- Clone
- UCHT1 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Workshop
- III 471
- Other Names
- T3, CD3ε
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
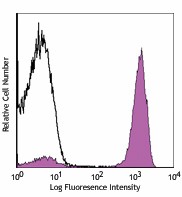
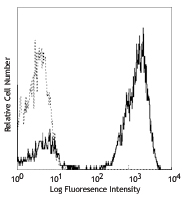
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with UCHT1 PE/Cyanine7 and overlayed with isotype control
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300419 | 25 tests | 115€ | ||||
| 300420 | 100 tests | 223€ | ||||
CD3ε is a 20 kD chain of the CD3/T-cell receptor (TCR) complex which is composed of two CD3ε, one CD3γ, one CD3δ, one CD3ζ (CD247), and a T-cell receptor (α/β or γ/δ) heterodimer. It is found on all mature T cells, NKT cells, and some thymocytes. CD3, also known as T3, is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that plays a role in antigen recognition, signal transduction, and T cell activation.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Reported Reactivity
- Chimpanzee
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA)
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with PE/Cyanine7 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunohistochemical staining of acetone-fixed frozen sections4,6,7 and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections11, immunoprecipitation1, activation of T cells2,3,5, Western blotting9, and spatial biology (IBEX)16,17. The LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin < 0.1 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for functional assays (Cat. No. 300413, 300414, and 300432). For highly sensitive assays, we recommend Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Cat. No. 300437, 300438, 300465, 300466, 300473, 300474) with a lower endotoxin limit than standard LEAF™ purified antibodies (Endotoxin < 0.01 EU/µg).
- Application References
-
- Salmeron A, et al. 1991. J. Immunol. 147:3047. (IP)
- Graves J, et al. 1991. J. Immunol. 146:2102. (Activ)
- Lafont V, et al. 2000. J. Biol. Chem. 275:19282. (Activ)
- Ryschich E, et al. 2003. Tissue Antigens 62:48. (IHC)
- Thompson AG, et al. 2004. J. Immunol. 173:1671. (Activ)
- Sakkas LI, et al. 1998. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immun. 5:430. (IHC)
- Mack CL, et al. 2004. Pediatr. Res. 56:79. (IHC)
- Thakral D, et al. 2008. J. Immunol. 180:7431. (FC) PubMed
- Van Dongen JJM, et al. 1988. Blood 71:603. (WB)
- Yoshino N, et al. 2000. Exp. Anim. (Tokyo) 49:97. (FC)
- Pollard, K. et al. 1987. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 35:1329. (IHC)
- Luckashenak N, et al. 2013. J. Immunol. 190:27. PubMed
- Laurent AJ, et al. 2014. PLoS One. 9:103683. PubMed
- Li J, et al. 2015. Cancer Res. 75:508. PubMed
- Stoeckius M, et al. 2017. Nat. Methods. 14:865-868. (PG)
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2020. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:33455-33465. (SB) PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2022. Nat Protoc. 17:378-401. (SB) PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_439780 (BioLegend Cat. No. 300419)
AB_439780 (BioLegend Cat. No. 300420)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Ig superfamily, with the subunits of CD3γ, CD3δ, CD3ζ (CD247) and TCR (α/β or γ/δ) forms CD3/TCR complex, 20 kD
- Distribution
-
Mature T and NK T cells, thymocyte differentiation
- Function
- Antigen recognition, signal transduction, T cell activation
- Ligand/Receptor
- Peptide antigen bound to MHC
- Cell Type
- NKT cells, T cells, Thymocytes, Tregs
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules, TCRs
- Antigen References
-
1. Barclay N, et al. 1993. The Leucocyte FactsBook. Academic Press. San Diego.
2. Beverly P, et al. 1981. Eur. J. Immunol. 11:329.
3. Lanier L, et al. 1986. J. Immunol. 137:2501-2507. - Gene ID
- 916 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD3 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All CD3 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
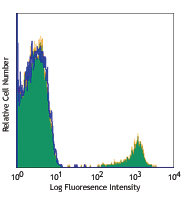
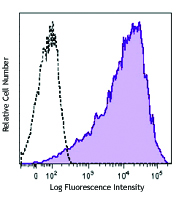
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
APC anti-human CD3
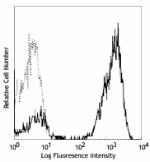
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with UCHT1 APC -
Biotin anti-human CD3
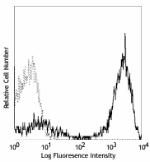
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with biotinylated... -
FITC anti-human CD3
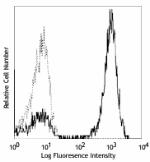
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with UCHT1 FITC -
PE anti-human CD3
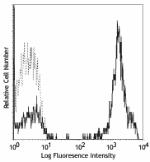
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with UCHT1 PE 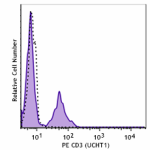
Pre-lysed human blood leukocytes were stained with PE anti-h... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-human CD3
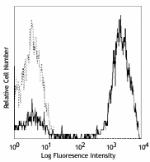
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with UCHT1 PE/Cya... -
Purified anti-human CD3
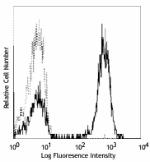
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with purified UCH... 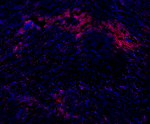
Human frozen spleen tissue slices were fixed with 4% PFA for... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-human CD3
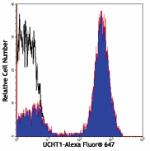
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with UCHT1 Alexa ... 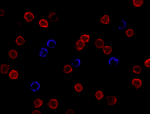
Human peripheral mononuclear cells were fixed with 2% parafo... 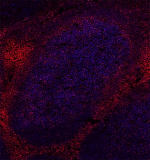
Human frozen tonsil tissue slices were fixed with 4% PFA for... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-human CD3
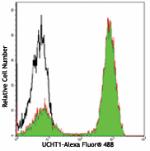
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with UCHT1 Alexa ... 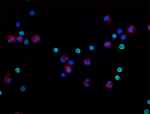
Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and neutrophil mixe... 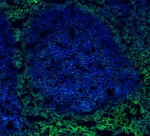
Human frozen tonsil tissue slices were fixed with 4% PFA for... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-human CD3
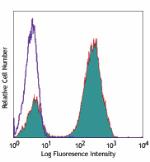
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with UCHT1 Pacifi... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-human CD3
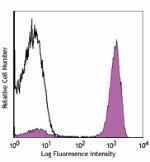
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with UCHT1 PE/Cya... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-human CD3
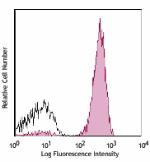
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with UCHT1 Alexa ... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-human CD3
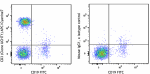
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 FI... -
PerCP anti-human CD3
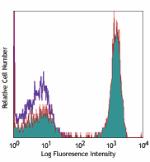
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with UCHT1 PerCP -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-human CD3
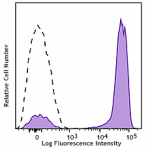
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 (cl... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-human CD3
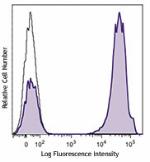
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 (cl... 
Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were fixed with 2% ... 
Human frozen tonsil tissue slices were fixed with 4% PFA for... -
Brilliant Violet 570™ anti-human CD3

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 AP... 
-
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-human CD3

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with LEAF™ purifi... 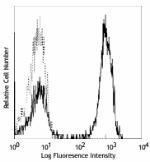
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with LEAF™ purifi... 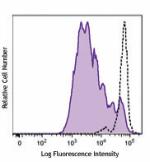
Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stained with C... -
Purified anti-human CD3 (Maxpar® Ready)

Human PBMCs stained with 154Sm-anti-CD45 (HI30) and 170Er-an... -
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-human CD3
Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were fixed with 2% ... 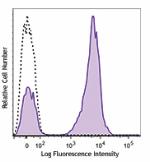
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 (cl... 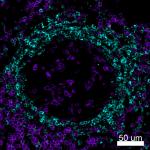
Confocal image of human lymph node sample acquired using the... 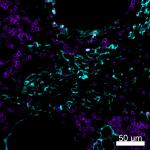
Confocal image of human lymph node sample acquired using the... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-human CD3
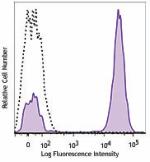
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 (cl... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-human CD3
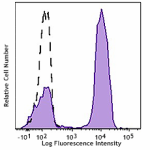
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 (cl... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-human CD3
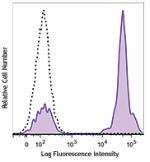
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with CD3 (clone U... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-human CD3
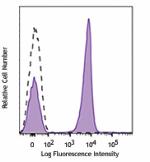
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 (cl... -
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-human CD3
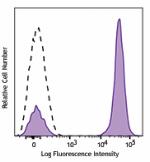
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 (cl... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-human CD3
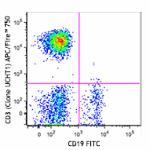
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 FI... 
-
Pacific Blue™ anti-human CD3
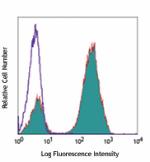
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-human CD3

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 PE... 
-
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-human CD3
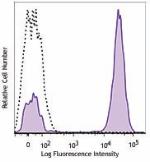
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
TotalSeq™-A0034 anti-human CD3
-
TotalSeq™-B0034 anti-human CD3
-
TotalSeq™-C0034 anti-human CD3
-
PE anti-human CD3

Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
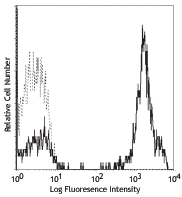
PE/Cyanine7 anti-human CD3

Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
KIRAVIA Blue 520™ anti-human CD3
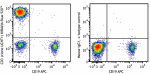
Human Peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 AP... -
Spark Violet™ 538 anti-human CD3 Antibody
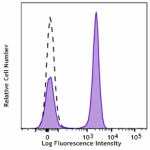
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD3 (cl... -
TotalSeq™-D0034 anti-human CD3
-
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-human CD3 Antibody
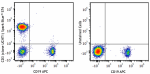
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
GMP Pacific Blue™ anti-human CD3
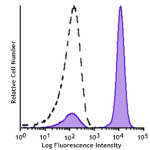
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
GMP PE anti-human CD3
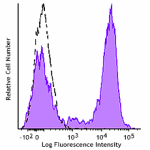
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
GMP PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-human CD3
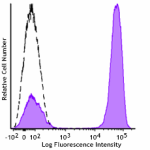
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
Spark Violet™ 423 anti-human CD3
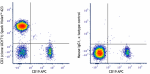
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... -
GMP PE/Cyanine7 anti-human CD3
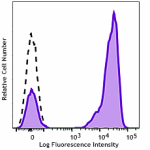
Typical results from human peripheral blood lymphocytes stai... -
Spark Blue™ 515 anti-human CD3
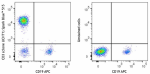
Human peripheral blood cells were surface stained with anti-...

 Login / Register
Login / Register 













Follow Us