- Clone
- FN50 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Workshop
- IV A91
- Other Names
- Very Early Activation Antigen (VEA), Activation inducer molecule (AIM)
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
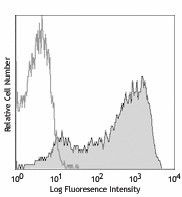
-

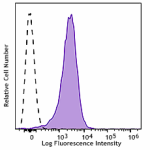
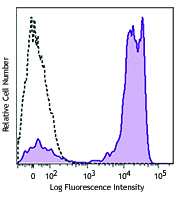
PMA+ionomycin-stimulated (5hours) human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with FN50 APC
| Cat # | Size | Price | Save |
|---|---|---|---|
| 310909 | 25 tests | ¥15,840 | |
| 310910 | 100 tests | ¥28,950 |
CD69 is a 27-33 kD type II transmembrane protein also known as activation inducer molecule (AIM), very early activation antigen (VEA), and MLR3. It is a member of the C-type lectin family, expressed as a disulfide-linked homodimer. Other members of this receptor family include NKG2, NKR-P1 CD94, and Ly49. CD69 is transiently expressed on activated leukocytes including T cells, thymocytes, B cells, NK cells, neutrophils, and eosinophils. CD69 is constitutively expressed by a subset of medullary mature thymocytes, platelets, mantle B cells, and certain CD4+ T cells in germinal centers of normal lymph nodes. CD69 is involved in early events of lymphocyte, monocyte, and platelet activation, and has a functional role in redirected lysis mediated by activated NK cells.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Reported Reactivity
- African Green, Baboon, Chimpanzee, Cynomolgus, Pigtailed Macaque, Rhesus
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA)
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with APC under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood.
- Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunohistochemical staining of acetone-fixed frozen tissue sections2, immunofluorescence microscopy3, and spatial biology (IBEX)8,9.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Knapp WB, et al. 1989. Leucocyte Typing IV. Oxford University Press. New York.
- Sakkas LI, et al. 1998. Clin. and Diag. Lab. Immunol. 5:430. (IHC)
- Kim JR, et al. 2005. BMC Immunol. 6:3. (IF)
- Verjans GM, et al. 2007. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104:3496.
- Lu H, et al. 2009. Toxicol Sci. 112:363. (FC) PubMed
- Thakral D, et al. 2008. J. Immunol. 180:7431. (FC) PubMed
- Yoshino N, et al. 2000. Exp. Anim. (Tokyo) 49:97. (FC)
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2020. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:33455-33465. (SB) PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2022. Nat Protoc. 17:378-401. (SB) PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_314844 (BioLegend Cat. No. 310909)
AB_314845 (BioLegend Cat. No. 310910)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- C-type lectin, type II glycoprotein, 28/32 kD
- Distribution
-
Activated T cells, B cells, NK cells, granulocytes, thymocytes, platelets, Langerhans cells
- Function
- Lymphocyte, monocyte, and platelet activation, NK cell killing
- Cell Type
- B cells, Granulocytes, Langerhans cells, NK cells, Platelets, T cells, Thymocytes, Tregs
- Biology Area
- Costimulatory Molecules, Immunology
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Schlossman S, et al. Eds. 1995. Leucocyte Typing V. Oxford University Press. New York.
2. Testi R, et al. 1994. Immunol. Today 15:479. - Gene ID
- 969 View all products for this Gene ID
- Specificity (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- CD69
- Specificity Alt (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- CD69
- App Abbreviation (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- FC
- Hidden Names (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- Basophil, B Cell, NK Cell, Platelets
- UniProt
- View information about CD69 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All CD69 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased

Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-human CD69
PHA-activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained wit... -
FITC anti-human CD69
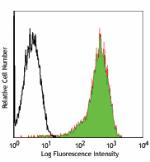
PMA + ionomycin stimulated (6 hours) human lymphocytes stain... -
PE anti-human CD69
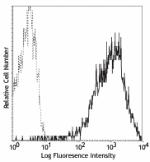
PMA + ionomycin stimulated (6 hours) human lymphocytes stain... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-human CD69
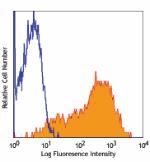
PHA-activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained wit... -
APC anti-human CD69
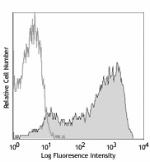
PMA+ionomycin-stimulated (5hours) human peripheral blood lym... -
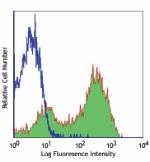
APC/Cyanine7 anti-human CD69
PMA + Ionomycin stimulated (6 hours) human peripheral blood ... -
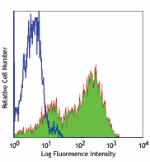
PE/Cyanine7 anti-human CD69
PMA+ionomycin activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes s... -
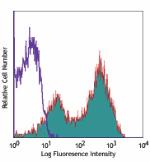
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-human CD69
PMA+ionomycin activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes s... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-human CD69
PMA+ionomycin activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes s... 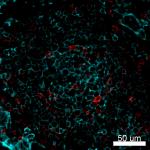
Confocal image of human lymph node sample acquired using the... 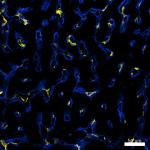
Confocal image of human liver sample acquired using the IBEX... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-human CD69
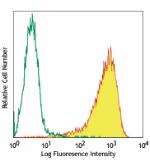
PMA+ionomycin-stimulated human peripheral blood mononuclear ... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-human CD69
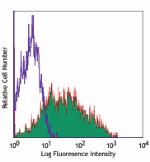
PMA + Ionomycin-stimulated (5 hours) human peripheral blood ... -
Biotin anti-human CD69
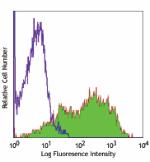
PHA-stimulated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (day... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-human CD69
PMA+ ionomycin stimulated (6 hours) human peripheral blood l... -
PerCP anti-human CD69
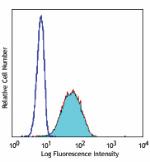
PMA + Inonomycin-stimulated (5 hours) human peripheral blood... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-human CD69
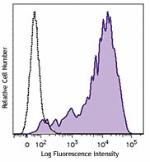
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stimulated with PMA ... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-human CD69
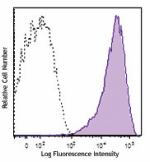
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stimulated with PMA ... -
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-human CD69
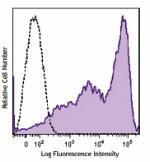
PMA + ionomycin-stimulated (6 hours) human peripheral blood ... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-human CD69
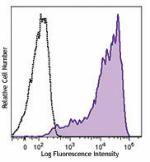
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stimulated with PMA+... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-human CD69
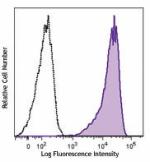
PMA+ ionomycin-stimulated (6 hours) human periphe... -
Purified anti-human CD69 (Maxpar® Ready)
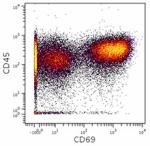
Human PBMCs were incubated for 6 hours in media alone (botto... 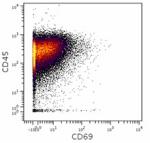
-
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-human CD69
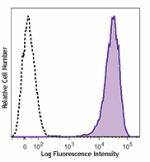
PMA + ionomycin-stimulated (6 hours) human peripheral blood ... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-human CD69
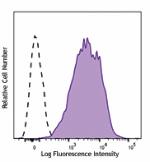
PMA + ionomycin-stimulated (six hours) human peripheral bloo... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-human CD69
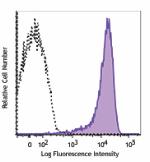
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stimulated with PMA ... -
TotalSeq™-A0146 anti-human CD69
-
TotalSeq™-B0146 anti-human CD69
-
TotalSeq™-C0146 anti-human CD69
-
Brilliant Violet 750™ anti-human CD69
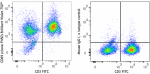
PMA+ ionomycin stimulated (6 hours) human peripheral blood l... -
KIRAVIA Blue 520™ anti-human CD69
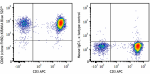
PMA + ionomycin stimulated human peripheral blood lymphocyte... -
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-human CD69 Antibody
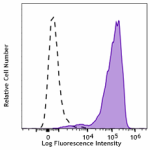
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stimulated with PMA+... -
PE/Fire™ 640 anti-human CD69
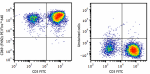
PMA+ionomycin activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes w... -
Spark YG™ 581 anti-human CD69
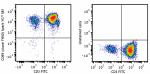
PMA+ionomycin activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes w... -
TotalSeq™-D0146 anti-human CD69
-
APC anti-human CD69
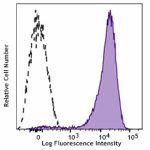
Typical results from Cell Activation Cocktail (without Brefe... -
Spark Blue™ 550 anti-human CD69
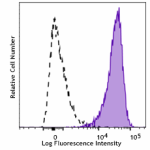
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stimulated with PMA... -
PE anti-human CD69
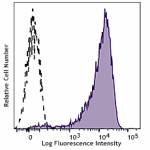
Typical results from Cell Activation Cocktail (without Brefe... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-human CD69
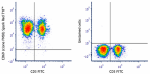
PMA+ ionomycin stimulated (6 hours) human peripheral blood l... -
GMP PE anti-human CD69
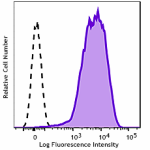
Typical results from Cell Activation Cocktail (without Brefe... -
PE/Fire™ 810 anti-human CD69
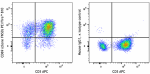
PMA+ ionomycin stimulated (6 hours) human peripheral blood l... -
PE/Fire™ 744 anti-human CD69

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with anti-hu... 
PMA+ionomycin activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes w... -
Spark PLUS UV395™ anti-human CD69

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stimulated with PMA/... -
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-human CD69 (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
GMP APC anti-human CD69

Typical results from Cell Activation Cocktail (without Brefe...













Follow Us