- Other Names
- Inhibin BA (INHBA), Inhibin B-1, Follicule stimulating hormone-releasing protein (FRP), FSH releasing protein, FSH releasing factor, Erythroid differentiation factor (EDF)
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
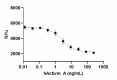
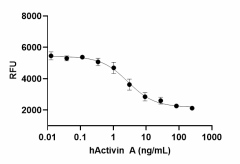
Human Activin A induces cytotoxic effect on MPC-11 mouse plasmacytoma cells in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is 1– 5 ng/mL.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592016 | 100 µg | 1080€ | ||||
Activin A was initially identified in ovarian fluid as a stimulator of FSH secretion from anterior pituitary cells. Activin A is a member of the TGFb1 family which includes TGFs, activins, Nodal, growth and differentiation factors (GDF), and bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). Activin A is a dimer of the beta A subunits of human inhibin; the beta A subunit binds the beta B subunit of inhibin to form Activin AB. The beta B subunit also exists as a heterodimer to form Activin B. Activin A binds two type I and two type II serine/threonine kinase receptors at the same time. The type II receptor kinase is constitutively active and phosphorylates the type I receptor after the formation of the ligand-receptor complex. Five type II receptors have been identified: ActRIIA, ActRIIB, BMPRII, TGFβRII, and MISRII. ActRIIB binds to Activin A, BMP-2, BMP-7, GDF-8, and GDF-11. The type I receptors are named activin receptor-like kinases 1 to 7 (ALK1~7), and Activins bind to ALK4 and ALK7. Follistatin (FS) is a natural Activin A antagonist; FS neutralizes its biologic activities by preventing Activin A interaction with its receptors. Activin A has pleiotropic functions. It is a morphogen during embryonal development, regulating chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells (MPC). Activin A has been associated with neuroprotection, apoptosis, and fibrosis. Also, high levels of Activin A have been found in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and gout. In addition, it has been speculated that Activin A, in collaboration with TGFb1 and IL-25, promotes TH9 generation and the development of allergic pathology.
Product DetailsBioLegend Cell-Vive™ GMP Recombinant proteins are manufactured and tested in accordance with USP Chapter 1043, Ancillary Materials for Cell, Gene and Tissue-Engineered Products and Ph. Eur. Chapter 5.2.12 in a dedicated GMP facility compliant with ISO 13485:2016. Specifications and processes include:
- Low endotoxin level (<0.1 EU/μg)
- Purity (≥ 95% or higher)
- Bioburden testing
- Mycoplasma testing
- Batch-to-batch consistency
- Vendor qualification
- Raw material traceability and documentation
- Documented procedures and employee training
- Equipment maintenance and monitoring records
- Lot-specific certificates of analysis
- Quality audits per ISO 13485:2016
- QA review of released products
Product Details
- Source
- Human Activin A, amino acids (Gly311-Ser426) (Accession# M13436) was expressed in CHO cells.
- Molecular Mass
- The 116 amino acid recombinant protein has a predicted molecular mass of approximately 12.9 kD. The DTT-reduced and non-reduced glycosylated protein migrate at approximately 14 kD and 26 kD respectively by SDS-PAGE. The N-terminal amino acid is Gly.
- Purity
- >95%, as determined by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE.
- Formulation
- Protein was lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution containing 0.1% TFA, 10% Acetonitrile containing no preservative.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.1 EU per μg of protein as determined by the LAL method.
- Concentration
- 100 μg size is lyophilized
- Storage & Handling
- Unopened vial can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to 2 weeks, at - 20°C or colder until the expiration date. Reconstitute lyophilized protein in sterile 4 mM HCL. Before reconstitution, make sure sterile 4 mM HCL acid and product are at room temperature. Quickly spin the vial or gently tap down on the vial to make sure the lyophilized product is at the bottom of the vial before opening. Use aseptic techniques to add the required volume of reconstitution buffer (sterile 4 mM HCL) to the vial, to obtain the recommended stock concentration 250 μg/mL. Close the vial and leave at ambient temperature for 15-20 minutes. Then gently invert the vial several times or until all of the lyophilized product dissolves. Leave the vial at room temperature for another 15 minutes. If small particulates are still observed after 15 minutes, incubate at room temperature for an additional 30 minutes and leave the vial at 2°C - 8°C overnight. Next day, invert the vial several times or gently pipette the solution up and down before use. If needed, transfer the reconstituted stock solution to a sterile container for additional dilution to no less than 100 μg/mL. Small working aliquots in polypropylene tubes can be made after reconstitution and store the vials at -20°C or lower. Avoid freeze/ thaw cycles. Carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% endotoxin-free BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to two weeks or stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months.
- Activity
- Human Activin A induces cytotoxic effect on MPC-11 mouse plasmacytoma cells in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 for this effect is 1– 5 ng/mL.
- Application
-
Bioassay
- Application Notes
-
Our lyophilized proteins are validated in-house to maintain activity after shipping at ambient temperature and are backed by our 100% satisfaction guarantee. If you have any concerns, contact us at tech@biolegend.com.
- Application References
-
- Wu B, et al. 2021. Immunity. 54(2):308-323.e6. PubMed
- Disclaimer
-
BioLegend Cell-Vive™ GMP Recombinant proteins are for research use only. Suitable for ex vivo cell processing. Not for injection or diagnostic or therapeutic use. Not for resale. BioLegend will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Homodimer
- Bioactivity
- Human Activin A induces cytotoxic effect on MPC-11 mouse plasmacytoma cells.
- Cell Sources
- Activin A is expressed by a wide range of cells such as BM-derived stromal fibroblasts, aortic smooth muscle cells, pulmonary epithelium, CD4 T cells.
- Cell Targets
- The receptors for Activin A are expressed by many stromal cells, among them fibroblasts, hepatocytes, myometral cells, vascular endothelial cells, and neuronal progenitor cells
- Receptors
- Type I receptors ALK4 and ALK7, Type II receptors ActRIIA and ActRIIB.
- Antigen References
-
- Schwall RH, et al. 1988. Mol. Endocrinol. 2:1237.
- Hashimoto M, et al. 1992. J. Biol. Chem. 267:4999.
- Shav-Tal Y and Zipori D. 2002. Stem Cells. 20:493.
- Dohi T, et al. 2005. Gastroenterology. 128:411.
- Tsuchida K, et al. 2008. Endocr. J. 55:11.
- Djouad F, et al. 2010. Steam Cell Res. Ther. 1:11.
- Sako D, et al. 2010. J. Biol. Chem. 285:21037.
- Jones CP, et al. 2012. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 129:1000.
- Regulation
- Activin A plays a key role in embryogenesis, neointimal formation after arterial injury, early stages of chondrogenesis, osteogenesis, and hemopoiesis. Activin A drives TH9 differentiation in vitro. It is induced by Angiotensin II and alpha Thrombin and regulated by Follistatin. Activin A is induced by inflammatory cytokines and inhibited by glucocorticoids.
- Gene ID
- 3624 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Activin A on UniProt.org

 Login / Register
Login / Register 














Follow Us