 |
| For neuron survival, the creation of new mitochondria and removal of defective ones is vital. Retinal ganglion cells in particular need a consistent source of energy as they face many stressors, like light, limited oxygen, and intraocular pressure. As the axon enables long distance communication and houses a majority of the cell's volume, mitochondria must be properly distributed throughout it to provide enough energy for the demanding tasks of moving organelles and synaptic functions. Davis et al. indicated these cells can expel mitochondria directly from the axon in membrane-bound vesicles to be collected by astrocytes, rather than ship them down the long arm of the axon for disposal. 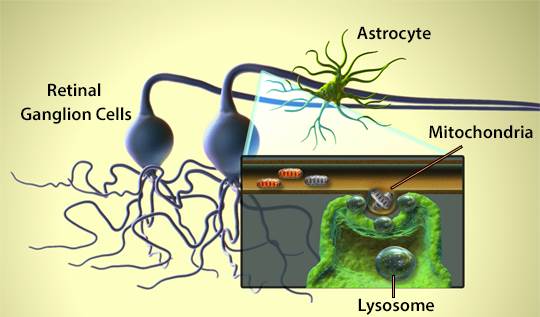 Adapted from Burdett, T.C. and Freeman, M.R. 2014. Science. 345:385. Pubmed BioLegend provides several reagents for the study of mitochondria, autophagy, and astrocytes: |
| Mitochondria Antibodies: | MitoSpy™ Mitochondrial Probes: |
|---|---|
| • Grp75 (Mortalin) • HSD17B10 • Mitofusin-1 • Mitofusin-2 • PINK1 • SIRT5 • UQCRC1 • VDAC1 |
• MitoSpy™ Green FM • MitoSpy™ Orange CMTMRos • MitoSpy™ Red CMXRos |
| Autophagy Antibodies: | Astrocyte Antibodies: |
|---|---|
| • LC3 • P62 (SQSTM1) • Parkin • Ubiquitin |
• S100B • CD80 • GFAP |
 |
 |
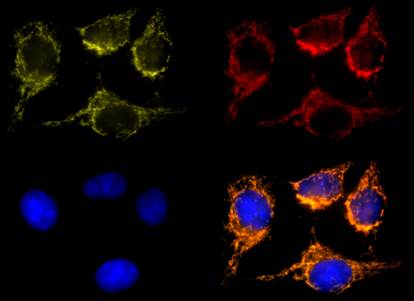
| To find more information and immunofluorescence and flow cytometry data for our MitoSpy™ mitochondrial probes, visit our webpage! |
 |
*Any references to promotions on this page may not be valid at this time. View our promotions page for the most up-to-date promotions.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 






Follow Us