- Clone
- A20088B (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- VEGFA165, MVCD1, VEGF, Vascular permeability factor (VPF)
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2b, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
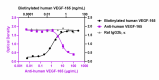
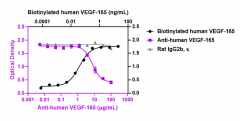
Biotinylated recombinant human VEGF-165 (black squares) binds to immobilized recombinant human VEGFR1 (Cat. No. 555804). Ultra- LEAF™ purified anti-human VEGF-165 (clone A20088B) (purple circles) inhibits the binding in a dose-dependent manner, whereas the GoInVivo™ purified rat IgG2b, κ isotype control (Cat. No. 400666) (gray triangles) does not have the effect. This antibody blocks the binding of 6 ng/mL biotinylated recombinant human VEGF-165 to 1 µg/mL immobilized recombinant human VEGFR1. ND50 range: 4 – 16 µg/mL.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 668053 | 100 µg | 331€ | ||||
| 668054 | 1 mg | 964€ | ||||
VEGF (known also as VEGFA) was initially identified in conditioned medium from bovine pituitary follicular cells. VEGFA belongs to the VEGF family, which has the following members: VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C (VEGF-2), VEGF-D, and PlGF (placental growth factor). In addition, viral VEGF homologs (collectively called VEGF-E) and snake venom VEGFs, such as T.f. (Trimeresurus flavoviridis) and svVEGF (called VEGF-F), have been described. VEGFA is alternatively spliced to generate variants with different numbers of amino acids, such as VEGFA121, VEGFA145, VEGFA165, and VEGFA189. VEGFA165 is predominant and responsible for VEGFA biological potency.
While VEGF121 is freely diffusible and does not bind to neuropilins (NRPs) or heparan sulphate (HS), VEGF165 and VEGF189 bind to both, resulting in retention on the cell surface or in the extracellular matrix. NRP1 lacks a typical kinase domain and acts as a co-receptor, and in response to VEGF165, NRP1 couples with VEGF-Rs to signal in endothelial cells. In addition, it has been suggested that bone marrow cells that are recruited to Ewing’s tumors are differentiated into vascular smooth muscle cells, and VEGF165 is responsible for this differentiation.
VEGFA is highly expressed in most of the solid tumors generated in breast, lung, renal, colorectal, and liver tissues. VEGFA has strong vascular permeability activity, and significantly contributes to the formation of ascites tumors. VEGFA can act as a direct proinflammatory mediator during the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and protect rheumatoid synoviocytes from apoptosis, which contributes to synovial hyperplasia. VEGFA is expressed in synovial macrophages and synovial fibroblasts in RA patients. Also, VEGFA is associated to age-related macular degeneration (AMD). AMD is due to neovascularization that originates from endothelial cells in the choroid that grow into neurosensory retina as choroidal neovascularization (CNV).
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- Recombinant human VEGF-165
- Formulation
- 0.2 µm filtered in phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing no preservative.
- Endotoxin Level
- Less than 0.01 EU/µg of the protein (< 0.001 ng/µg of the protein) as determined by the LAL test.
- Preparation
- The Ultra-LEAF™ (Low Endotoxin, Azide-Free) antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- The antibody is bottled at the concentration indicated on the vial, typically between 2 mg/mL and 3 mg/mL. To obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C. This Ultra-LEAF™ solution contains no preservative; handle under aseptic conditions.
- Application
-
Blocking - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by blocking the binding of 6 ng/mL biotinylated recombinant human VEGF-165 to 1 µg/mL immobilized recombinant human VEGFR1 (Cat. No. 555804). ND50 range: 4 – 16 µg/mL. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
This antibody has not been tested for ICC.
- RRID
-
AB_2922643 (BioLegend Cat. No. 668053)
AB_2922643 (BioLegend Cat. No. 668054)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Homodimer
- Distribution
-
Widely expressed
- Function
- VEGFA is a key player in vasculogenesis, the formation of blood vessels from progenitor cells, as well as angiogenesis. The expression of the VEGFA gene is upregulated via hypoxia, estrogen, and NF-κB pathways. In addition, VEGFA is upregulated by PDGF-BB, P1GF, TGFβ1, IGF1, FGFs, HGF, TNFα, and IL-1. VEGFA induces proliferation and cell migration in endothelial cells, and plays important roles during wound healing. Also, VEGFA regulates haematopoietic stem cell survival. VEGFA interacts with vascular endothelial cells and monocytes/macrophages, which express VEGFR1. This interaction induces proliferation of endothelial cells and stimulates migration of monocytes/macrophages. VEGFR2 is expressed in endothelial cells and VEGFR2-signaling is essential for the development of vascular systems in the embryo.
- Interaction
- Embryonic Stem Cells, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Neural Stem Cells
- Ligand/Receptor
- VEGFA binds and activates two tyrosine kinase receptors, VEGFR1 (Flt-1), VEGFR2 (KDR/Flk-1)
- Cell Type
- Embryonic Stem Cells, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Neural Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Angiogenesis, Cell Biology, Neuroscience, Stem Cells, Synaptic Biology
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines, Growth Factors
- Antigen References
-
- Conn G, et al. 1990. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 87:1323-7.
- Gerber H, et al. 2002. Nature. 417:954-8.
- Shibuya M. 2006. J Biochem Mol Biol. 39:469-78.
- Reddy K, et al. 2008. Angiogenesis. 11:257-67.
- Shibuya M. 2008. BMB Rep. 41:278-86.
- Monaghan-Benson E, et al. 2010. Am J Pathol. 177:2091-102.
- Koch S and Claesson-Welsh L. 2012. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2:a006502.
- Gene ID
- 7422 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about VEGF-165 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- Do you guarantee that your antibodies are totally pathogen free?
-
BioLegend does not test for pathogens in-house aside from the GoInVivo™ product line. However, upon request, this can be tested on a custom basis with an outside, independent laboratory.
- Does BioLegend test each Ultra-LEAF™ antibody by functional assay?
-
No, BioLegend does not test Ultra-LEAF™ antibodies by functional assays unless otherwise indicated. Due to the possible complexities and variations of uses of biofunctional antibodies in different assays and because of the large product portfolio, BioLegend does not currently perform functional assays as a routine QC for the antibodies. However, we do provide references in which the antibodies were used for functional assays and we do perform QC to verify the specificity and quality of the antibody based on our strict specification criteria.
- Does BioLegend test each Ultra-LEAF™ antibody for potential pathogens?
-
No, BioLegend does not test for pathogens in-house unless otherwise indicated. However, we can recommend an outside vendor to perform this testing as needed.
- Have you tested this Ultra-LEAF™ antibody for in vivo or in vitro applications?
-
We don't test our antibodies for in vivo or in vitro applications unless otherwise indicated. Depending on the product, the TDS may describe literature supporting usage of a particular product for bioassay. It may be best to further consult the literature to find clone specific information.
Other Formats
View All VEGF-165 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-human VEGF-165 | A20088B | Block |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-human VEGF-165
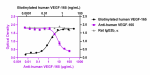
Biotinylated recombinant human VEGF-165 (black squares) bind...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us