- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- SAv-PE/Cyanine7
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-

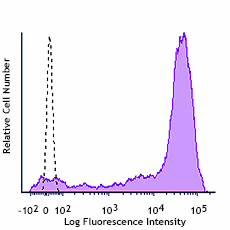
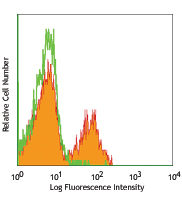
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with PE/Cyanine7 streptavidin alone (open histogram) or Biotin anti-human CD3 (clone UCHT1) followed by (PE/Cyanine7) Streptavidin (filled histogram).
Streptavidin binds to biotin with high affinity. Streptavidin - Phycoerythrin/Cyanine7 (PE/Cyanine7) is useful for detecting biotinylated antibodies. The excitation of PE/Cyanine7 by 488 nm laser light induces a light emission maximum of 775 nm.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat, All Species
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- Streptavidin is conjugated with PE/Cyanine7 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml (concentration relates to the Streptavidin only component of the conjugate)
- Storage & Handling
- The Streptavidin-PE/Cyanine7 solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
ICFC - Verified
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this Streptavidin-PE/Cyanine7 is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. The concentration provided is based upon molecular molar mass of streptavidin independent of any additional molecular mass that might be added by the PE/Cyanine7 conjugation. For immunofluorescent staining, the recommended use of this reagent is =0.125 µg per 106 cells in 100 µl staining volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Streptavidin - Phycoerythrin/Cyanine7 (PE/Cyanine7) is useful as a second step reagent for indirect immunofluorescent staining, when used in conjunction with biotinylated primary antibodies. The average molecular weight of Streptavidin-PE/Cyanine7 is 360 kD and Streptavidin alone is 52 kD.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Kamimura D, et al. 2006. J. Immunol. 177:306.
- Chappaz S, et al. 2007. Blood doi:10.1182/blood-2007-02-074245.
- Anderson SM, et al. 2007. J. Exp. Med. doi:10.1084/jem.20062571. PubMed
- Rigolio R, et al. 2008. J Neuroimmunol. 199:67. PubMed
- Chappaz S, et al. 2010. J. Immunol. 184:3562. PubMed
- Weber SE, et al. 2011. J. Immunol. 186:432. PubMed
- Chamoto, K., et al. 2011. Am J Respir Cel Mol Biol. PubMed
- Ahuja, A., et al. 2011. J. Immunol. 187:3888. PubMed
- Chamoto K, et al. 2012. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 46:283. PubMed
- Sugiura D, et al. 2012. PLoS One. 7:e44770. PubMed
- Nakamura M, et al. 2014. Mult Scler. PubMed
- Lyngaa R, et al. 2014. Clin Cancer Res. 20:1768. PubMed
- Shaw OM, et al. 2014. Rheumatology. PubMed
- Markey KA, et al. 2014. J Immunol. 192:5426. PubMed
- Yasunaga M, et al. 2014. Sci Rep. 4:4852. PubMed
- Nakamura M, et al. 2014. Mult Scler. 20:1371. PubMed
- Shaw OM, et al. 2014. Rheumatology. 53:1901. PubMed
- Tang AH, et al. 2014. EMBO J. 33:2782. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Gene ID
- NA
- UniProt
- View information about Biotin on UniProt.org













Follow Us