- Clone
- 15-2 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- MMR (macrophage mannose receptor), MR (mannose receptor), CD206, MRC1
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
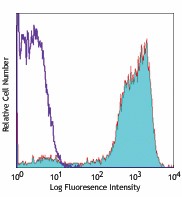
-

GM-CSF- stimulated (day-3) human monocytes stained with 15-2 APC
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 321109 | 25 tests | 120€ | ||||
| 321110 | 100 tests | 252€ | ||||
Macrophage mannose receptor (MMR) is a 162-175 kD type I membrane protein also known as CD206, MRC1, or mannose receptor (MR). It is a pattern recognition receptor (PRR) that belongs to C-type lectin superfamily. MMR is expressed on macrophages, dendritic cells, and hepatic or lymphatic endothelial cells, but not on monocytes. MMR recognizes a range of microbial carbohydrates bearing mannose, fucose, or N-acetyl glucosamine. MMR mediates endocytosis and phagocytosis, induces activation of macrophages and antigen presentation, plays an important role in host defense, and provides a link between innate and adaptive immunity.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Purified human mannose receptor
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA)
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with APC under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µL per million cells in 100 µL staining volume or 5 µL per 100 µL of whole blood. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
- Application Notes
-
The 15-2 antibody blocks the interaction of MMR with its ligand, and inhibits mannose receptor-mediated degradation of t-PA by macrophages. Additional reported applications of this antibody (for the relevant formats) include: Western blotting1, blocking of ligand binding1,2, immunofluorescence3, and immunohistochemical staining of acetone-fixed frozen tissue sections1. The Utra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin < 0.01 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for functional assays (Cat. No. 321149 and 321150).
- Application References
-
- Noorman F, et al. 1997. J. Leukocyte Biol. 61:63. (WB, IHC, Block)
- Barrett-Bergshoeff M, et al. 1997. Thromb Haemost. 77:718. (Block)
- Kato M, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:6052. (IF)
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_571884 (BioLegend Cat. No. 321109)
AB_571885 (BioLegend Cat. No. 321110)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Type I membrane protein, Pattern Recognition Receptor (PRR) family, C-type lectin superfamily, 162-175 kD
- Distribution
-
Macrophages, dendritic cells, hepatic and lymphatic endothelial cells
- Function
- Pathogen binding, facilitate phagocytosis and endocytosis, macrophage activation and antigen presentation
- Ligand/Receptor
- Mannose, fucose, N-acetyl glucosamine
- Cell Type
- Dendritic cells, Endothelial cells, Macrophages
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Immunology, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Mason D, et al. Eds. 2002. Leukocyte Typing VII. Oxford University Press. p303
2. Wileman TE, et al. 1986. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:2501.
3. Apostolopoulos V and McKenzie IF. 2001. Curr. Mol. Med. 1:469.
4. Le Cabec V, et al. 2005. J. Leukocyte Biol. 77:934.
5. Barrett-Bergshoeff M, et al. 1997. Thromb. Haemostatis 77:718. - Gene ID
- 4360 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD206 on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All CD206 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
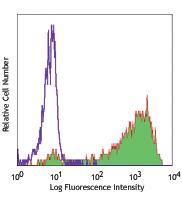
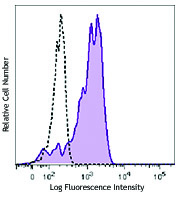


Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-human CD206 (MMR)
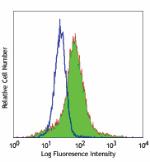
GM-CSF-stimulated (day-3) human monocytes stained with purif... -
FITC anti-human CD206 (MMR)
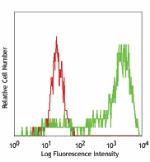
GM-CSF stimulated (day3) human peripheral blood monocytes st... -
PE anti-human CD206 (MMR)
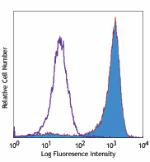
GM-CSF-stimulated (day-3) human monocytes stained with 15-2 ... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
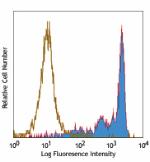
GM-CSF-stimulated human peripheral blood monocytes (day-3) s... -
APC anti-human CD206 (MMR)
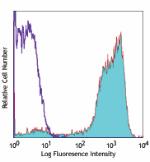
GM-CSF- stimulated (day-3) human monocytes stained with 15-2... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
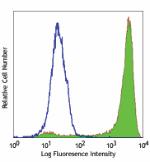
GM-CSF-stimulated (day-3) human monocytes stained with 15-2 ... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
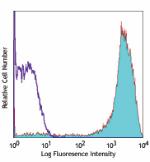
GM-CSF-stimulated (day-3) human monocytes stained with 15-2 ... -
Biotin anti-human CD206 (MMR)
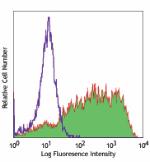
GM-CSF-stimulated human peripheral blood monocytes (day-3) s... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
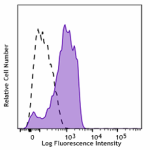
GM-CSF-stimulated (6 days) human peripheral blood monocytes ... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
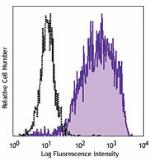
GM-CSF-stimulated (3 days) human peripheral blood monocytes ... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
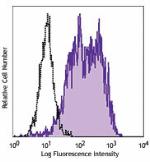
GM-CSF-stimulated (3 days) human peripheral blood monocytes ... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-human CD206 (MMR)
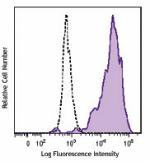
GM-CSF-stimulated (3 days) human peripheral blood monocytes ... -
Purified anti-human CD206 (MMR) (Maxpar® Ready)

Human PBMCs were incubated for 3 days in media alone (top) o... 
-
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
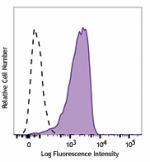
GM-CSF-stimulated (3 days) human peripheral blood monocytes ... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
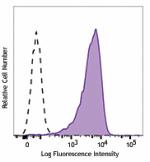
GM-CSF-stimulated (3 days) human peripheral blood monocytes ... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
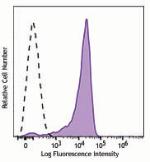
GM-CSF-stimulated (3 days) human peripheral blood monocytes ... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-human CD206 (MMR)
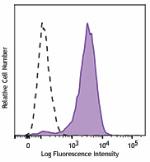
GM-CSF-stimulated (3 days) human peripheral blood monocytes ... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-human CD206 (MMR)
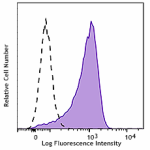
GM-CSF stimulated (3 days) human peripheral blood monocytes ... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-human CD206 (MMR)
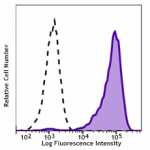
GM-CSF induced human monocytes (3 days) were stained with CD... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-human CD206 (MMR)
-
TotalSeq™-A0205 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
-
TotalSeq™-B0205 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
-
TotalSeq™-C0205 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
-
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-human CD206 (MMR)

GM-CSF-stimulated (day-3) human monocytes stained with purif... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-human CD206 (MMR)
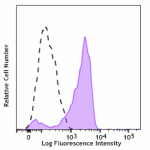
Human peripheral blood monocytes were stimulated with GM-CSF... -
PE/Fire™ 700 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
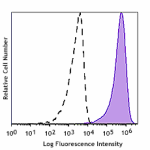
GM-CSF stimulated (3 days) human peripheral blood monocytes ... -
TotalSeq™-D0205 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
-
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-human CD206 (MMR)
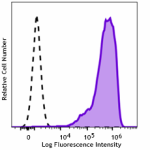
GM-CSF stimulated (3 days) human peripheral blood monocytes ... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-human CD206 (MMR) (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-human CD206 (MMR)

GM-CSF stimulated (3 days) human peripheral blood mononuclea... 
GM-CSF stimulated (3 days) human peripheral blood mononuclea... -
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-human CD206 (MMR) (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Spark Blue™ 550 anti-human CD206 (MMR) (Flexi-Fluor™)
 Login / Register
Login / Register 













Follow Us