- Clone
- PK136 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- NKR-P1C, NKR-P1B, Ly-55, CD161, CD161b, CD161c
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
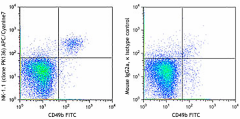
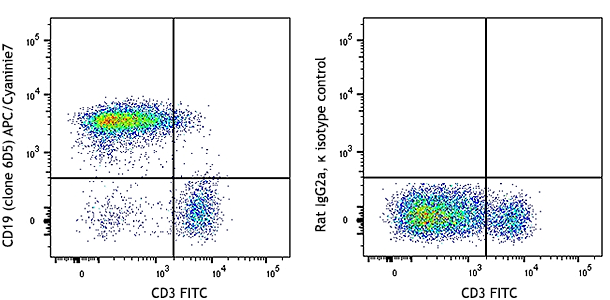
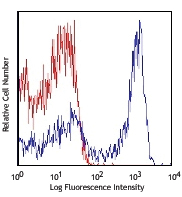
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b (clone DX5) FITC and NK1.1 (clone PK136) APC/Cyanine7 (left) or mouse IgG2a, κ APC/Cyanine7 isotype control (right).
| Cat # | Size | Price | Save |
|---|---|---|---|
| 108723 | 25 µg | ¥16,740 | |
| 108724 | 100 µg | ¥51,980 |
NK-1.1 surface antigen, also known as CD161b/CD161c and Ly-55, is encoded by the NKR-P1B/NKR-P1C gene. It is expressed on NK cells and NK-T cells in some mouse strains, including C57BL/6, FVB/N, and NZB, but not AKR, BALB/c, CBA/J, C3H, DBA/1, DBA/2, NOD, SJL, and 129. Expression of NKR-P1C antigen has been correlated with lysis of tumor cells in vitro and rejection of bone marrow allografts in vivo. NK-1.1 has also been shown to play a role in NK cell activation, IFN-γ production, and cytotoxic granule release. NK-1.1 and DX5 are commonly used as mouse NK cell markers.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- NK-1+ cells from mouse spleen and bone marrow
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with APC/Cyanine7 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤1.0 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunoprecipitation1,2, complement-dependent cytotoxicity3, in vivo depletion4,5,9,10, mediation of in vitro redirected lysis6, blocking of NK cell function7, induction of proliferation8, immunohistochemical staining of frozen sections11, immunofluorescence microscopy11, and spatial biology (IBEX)16,17. The LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin <0.1 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for functional assays (Cat. No. 108712).
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Carlyle JR, et al. 1999. J. Immunol. 162:5917. (IP)
- Sentman CL, et al. 1989. Hybridoma 8:605. (IP)
- Koo GC, et al. 1984. Hybridoma 3:301. (Cyt)
- Sentman CL, et al. 1989. J. Immunol. 142:1847. (Deplete)
- Koo GC, et al. 1986. J. Immunol. 137:3742. (Deplete)
- Karlhofer FM, et al. 1991. J. Immunol. 146:3662.
- Kung SK, et al. 1999. J. Immunol. 162:5876. (Block)
- Reichlin A, et al. 1998. Immunol. Cell Biol. 76:143.
- Drobyski W, et al. 1996. Blood 87:5355. (Deplete)
- Andoniou CE, et al. 2005. Nat. Immunol. 6:1011. (Deplete)
- Kanwar JR, et al. 2001. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 93:1541. (IHC, IF)
- Kroemer A, et al. 2008. J. Immunol. 180:7818. PubMed
- Kim JY, et al. 2009. Exp Mol Med. 30:288. PubMed
- Bankoti J, et al. 2010. Toxicol. Sci. 115:422. (FC) PubMed
- Lee H, et al. 2014. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 55:2885. PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2020. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117:33455-65. (SB) PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2022. Nat Protoc. 17:378-401. (SB) PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_830870 (BioLegend Cat. No. 108723)
AB_830871 (BioLegend Cat. No. 108724)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- NKR-P1 gene family
- Distribution
-
NK and NK-T cells in the NK1.1 mouse strains (C57BL, FVB/N, NZB)
- Function
- NK cell activation, IFN-γ production, cytotoxic granule release
- Cell Type
- NK cells, NKT cells
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Antigen References
-
1. Lanier LL. 1997. Immunity 6:371.
2. Yokoyama WM, et al. 1993. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 11:613.
3. Koo GC, et al. 1986. J. Immunol. 137:3742.
4. Giorda R, et al. 1991. J. Immunol. 147:1701. - Gene ID
- 17059 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about NK-1.1 on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All NK-1.1 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
APC anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b (DX5) FITC... 
-
Biotin anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b (DX5) APC ... 
-
FITC anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with NK1.1 (clone PK1... -
PE anti-mouse NK-1.1
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b (DX5) APC ... -
Purified anti-mouse NK-1.1
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b (DX5) APC ... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b (pan-NK ce... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b (pan-NK ce... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b (DX5) APC ... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse NK-1.1
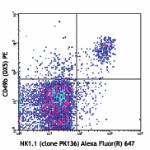
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b (DX5) PE a... 
-
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse NK-1.1
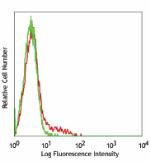
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with PK136 Pacific Blue™ -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b/DX5 FITC a... 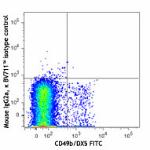
-
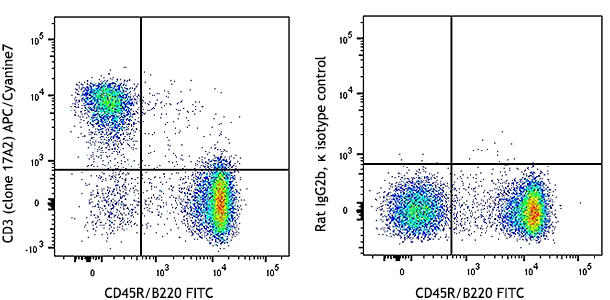
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse NK-1.1
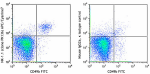
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b (clone DX5... -
PerCP anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b (DX5) FITC... 
-
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse NK-1.1
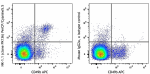
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b (pan-NK ce... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse NK-1.1
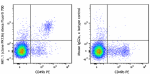
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD49b (clone DX5) PE a... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b/DX5 PE and... 
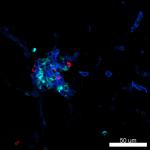
Confocal image of C57BL/6 mouse liver sample acquired using ... 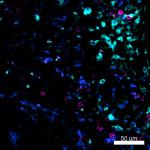
Mice were injected subcutaneously with sheep red blood cells... -
Brilliant Violet 570™ anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b/DX5 FITC a... 
-
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse NK-1.1
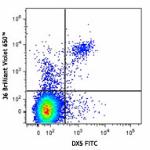
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with NK1.1 (clone PK1... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b/DX5 APC an... 
-
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b/DX5 APC an... 
-
Purified anti-mouse NK-1.1 (Maxpar® Ready)
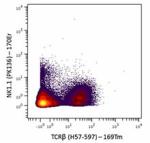
Mouse splenocytes stained with 169Tm-anti-TCRβ (H57-597) and... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b FITC and N... 
-
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b/DX5 FITC a... 
-
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b FITC and N... 
-
TotalSeq™-A0118 anti-mouse NK-1.1
-
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD49b (DX5) APC ... -
TotalSeq™-B0118 anti-mouse NK-1.1
-
TotalSeq™-C0118 anti-mouse NK-1.1
-
PE/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse NK-1.1
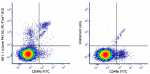
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD49b... -
PE/Fire™ 640 anti-mouse NK-1.1
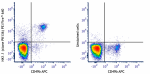
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD49b... -
Spark UV™ 387 anti-mouse NK-1.1
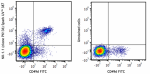
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD49d... -
PE/Fire™ 700 anti-mouse NK-1.1

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD49b...












Follow Us