- Clone
- 5F2 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Entpd1, NTPDase1
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
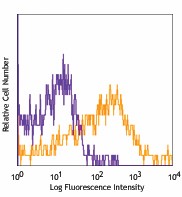
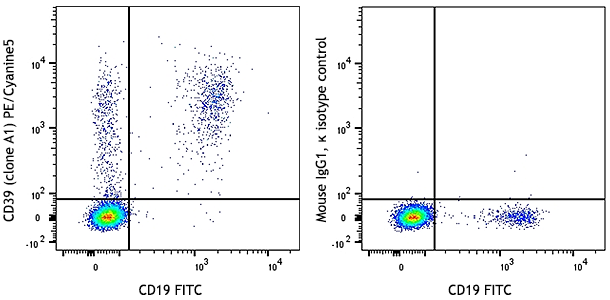
CD4+CD25+ (top) and CD4+CD25- cells (bottom) from C57BL/6 lymph node stained with biotinylated 5F2, followed by Sav-PE -
CD39, nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1 (NTPDase 1), is an ectoenzyme that degrades ATP to AMP. It is a member of ectonucleoside triphosphate dihydrolases (E-NTPDases) which are involved in regulation of extracellular nucleotide catabolism and controlling the extracellular nucleoside triphosphate pool (NTP). CD39 is the dominant member of this family in the immune system and involved in suppression of inflammation and control of platelet activation. CD39 is expressed on B cells, dendritic cells, and a subset of T cells including regulatory T cells and memory T cells. The coordinated expression of CD39/CD73 on Tregs and the adenosine A2A receptor on activated T effector cells generates immunosuppressive loops. In human studies, it has been reported that CD4+CD25-CD39+ T cells are T inducers.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Purified recombinant mCD39-Ig, mCD39-expressing pcDNA3.1 plasmid, and B cells (CD39+)
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with biotin under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
WB, ELISA - Reported in the literature, not verified in house - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤0.25 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Zhou Q, et al. 2009. Am J. Transplant. 9(10):2303
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_2099921 (BioLegend Cat. No. 135703)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- A member of ectonucleoside triphosphate dihydrolases (E-NTPDases), an ectoenzyme that degrades ATP to AMP.
- Distribution
-
CD39 is expressed on B cells, dendritic cells, and a subset of T cells
- Function
- CD39 is involved in suppression of inflammation and control of platelet activation. Coordinated expression of CD39/CD73 on Tregs and the adenosine A2A receptor on activated T effector cells generates immunosuppressive loops.
- Cell Type
- B cells, Dendritic cells, T cells, Tregs
- Biology Area
- Immunology
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Borsellino G et al. 2007. Blood 110(4):1225
2. Deaglio S et al. 2007. J. Exp. Med. 204(6):1257
3. Bynoe MS. et al. 2008. Trends Immunol. 29(3):99
4. Ndhlovu LC. et al. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009 Oct 28. [Epub ahead of print] - Gene ID
- 12495 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD39 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- How many biotin molecules are per antibody structure?
- We don't routinely measure the number of biotins with our antibody products but the number of biotin molecules range from 3-6 molecules per antibody.
Other Formats
View All CD39 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Biotin anti-mouse CD39 | 5F2 | FC,WB,ELISA |
| Purified anti-mouse CD39 | 5F2 | FC,WB,ELISA |
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Biotin anti-mouse CD39
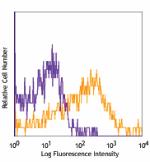
CD4+CD25+ (top) and CD4+CD25- cells (bottom) from C57BL/6 ly... 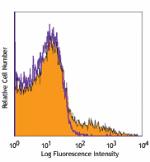
-
Purified anti-mouse CD39
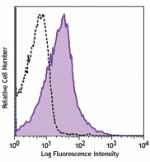
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained purified CD39 (clone ...








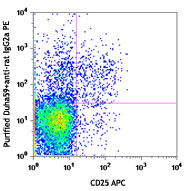
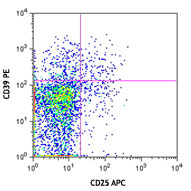



Follow Us