- Clone
- Poly6190 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- p63, δN p63-α, -β, -γ
- Isotype
- Rabbit Polyclonal IgG
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
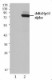
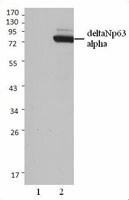
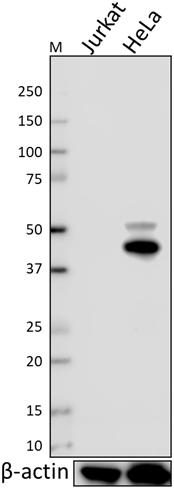
Non-transfected 293 cell lysates (Lane 1) and p63 (deltaN) transfected 293 cell lysates (Lane 2) were resolved by electrophoresis, transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with anti-p63 (deltaN) antibody (clone Poly6190). Proteins were visualized using a donkey anti-rabbit-IgG secondary conjugated to HRP and chemiluminescence detection.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 619001 | 50 µL | 118€ | ||||
| 619002 | 200 µL | 329€ | ||||
p63 (ΔN) is a member of the p53 family. This protein has multiple isoforms TA p63-α, -β, γ, ΔN p63-α, -β, and -γ. The molecular weights of the p63 isoforms α=66 kD, β=52 kD, and γ=45 kD. This nuclear protein is essential for limb formation, epidermal morphogenesis, and epithelial stem cell regeneration. ΔN isoforms are antagonistic to p53; TA isoforms can transactivate p53 targets. The p63 ΔN isoforms repress TA isoforms; mutant p53 abrogates p63 transactivation. This protein interacts with p53, p73, and the various TA- and ΔN isoforms. The Poly6190 antibody recognizes human p63 ΔN isoforms and has been shown to be useful for Western blotting.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Antibody Type
- Polyclonal
- Host Species
- Rabbit
- Immunogen
- Modified peptide
- Formulation
- This antibody is provided in phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and 50% glycerol.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by antigen-affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- Upon receipt, store frozen at -20°C.
- Application
-
WB - Quality tested
IHC - Reported in the literature, not verified in house - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by Western blotting. Western blotting, suggested working dilution(s): Use 10 µl per 5 ml antibody dilution buffer for each mini-gel. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
This product may contain other non-IgG subtypes. - Additional Product Notes
- The 50 µL size can be used for approximately 5 Western blots, and the 200 µL size can be used for approximately 20 Western blots.
- Application References
-
- Medawar A, et al. 2008. PLoS ONE 3:e3441. PubMed
- Di Girolamo N, et al. 2009. Transplantation. 87:1571. PubMed
- Bray LJ, et al. 2012. Biomaterials. 33:3529. PubMed
- Zhou Y, et al. 2011. Clin. Invest. Med. 34:E184. (IHC)
- Stewart RM, et al. 2015. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 56:2021. PubMed
- Curtis KM, et al. 2015. PLoS One. 10:123642. PubMed
- Ahronian LG, et al. 2015. PLoS One.10:123816. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
SCR_001134 (BioLegend Cat. No. 619001)
SCR_001134 (BioLegend Cat. No. 619002)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- p53 family, six isoforms, ΔN p63α, β, γ, approximately 66 kD, 52 kD, 45 kD
- Distribution
-
Nuclear
- Function
- Essential for limb formation, epidermal morphogenesis, epithelial stem cell regeneration. ΔN isoforms antagonistic to p53; TA isoforms can transactivate p53 targets
- Interaction
- p53, p73, TA- and ΔN isoforms
- Biology Area
- Apoptosis/Tumor Suppressors/Cell Death, Cell Biology, Cell Cycle/DNA Replication, Transcription Factors
- Antigen References
-
1. Yang A, et al. 1998. Mol Cell. 2:305.
2. Celli J, et al. 1999. Cell. 99:143.
3. Gaiddon C, et al. 2001. Mol Cell Biol. 21:1874.
4. Benard J, et al. 2003. Hum Mutat. 21:182. - Regulation
- ΔN isoforms repress TA isoforms, mutant p53 abrogates p63 transactivation
- Gene ID
- 8626 View all products for this Gene ID
- Specificity (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- p63
- Specificity Alt (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- p63
- App Abbreviation (DOES NOT SHOW ON TDS):
- WB,IHC
- UniProt
- View information about p63 on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Other Formats
View All p63 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-p63 (ΔN) | Poly6190 | WB,IHC |
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-p63 (ΔN)

Non-transfected 293 cell lysates (Lane 1) and p63 (deltaN) t...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us