- Clone
- 3F8-E6-B9 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- RNA-binding protein Musashi homolog 1, Musashi-1, MSI1, Musashi RNA Binding Protein 1
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG2b, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
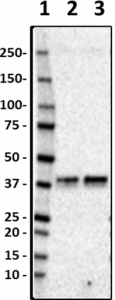
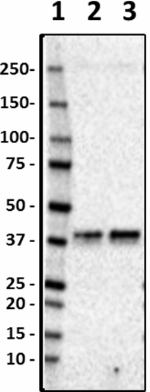
Western blot of purified anti-Musashi-1 antibody (clone 3F8-E6-B9). Lane 1: Molecular weight marker; Lane 2: 20 μg of normal human brain lysate; Lane 3: 20 μg of Alzheimer's disease brain lysate. The blot was incubated with 0.5 μg/mL of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C, followed by incubation with HRP-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG (Cat. No. 405306). Enhanced chemiluminescence was used as the detection system. -
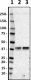
Western blot of purified anti-Musashi-1 antibody (clone 3F8-E6-B9). Lane 1: Molecular weight marker; Lane 2: 20 μg of rat brain lysate; Lane 3: 20 μg of mouse brain lysate. The blot was incubated with 0.5 μg/mL of anti-Musashi-1 (left panel) or anti-mouse IgG2b (right panel, isotype control) antibodies, followed by incubation with HRP-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG (Cat. No. 405306). Enhanced chemiluminescence was used as the detection system. -
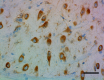
IHC staining of purified anti-Musashi-1 antibody (clone 3F8-E6- B9) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded mouse brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Sodium Citrate H.I.E.R., the tissue was incubated with 0.5 µg/mL of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C. BioLegend's Ultra Streptavidin (USA) HRP Detection Kit (Multi-Species, DAB, Cat. No. 929901) was used for detection followed by hematoxylin counterstaining, according to the protocol provided. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm -
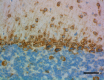
IHC staining of purified anti-Musashi-1 antibody (clone 3F8-E6- B9) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded mouse brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Sodium Citrate H.I.E.R., the tissue was incubated with 0.5 µg/mL of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C. BioLegend's Ultra Streptavidin (USA) HRP Detection Kit (Multi-Species, DAB, Cat. No. 929901) was used for detection followed by hematoxylin counterstaining, according to the protocol provided. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm -
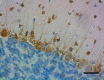
IHC staining of purified anti-Musashi-1 antibody (clone 3F8-E6- B9) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded rat brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Sodium Citrate H.I.E.R., the tissue was incubated with 0.5 µg/mL of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C. BioLegend's Ultra Streptavidin (USA) HRP Detection Kit (Multi-Species, DAB, Cat. No. 929901) was used for detection followed by hematoxylin counterstaining, according to the protocol provided. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm -
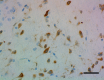
IHC staining of purified anti-Musashi-1 antibody (clone 3F8-E6- B9) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded rat brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Sodium Citrate H.I.E.R., the tissue was incubated with 0.5 µg/mL of the primary antibody overnight at 4°C. BioLegend's Ultra Streptavidin (USA) HRP Detection Kit (Multi-Species, DAB, Cat. No. 929901) was used for detection followed by hematoxylin counterstaining, according to the protocol provided. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm
| Cat # | Size | Price | Save |
|---|---|---|---|
| 869101 | 25 µg | ¥23,320 | |
| 869102 | 100 µg | ¥60,720 |
Musashi-1 (MSI1) is an evolutionarily conserved RNA-binding protein with essential role in stem cell maintenance, nervous system development, and tumorigenesis. It was first identified in Drosophila as a protein required for the development of adult external sensory organs (sensilla) and neuronal potential in asymmetric cell division. In mammalian nervous systems, MSI1 is one of the key oncogenic factors for glioblastomas and medulloblastomas. The expression of MSI1 is associated with Notch signaling. The high expression of MSI1 is a marker of poor prognosis in medulloblastoma. Genomic analysis indicates that MSI1 functions as a master regulator of genes during development and tumor formation.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Human Musashi-1 recombinant protein
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
WB - Quality tested
IHC-P - Verified - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by Western blotting. For Western blotting, the suggested use of this reagent is 0.5 - 10 µg per ml. For immunohistochemistry, a concentration range of 0.5 - 10 µg/ml is suggested. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_2814629 (BioLegend Cat. No. 869101)
AB_2814629 (BioLegend Cat. No. 869102)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Human MSI1 is a 362 amino acid protein with a predicted and observed molecular mass of 39 kD.
- Distribution
-
Tissue distribution: Central nervous system, fetal kidney, liver, lung, and pancreas
Cellular distribution: Nucleus and cytoplasm
- Function
- MSI1 is an RNA binding protein that regulates the expression of target mRNAs at the translation level.
- Cell Type
- Neural Stem Cells, Neurons, Oligodendrocytes
- Biology Area
- Cancer Biomarkers, Neurodegeneration, Neuroscience
- Molecular Family
- Enzymes and Regulators
- Antigen References
-
- Okabe M, et al. 2001. Nature. 411:94-8.
- de Sousa Abreu R. et al. 2009. J Biol Chem. 284(18):12125-35.
- Vo DT. et al. 2012. Am J Pathol. 181(5):1762-72.
- Sengupta U. et al. 2018. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 6(1):113.
- Gene ID
- 4440 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Musashi-1 on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Other Formats
View All Musashi-1 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-Musashi-1 | 3F8-E6-B9 | WB,IHC-P |
| Biotin anti-Musashi-1 | 3F8-E6-B9 | IHC-P |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-Musashi-1
Western blot of purified anti-Musashi-1 antibody (clone 3F8-... 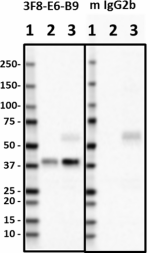
Western blot of purified anti-Musashi-1 antibody (clone 3F8-... 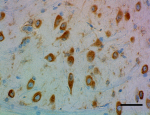
IHC staining of purified anti-Musashi-1 antibody (clone 3F8-... 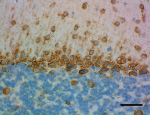
IHC staining of purified anti-Musashi-1 antibody (clone 3F8-... 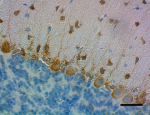
IHC staining of purified anti-Musashi-1 antibody (clone 3F8-... 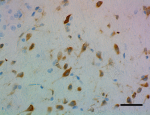
IHC staining of purified anti-Musashi-1 antibody (clone 3F8-... -
Biotin anti-Musashi-1
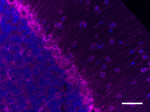
IHC staining of biotin anti-Musashi-1 antibody (clone 3F8-E6... 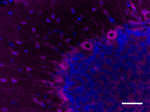
IHC staining of biotin anti-Musashi-1 antibody (clone 3F8-E6...







Follow Us