- Clone
- QE5 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- HNUP153, N153, Nuclear Pore Complex Protein NUP153, Nucleoporin Nup153, 153 kD nucleoporin, nuclear pore complex protein hnup153
- Previously
-
Covance Catalog# MMS-102P
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
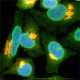
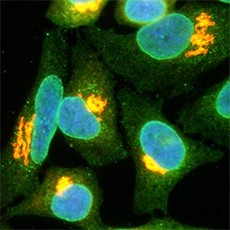
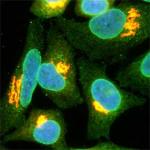
Methanol fixed HeLa stained with the antibody QE5. This antibody brilliantly highlights the nuclear membrane (green). The golgi is stained with the antibody to Giantin. -
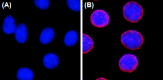
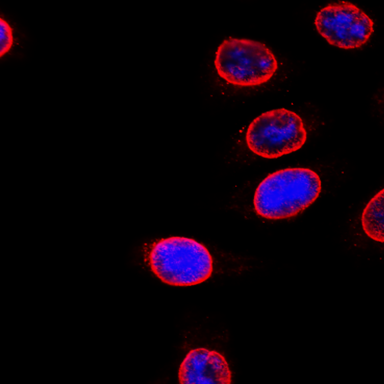
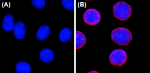
Immunofluorescence of HeLa cells with (A) mouse IgG1, κ isotype control (Negative, Cat. No. 401402) or (B) NUP153 Mouse primary antibody (Clone QE5). 2 μg/ml (1:250 dilution) Alexa Fluor® 594 (Red) Goat anti-Mouse IgG (Cat. No. 405326) was used as secondary antibody. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (Blue, Cat. No. 422801). The image was captured with a 60X objective objective using KEYENCE BZ-X700 fluorescence microscope. Exposure time is 300 ms. Concentrations 4 µg/ml. -
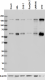
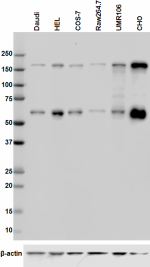
Total lysates (15 µg protein) from Daudi, HEL (Human), COS-7 (Monkey), Raw264.7 (Mouse), UMR106 (Rat) and CHO (Hamster) were resolved by electrophoresis (4-20% Tris-glycine gel), transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with 1:1000 (1 µg/ml) purified NUP153 antibody, clone QE5. Proteins were visualized using chemiluminescence detection by incubation with HRP Goat anti-Mouse secondary antibody (Cat. No. 405306, 1:3000 dilution). Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-&betal-actin was used as a loading control (Cat. No. 643807, 1:8000 dilution).
Nucleoporin 153 (Nup153) is a component of the nuclear pore complex, and is required for the anchoring of the nuclear pore complex to the nuclear pore membrane. Nup153 has a critical role in the nuclear export of proteins and RNA, and is involved in the retention of unspliced mRNAs in the nucleus.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat, Non-Human Primate, Hamster
- Reported Reactivity
- Other species
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- The QE5 monoclonal antibody was generated against rat liver nuclear envelope proteins.
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution + 0.03% thimerosal.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C. Please note the storage condition for this antibody has been changed from -20°C to between 2°C and 8°C. You can also check your vial or your CoA to find the most accurate storage condition for this antibody.
- Application
-
ICC - Quality tested
WB, IP - Verified
IEM - Reported in the literature, not verified in house - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunocytochemistry. For immunocytochemistry, a concentration of 4.0 μg/ml (1:250 dilution) is recommended. For Western blotting, the suggested use of this reagent is 1.0 - 2.0 µg per ml (1:500-1:1000 dilution). For immunoprecipitation, the suggested use of this reagent is 1:50 dilution. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
This antibody is effective in immunoblotting, immunocytochemistry (ICC) and immunoprecipitation (IP).
*Predicted MW = 250 kD
This antibody recognizes NUP153 as well as two related nuclear pore complex proteins: NUP214 and p62. By immunofluorescence, QE5 labels the nuclear envelope of eukaryotic cells giving a punctate staining pattern.
Predicted MW is ~ 250 kD, observed MW is ~154 kD. Lower bands (~ 60 kD) maybe the tripartite structure of NUP153, which consists of a zinc finger domain flanked by large (60-70 kD) NH2- and COOH-terminal domains9.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Pare GC, et al. 2005. Exp Cell Res. 303:388.
- N Pante, et al. 1994. J Cell Biol 126:603.
- Smythe C, et al. 2000. EMBO J. 19:3918. (WB)
- Goujon C, et al. 2008. J Virol. 82:12335. (IF) PubMed
- Holzenspies JJ, et al. 2009. BMC Dev Biol.9:8. (IF) PubMed
- Green JE, et al. 2014. Dev Biol. 392:419. (IF) PubMed
- Chen CY, et al. 2012. Cell. 149:565. (IF, WB)
- Iborra FJ, et al.2000. J Cell Sci. 113:291. (IEM)
- Bastos R, et al. 1997. J Cell Biol. 137:989. (IF, IP)
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_2565060 (BioLegend Cat. No. 906201)
Antigen Details
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Cell Motility/Cytoskeleton/Structure, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers
- Molecular Family
- Nuclear Markers
- Gene ID
- 9972 View all products for this Gene ID
- Specificity (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- NUP153
- Specificity Alt (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- NUP153
- App Abbreviation (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- ICC,WB,IP,IEM
- UniProt
- View information about NUP153 on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All NUP153 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-NUP153 | QE5 | ICC,WB,IP,IEM |
Customers Also Purchased
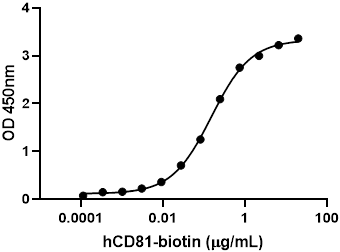
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.








Follow Us