format are shipped on blue-ice. Our comparison testing data indicates that when handled and stored as recommended, the liquid format has equal or better stability and shelf-life compared to commercially available lyophilized proteins after reconstitution. Our liquid proteins are verified in-house to maintain activity after shipping on blue ice and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- de Lau W, et al. 2012. Mol Cell Biol. 32:3639. PubMed.
- Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Distribution
-
T cells, osteoblasts, bone marrow stromal cells, hypertrophic and prehypertrophic chondrocytes, stromal fibroblasts, synovial cells, and megakaryocytes.
- Function
- RANKL is a potent stimulator of osteoclast formation from precursor cells and bone-resorbing activity in mature osteoclasts. The expression of RANKL in human and murine osteoblastic cells is stimulated by various cytokines (IL-1, TNFa and IL-11) and calciotrophic hormones including PTH, 1,25dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25D3) and prostaglandin E2. RANKL augments the ability of dendritic cells to stimulate naïve T-cell proliferation. RANKL activates JNK and NF-κB and induces the expression of IL-1, IL-6, IL-12, and IL-15 in dendritic cells. In addition, RANKL is a crucial factor in lymphocyte development and lymph node organogenesis. RANKL stimulates proliferation, adhesion, and IL-7 expression of thymic epithelial cells.
- Interaction
- T cells, dendritic cells, bone marrow derived macrophages, osteoclast precursors and mature osteoclasts.
- Ligand/Receptor
- TNFRSF11A (Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 11A) also called RANK and TNFRSF11B (OPG) which acts as a decoy receptor for RANKL and as a potent inhibitor of osteoclast formation.
- Cell Type
- Dendritic cells, Embryonic Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines, Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
1. Dehm SM, et al. 2004. Biochem. Cell Biol. 82:263.
2. Hikita A, et al. 2006. J. Biol. Chem. 281:36846.
3. Kim NS, et al. 2006. Mol. Cell. Biol. 26:1002.
4. Wada T, et al. 2006. TRENDS Mol. Med. 12:17.
5. Lee HW, et al. 2008. Exp. Mol. Med. 40:59.
6. Ha J, et al. 2010. J. Immunol. 184:4717. - Gene ID
- 21943 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about TRANCE on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- Why choose BioLegend recombinant proteins?
-
• Each lot of product is quality-tested for bioactivity as indicated on the data sheet.
• Greater than 95% Purity or higher, tested on every lot of product.
• 100% Satisfaction Guarantee for quality performance, stability, and consistency.
• Ready-to-use liquid format saves time and reduces challenges associated with reconstitution.
• Bulk and customization available. Contact us.
• Learn more about our Recombinant Proteins. - How does the activity of your recombinant proteins compare to competitors?
-
We quality control each and every lot of recombinant protein. Not only do we check its bioactivity, but we also compare it against other commercially available recombinant proteins. We make sure each recombinant protein’s activity is at least as good as or better than the competition’s. In order to provide you with the best possible product, we ensure that our testing process is rigorous and thorough. If you’re curious and eager to make the switch to BioLegend recombinants, contact your sales representative today!
- What is the specific activity or ED50 of my recombinant protein?
-
The specific activity range of the protein is indicated on the product datasheets. Because the exact activity values on a per unit basis can largely fluctuate depending on a number of factors, including the nature of the assay, cell density, age of cells/passage number, culture media used, and end user technique, the specific activity is best defined as a range and we guarantee the specific activity of all our lots will be within the range indicated on the datasheet. Please note this only applies to recombinants labeled for use in bioassays. ELISA standard recombinant proteins are not recommended for bioassay usage as they are not tested for these applications.
- Have your recombinants been tested for stability?
-
Our testing shows that the recombinant proteins are able to withstand room temperature for a week without losing activity. In addition the recombinant proteins were also found to withstand four cycles of freeze and thaw without losing activity.
- Does specific activity of a recombinant protein vary between lots?
-
Specific activity will vary for each lot and for the type of experiment that is done to validate it, but all passed lots will have activity within the established ED50 range for the product and we guarantee that our products will have lot-to-lot consistency. Please conduct an experiment-specific validation to find the optimal ED50 for your system.
- How do you convert activity as an ED50 in ng/ml to a specific activity in Units/mg?
-
Use formula Specific activity (Units/mg) = 10^6/ ED50 (ng/mL)
 Login / Register
Login / Register 









Follow Us