- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Fixable Dye, Fixable Viability Dye
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
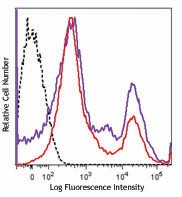
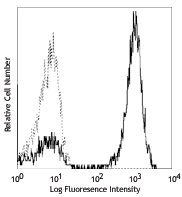
One day old C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with Zombie NIR™ and analyzed before fixation (purple) or after fixation and permeabilization (red). Cells alone, without Zombie NIR™ staining, are indicated in black.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 423105 | 100 tests | 72€ | ||||
| 423106 | 500 tests | 268€ | ||||
Zombie NIR™ is an amine reactive fluorescent dye that is non-permeant to live cells, but permeant to the cells with compromised membranes. Thus, it can be used to assess live vs. dead status of mammalian cells. Zombie NIR™ is a polar water soluble dye, providing red fluorescence, making it suitable for multi-color detection.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Preparation
- Zombie NIR™ Fixable Viability kit is composed of lyophilized Zombie NIR™ dye and anhydrous DMSO. For reconstitution, bring the kit to room temperature; add 100 µl of DMSO to one vial of Zombie NIR™ dye until fully dissolved. 100 tests = 1 vial of Zombie NIR™ + DMSO, 500 tests = 5 vials of Zombie NIR™ + DMSO.
- Storage & Handling
- Store kit at -20°C upon receipt. Do not open vials until needed. Once the DMSO is added to the Zombie NIR™ dye, use immediately, or store at -20°C in a dry place and protected from light, preferably in a desiccator or in a container with desiccant for no more than one month.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this product is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis.
For flow cytometry, the suggested dilution is 1:100-1:1000 for 1-10 million cells. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application, as optimal dosage varies with cell type. - Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Zombie NIR™ dye is excited by the red laser and has fluorescence emission maximum at 746 nm. If using in a multi-color panel design, filter optimization may be required depending on other fluorophores used. Zombie NIR™ dye has similar emission to APC/Cyanine7.
Standard Cell Staining Protocol:- Prior to reconstitution, spin down the vial of lyophilized reagent in a microcentrofuge to ensure the reagent is at the bottom of the vial.
- For reconstitution, pre-warm the kit to room temperature; add 100 µL of DMSO to one vial of Zombie NIR™ dye and mix until fully dissolved
- Wash cells with PBS buffer (no Tris buffer and protein free).
- Dilute Zombie NIR™ dye at 1:100-1000 in PBS. Resuspend 1-10 x 106 cells in diluted 100 µL Zombie NIR™ solution. To minimize background staining of live cells, titrate the amount of dye and/or number of cells per 100 µL for optimal performance. Different cell types can have a wide degree of variability in staining based on cell size and degree of cell death.
- Note: Don’t use Tris buffer as a diluent and be sure that the PBS does not contain any other protein like BSA or FBS.
- Note: The amount of dye used can also influence the ability to detect apoptotic as well as live and dead cells.
- Incubate the cells at room temperature (or 4°C), in the dark, for 15-30 minutes.
- Wash one time with 2 mL BioLegend’s Cell Staining Buffer (Cat. No. 420201) or equivalent buffer containing serum or BSA.
- Continue performing antibody staining procedure as desired.
- Cells can be fixed with paraformaldehyde or methanol prior to permeabilization or can be analyzed without fixation.
No-wash Sequential Staining Protocol:
- Wash cells with PBS buffer (no Tris buffer and protein free).
- For reconstitution, pre-warm the kit to room temperature; add 100 µL of DMSO to one vial of Zombie NIR™ dye and mix until fully dissolved
- Determine the total µL volume of antibody cocktail previously titrated and optimized for the assay that will be added to each vial/well of cells based on a final volume of 100 µL. Subtract that antibody volume from the 100 µL total staining volume intended for the assay. In the remaining volume, dilute Zombie NIR™ dye at 1:100-1000 in PBS as determined by prior optimization at that volume. For example, if you are adding 20 µL of antibody cocktail for a 100 µL total staining volume, use 80 µL of Zombie NIR™ solution. Resuspend 1-10 x 106 cells in the appropriate volume of Zombie NIR™ solution. Different cell types can have a wide degree of variability in staining based on cell size and degree of cell death.
- Note: Don’t use Tris buffer as a diluent and be sure that the PBS does not contain any other protein like BSA or FBS.
- Note: The amount of dye used can also influence the ability to detect apoptotic as well as live and dead cells.
- Incubate for 10-15 minutes at RT (or 4°C), protected from light. Without washing the cells, add the cell surface antibody cocktail and incubate for another 15-20 minutes.
- Add 1-2 mL Cell Staining Buffer (Cat. No. 420201) or equivalent buffer containing BSA or serum. Centrifuge to pellet.
- Continue with normal fixation and permeabilization procedure. If planning to skip fixation and analyze cells live, complete an additional wash step to minimize any unnecessary background of the live cells.
- Notes: If the cell type in use cannot tolerate a protein-free environment, then titrate the Zombie NIR™ dye in the presence of the same amount of BSA/serum as will be present in the antibody staining procedure. A higher amount of Zombie NIR™ may be required since the BSA/serum will react with and bind up some proportion of the Zombie NIR™.
- Additional Product Notes
-
View more applications data for this product in our Scientific Poster Library.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) - Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Biology Area
- Apoptosis/Tumor Suppressors/Cell Death, Cell Biology, Neuroscience
- Gene ID
- NA
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
- I am concerned about the spillover I am observing from the Zombie dye into its neighboring channels.
- Rule of thumb with Zombie dyes is to titrate them down as much as possible to fit your application. This should potentially help with spillover. Secondly, Zombie positive events represent dead cells and are typically gated out from analysis.
- How does the performance of your Zombie dye compare with competitors?
-
Zombie dyes have been tested against other leading competitors' fixable viability kits and given comparable results. We also highly recommend that you titrate down the amount of each dye used in order to best match the negative signals of your unstained sample and MFI- (mean fluorescence intensity) stained samples.
- Can I use methanol/ethanol for fixation after using a Zombie dye?
-
Yes, most fixation reagents are fine to be used with Zombie dyes. However, it should be noted that Zombie dyes can still be sensitive to reactive oxygen species. Light exposure or reagents with hydrogen peroxide can lead to free radical formation, affecting fluorescence.
- Can Zombie be used to determine bacteria, yeast viability?
- We have not tested in house bacterial or yeast viability using Zombie dyes. It is not clear whether the difference between surface and intracellular signals will be significantly different in case of non mammalian cells.
- Can I use Zombie with cells suspension containing serum?
- Serum is full of proteins which will sequester the dye and thereby reducing its effective concentration. The basic rule of thumb with zombie is to titrate it based on your specific condition. Titration also helps reduce the background and spillover into other channels.
- Can I use Zombie dyes for microscopy?
-
Zombie dyes tested in-house for microscopy applications will display data on the product technical datasheet. It should be noted that Zombie dyes may not work for dead cell discrimination in every microscopy application. Important considerations that may impact analysis are determining the signal level that constitutes a dead cell and identifying the proper plane to observe the dead cells.
- Why can't I fix my cells prior to using Zombie dyes?
-
The fixation process can contort and alter the membrane of cells, effectively rendering them dead. Since the ability of the Zombie dyes to stain dead cells is correlated with cell permeability, your results may no longer be a valid representation of dead versus live cells.
- Can I use Zombie dyes to detect apoptotic cells?
-
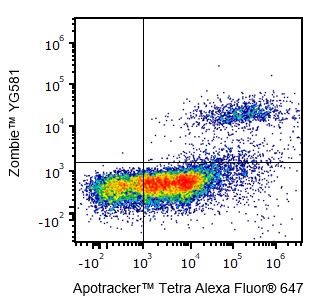
Yes, Zombie dyes can be used with apoptosis markers, such as Annexin V or Apotracker™ (shown below), to discriminate live, apoptotic, and dead cells.
One day-old C57BL/6 mouse thymocytes were stained with Apotracker™ Tetra Alexa Fluor® 647 and Zombie™ YG581. Zombie-dim/Apotracker™-positive cells are apoptotic, while double-positive cells are dead. Live cells are negative for both markers.
- How should I store Zombie dyes?
-
Store the Zombie dye kit at -20°C upon receipt. Do not open vials until needed. Once DMSO is added, use immediately or store at -20°C in a dry place and protected from light, preferably in a desiccator or in a container with desiccant for no more than one month.

 Login / Register
Login / Register 














Follow Us