- Clone
- H1.2F3 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Very Early Activation Antigen (VEA), AIM, EA1, MLR3, gp34/28
- Isotype
- Armenian Hamster IgG
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
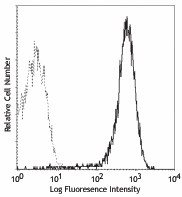
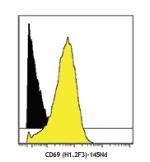
PMA-stimulated (6 hours) splenocytes stained with H1.2F3 FITC
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 104505 | 50 µg | 67€ | ||||
| 104506 | 500 µg | 235€ | ||||
CD69 is a 60 kD type II membrane protein composed of a 27/33 kD disulfide-linked homodimer, also known as Very Early Activation Antigen (VEA), AIM, EA1, MLR3, and gp34/28. It is expressed on a subset of thymocytes and platelets. CD69 is rapidly induced on activated T and B cells, neutrophils, and NK cells. It is a C-type lectin, closely related to the NKR-P1 and Ly-49 NK cell activation molecules. CD69 is involved in the early events of cell activation and thymocyte positive selection.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Armenian Hamster
- Immunogen
- Mouse dendritic epidermal T cell line Y245
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with FITC under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤1.0 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
- Application Notes
-
The H1.2F3 antibody has been reported to augment T cell activation. Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: in vitro T cell and NK cell activation1-3, immunohistochemistry4,5, and immunoprecipitation1.
This antibody has been characterized in the literature as containing a lambda light chain. - Application References
-
- Yokoyama WM, et al. 1988. J. Immunol. 141:369. (IP)
- Sobel ES, et al. 1993. J. Immunol. 150:673.
- Karlhofer FM, et al. 1991. J. Immunol. 146:3662.
- Zhou X, et al. 2005. J. Biol. Chem. 280:31240. (IHC)
- Podd BS, et al. 2006. J. Immunol. 176:6532. (IHC)
- Lawson BR, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:5366.
- Lee JW, et al. 2006. Nature Immunol. 8:181.
- Epardaud M, et al. 2008. Cancer Res. 15:2972. PubMed
- Jordan JM, et al. 2008. 76:3717. PubMed
- Kenna TJ, et al. 2008. Blood 111:2091. PubMed
- Ishikawa C, et al. 2013. Biochim Biophys Acta. 167:99. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_313108 (BioLegend Cat. No. 104505)
AB_313109 (BioLegend Cat. No. 104506)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- C-type lectin, 27/33 kD
- Distribution
-
Activated T cells and B cells, NK cells, granulocytes, thymocytes, platelets
- Function
- Lymphocyte activation
- Cell Type
- B cells, Granulocytes, NK cells, Platelets, T cells, Thymocytes, Tregs
- Biology Area
- Costimulatory Molecules, Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Barclay AN, et al. 1997. The Leukocyte Antigen FactsBook Academic Press.
2. Testi R, et al. 1994. Immunol. Today 15:479.
3. Moretta A, et al. 1991. J. Exp. Med. 174:1393.
4. Yokoyama WM, et al. 1988. J. Immunol. 141:369. - Gene ID
- 12515 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD69 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All CD69 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
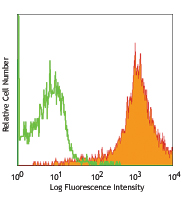
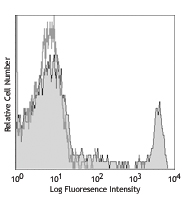
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Biotin anti-mouse CD69
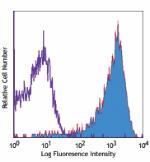
Con A-stimulated Balb/c mouse splenocytes (24 hours) stained... -
FITC anti-mouse CD69
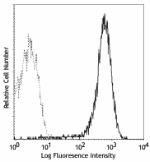
PMA-stimulated (6 hours) splenocytes stained with H1.2F3 FIT... -
PE anti-mouse CD69
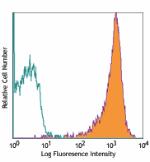
PMA+ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (6 hours)... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse CD69
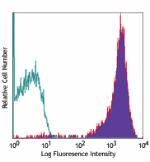
PMA+ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (6 hours)... -
Purified anti-mouse CD69
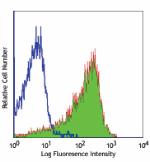
Con A-stimulated Balb/c mouse splenocytes (24 hours) stained... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD69
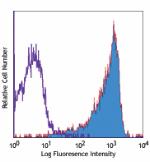
Con A-stimulated Balb/c mouse splenocytes (24 hours) stained... -
APC anti-mouse CD69
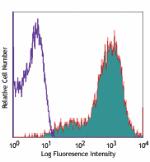
Con A-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (2 days) stained ... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD69
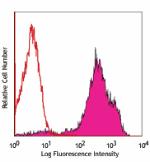
PMA and Ionomycin stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (6 hr... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD69
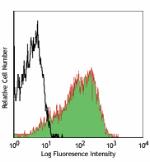
PMA+ionomycin-stimulated (6 hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes... -
PerCP anti-mouse CD69
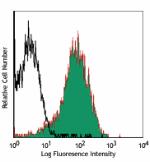
PMA + ionomycin-stimulated (6 hrs) C57BL/6 splenocytes stain... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD69
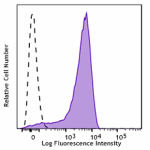
PMA+ionomycin stimulated (6 hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse CD69
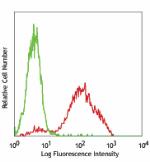
PMA + ionomycin-stimulated (6 hrs) C57BL/6 splenocytes stain... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse CD69
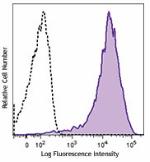
PMA+ionomycin-stimulated (6 hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD69
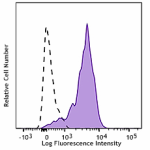
PMA+ionomycin-stimulated (6 hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse CD69
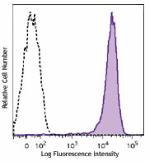
PMA+ionomycin-stimulated (6 hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse CD69
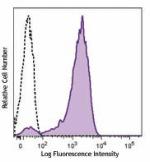
PMA and ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (6 ho... -
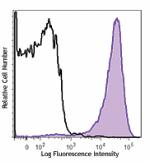
Purified anti-mouse CD69 (Maxpar® Ready)
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were incubated for 18 hours in med... -
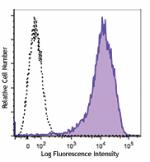
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD69
PMA+ionomycin-stimulated (six hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocyt... -
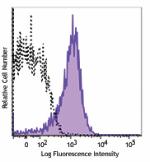
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse CD69
PMA and ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (six ... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse CD69
PMA and ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (six ... -
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse CD69
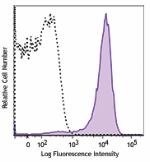
PMA+ionomycin-stimulated (six hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocyt... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse CD69
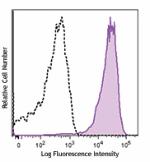
PMA + ionomycin-stimulated (six hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenoc... -
TotalSeq™-A0197 anti-mouse CD69
-
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse CD69
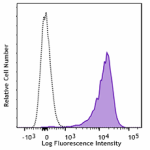
PMA+ionomycin-stimulated (4 hours) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes... -
TotalSeq™-C0197 anti-mouse CD69
-
TotalSeq™-B0197 anti-mouse CD69
-
KIRAVIA Blue 520™ anti-mouse CD69
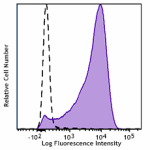
PMA and Ionomycin stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (6 hr... -
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-mouse CD69
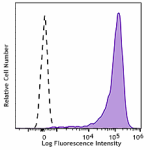
PMA and ionomycin stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (six ... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-mouse CD69
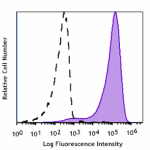
PMA+ ionomycin-stimulated (6 hrs) C57BL/6 splenocytes were s... -
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-mouse CD69 (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Spark PLUS B550™ anti-mouse CD69

PMA+ionomycin-stimulated C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes (6 hours)...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 













Follow Us