- Clone
- H14 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB1, RNA polymerase II subunit B1, DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit A, RNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB1, DNA-directed RNA polymerase III largest subunit
- Isotype
- Mouse IgM, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
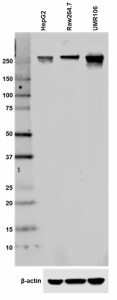
-

Total lysates (15 µg protein) from HepG2 (human), Raw264.7 (mouse) and UMR106 (rat) were resolved by electrophoresis (4-20% Tris-glycine gel), transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with 1 µg/ml purified anti-RNA Polymerase II antibody (clone H14). Proteins were visualized using chemiluminescence detection by incubation with HRP goat anti-mouse IgG secondary antibody (Cat. No. 405306, 1:3000 dilution). Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-β-actin was used as a loading control (Cat. No. 643807, 1:8000 dilution). -
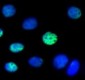
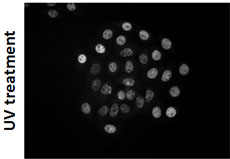
HeLa cells were fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde (PFA) then permeabilized using 0.5% Triton X-100 for five minutes at room temperature. The cells were then blocked using 5% FBS in PBS for one hour at room temperature followed by incubation with anti-RNA Polymerase II RPB1 (clone H14) antibody at 4 µg/ml for 24 hours at 4°C. Following primary antibody incubation, the cells were incubated with Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugated goat anti-mouse IgM secondary antibody and counterstained with DAPI.
RPB1 is the catalytic and largest component of RNA polymerase II, which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. It forms the polymerase active center together with RPB2, the second largest subunit. Polymerase II (Pol II) is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. It is composed of mobile elements that move relatively to each other. RPB1 is part of the core element with the central large cleft, the clamp element that moves to open and close the cleft, and the jaws that are thought to grab the incoming DNA template. At the start of transcription, a single DNA template strand of the promoter is positioned within the central active site cleft of Pol II. Then, a bridging helix emanates from RPB1 and crosses the cleft near the catalytic site, which acts as a ratchet that moves the RNA-DNA hybrid through the active site by switching from straight to bent conformations during each nucleotide addition. This promotes translocation of Pol II. Pol II moves on the template during transcription elongation. Elongation is influenced by the phosphorylation status of the C-terminal domain (CTD) of Pol II's largest subunit (RPB1), which serves as a platform for assembling factors that regulate transcription initiation, elongation, termination, and mRNA processing. It can act as a RNA-dependent RNA polymerase when associated with small delta antigen of Hepatitis delta virus, being able to conform as both a replicate and transcriptase for the viral RNA circular genome.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
WB - Quality tested
ICC - Verified
IP - Reported in the literature, not verified in house - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by Western blotting. For Western blotting, the suggested use of this reagent is 1.0 - 10.0 µg/ml. In Western blotting it is recommended to use casein or BSA in the blocking solution rather than non-fat-dry milk. For immunocytochemistry, a concentration range of 1.0 - 5.0 μg/ml is recommended. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunoprecipitation2,3.
The clone H14 was developed against a purified phosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II extracted from a transformed cell line. Pol II has two physiologically important phosphorylation sites: ser-2 and ser-5. Both sites are found in the heptapeptide repeat YSPTSPS at the C-terminal domain. Clone H14 recognizes the phosphoserine 5 (ser-5) of Pol II. Clone H14 is useful for immunofluorescence and Western blotting.
This clone is not recommended for ChIP (Chromatin Immunoprecipitation) assays (as determined by in-house testing). -
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Brown JM, et al. 2008. J. Cell. Biol. 182:1083. (WB, IF)
- Bregman DB, et al. 1995. Cell Biol. 129:287-98. (IP)
- Ahn SH, et al. 2004. Mol. Cell. 13:67. (IP)
- Pellizzoni L, et al. 2001. Cell Biol. 152(1):75. (IF)
- Patturajan M, et al. 1998. J. Biol. Chem. 273(8):4689. (WB)
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_2616696 (BioLegend Cat. No. 920304)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- RPB1 contains a C-terminus composed of heptapeptide repeats that are essential for polymerase activity. These repeats contain Ser and Thr residues that are phosphorylated in actively transcribing RNA polymerase. The predicted molecular weight is 220 kD.
- Distribution
-
Nucleus and cytosol.
- Function
- RPB1 is the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II, the polymerase responsible for synthesizing messenger RNA in eukaryotes.
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Cell Cycle/DNA Replication, Transcription Factors
- Gene ID
- 5430 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about RNA Polymerase II RPB1 on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All RNA Polymerase II RPB1 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-RNA Polymerase II RPB1 | H14 | WB,ICC,IP |
| Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-RNA Polymerase II RPB1 | H14 | WB |
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-RNA Polymerase II RPB1
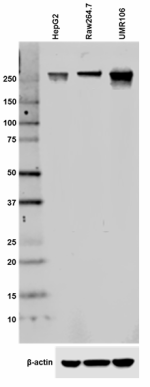
Total lysates (15 µg protein) from HepG2 (human), Raw264.7 (... 
HeLa cells were fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde (PFA) then pe... -
Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-RNA Polymerase II RPB1
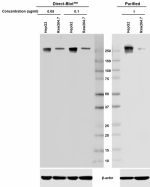
Western blot analysis of 15 µg cell lysates from HT29 and Ra...









Follow Us