- Clone
- GL7 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Ly77, T and B cell activation marker
- Isotype
- Rat IgM, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
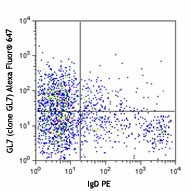
-

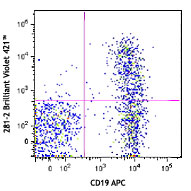
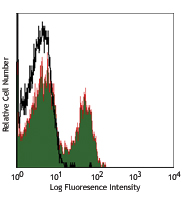
Balb/c mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse IgD PE and anti-mouse GL7 (clone GL7) Alexa Fluor® 647 (top) or rat IgM, κ Alexa Fluor® 647 isotype control (bottom). -

-
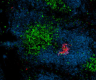
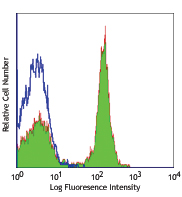
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10 minutes at room temperature and blocked with 5% FBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Then the section was stained with 10 µg/ml of GL7 (clone GL7) Alexa Fluor® 647 (red), CD3 (clone 17A2) Alexa Fluor® 594 (green) and B220 (clone RA3-6B2) Alexa Fluor® 488 (blue) overnight at 4°C. The image was captured by 10X objective. -
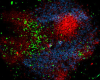
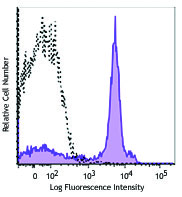
LPS-challenged C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10 minutes at room temperature and blocked with 5% FBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Then the section was stained with 10 μg/ml of GL7 (clone GL7) Alexa Fluor® 647 (red), CD3 (clone 17A2) Alexa Fluor® 594 (green) and B220 (clone RA3-6B2) Alexa Fluor® 488 (blue) overnight at 4°C. The image was captured by 10X objective.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 144605 | 25 µg | 76€ | ||||
| 144606 | 100 µg | 212€ | ||||
The GL7 antigen, also known as Ly77, is a 35 kD protein. The GL7 antigen has an epitope containing non-sulfated α2-6-sialyl-LacNAc recognized by the GL7 antibody. The GL7 antigen is expressed by pre-B and immature B cells, activated T and B cells, and about 20% of TCR-bright thymocytes. It is upregulated on mouse splenocytes following activation. It may play a role in regulation or adhesion. GL7 high-expressing B cells show higher antibody production and antigen presenting capacity.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse, Human
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- LPS activated DBA/J mouse B cells
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with Alexa Fluor® 647 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
IHC-F - Verified - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤0.5 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. For immunohistochemistry, a concentration range of 2.5 - 5 µg/ml is suggested. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
* Alexa Fluor® 647 has a maximum emission of 668 nm when it is excited at 633 nm / 635 nm.
Alexa Fluor® and Pacific Blue™ are trademarks of Life Technologies Corporation.
View full statement regarding label licenses - Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
- Application Notes
-
The GL7 antibody does not block the binding of CD22 with sulfated a2-6-sialyl-LacNAc.
Cross-reactivity to ferret has been reported by a collaborator, but not verified in house. - Application References
-
- Laszlo G, et al. 1993. J. Immunol. 150:5252. (FC, IP)
- Hartgring SA, et al. 2012. Arthritis Res. Ther. 14:R137. (FC)
- Taylor JJ, et al. 2012. J. Exp. Med. 209:597. (FC, IHC)
- Balogh A, et al. 2010. Immunol. Lett. 130:89. (IHC)
- Kimura N, et al. 2007. J. Biol. Chem. 282:32200. (ELISA, FC)
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_2562184 (BioLegend Cat. No. 144605)
AB_2562184 (BioLegend Cat. No. 144606)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- 35 kD
- Distribution
-
Germinal center B cells, activated B and T cells
- Function
- Upregulated on activated B cells via in situ repression of CMP-Neu5Ac-hydroxylase
- Ligand/Receptor
- Neu5Ac-recognizing lectins
- Cell Type
- B cells, T cells
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Laszlo G, et al. 1993. J. Immunol. 150:5252.
2. Hathcock KS, et al. 1995. J. Immunol. 155:4575.
3. Cervenak K, et al. 2001. Immunol. Lett. 78:89. - Gene ID
- NA
- UniProt
- View information about GL7 on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All GL7 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse/human GL7 Antigen (T and B cell Activation Marker)

BALB/c mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse ... 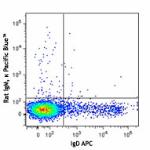
-
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse/human GL7 Antigen (T and B cell Activation Marker)
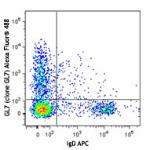
BALB/c mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse ... 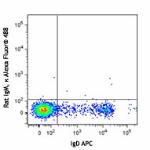
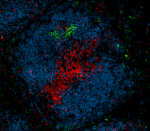
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... 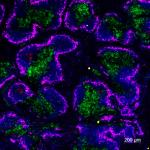
Tetanus toxin immunized mouse spleen, frozen in OCT and slic... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse/human GL7 Antigen (T and B cell Activation Marker)

Balb/c mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse ... 
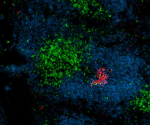
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... 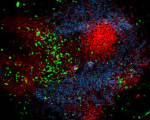
LPS-challenged C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed... -
Purified anti-mouse/human GL7 Antigen (T and B cell Activation Marker)

Balb/c mouse bone marrow cells were stained with IgD APC and... 
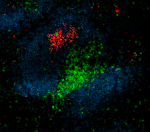
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... 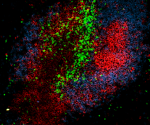
LPS-challenged C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed... -
FITC anti-mouse/human GL7 Antigen (T and B cell Activation Marker)

Balb/c mouse bone marrow cells were stained with IgD Pacific... 
-
PE anti-mouse/human GL7 Antigen (T and B cell Activation Marker)

BALB/c mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse ... 
-
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse/human GL7 Antigen (T and B cell Activation Marker)
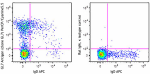
BALB/c mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse ... -
Biotin anti-mouse/human GL7 Antigen (T and B cell Activation Marker)
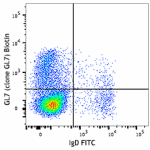
BALB/c mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse ... 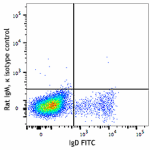
-
APC anti-mouse/human GL7 Antigen (T and B cell Activation Marker)
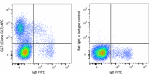
BALB/c mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse ... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse/human GL7 Antigen (T and B cell Activation Marker)
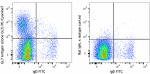
BALB/c mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse ...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 












Follow Us