- Clone
- 390 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- PECAM-1, EndoCAM
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
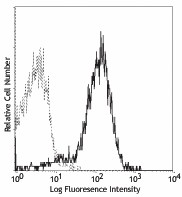
-
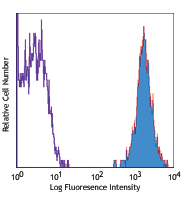
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with 390 PE
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 102407 | 50 µg | 88€ | ||||
| 102408 | 200 µg | 244€ | ||||
CD31 is a 130-140 kD glycoprotein, also known as platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM-1) and EndoCAM. It is a member of the Ig superfamily, expressed on endothelial cells, platelets, granulocytes, monocytes/macrophages, dendritic cells, and T and B cell subsets, and is critical for cell-cell interactions. The primary ligands for CD31 have been reported to be CD38 and the vitronectin receptor (αv β3 integrin, CD51/CD61). Other reported functions of CD31 are neutrophil emigration to sites of inflammation and angiogenesis.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- C3H/HeJ mouse hematopoietic progenitor cell line 3
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with PE under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤1.0 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Anti-mouse CD31 clones 390 and MEC13.3 bind to their respective non-overlapping epitopes in IgD2 of CD31.8 Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunoprecipitation1, in vitro and in vivo blocking of CD31-mediated cell-cell interactions1-4, and immunohistochemical staining5,6,7 of acetone-fixed frozen sections and zinc-fixed paraffin-embedded sections. Special Note: This antibody is not recommended for formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections. The LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin < 0.1 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for functional assays (Cat. No. 102412).
- Application References
-
- Baldwin HS, et al. 1994. Development 120:2539. (IP, Block)
- DeLisser HM, et al. 1997. Am. J. Pathol. 151:671. (Block)
- Rosenblum WI, et al. 1996. Stroke 27:709. (Block)
- Iguchi A, et al. 1997. Cell Struct. Funct. 22:357. (Block)
- Wyder L, et al. 2000. Cancer Res. 60:4682. (IHC)
- Wiewrodt R, et al. 2002. Blood 99:912. (IHC)
- McQualter JL, et al. 2009. Stem Cells. 27:623. (IHC) PubMed
- Chacko AM, et al. 2012. PLoS One 7:e34958.
- Greineder CF, et al. 2013. PLoS One. 14:80110. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_312902 (BioLegend Cat. No. 102407)
AB_312902 (BioLegend Cat. No. 102408)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Ig superfamily, 130-140 kD
- Distribution
-
Endothelial cells, platelets, granulocytes, monocytes/macrophages, dendritic cells, T and B cell subsets
- Function
- Adhesion
- Ligand/Receptor
- CD38, αV/β3 integrin
- Cell Type
- B cells, Dendritic cells, Endothelial cells, Granulocytes, Macrophages, Monocytes, Neutrophils, Platelets, T cells
- Biology Area
- Angiogenesis, Cell Adhesion, Cell Biology, Immunology, Neuroinflammation, Neuroscience
- Molecular Family
- Adhesion Molecules, CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Barclay AN, et al. 1997. The Leukocyte Antigen FactsBook Academic Press.
2. DeLisser HM, et al. 1994. Immunol. Today 15:490.
3. Newman PJ, et al. 1990. Science 247:1219. - Gene ID
- 18613 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD31 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- What type of PE do you use in your conjugates?
- We use R-PE in our conjugates.
Other Formats
View All CD31 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
APC anti-mouse CD31
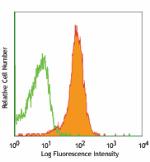
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with 390 APC -
Biotin anti-mouse CD31
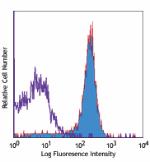
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with biotinylated 390, fol... -
FITC anti-mouse CD31
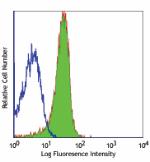
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 390 FITC -
PE anti-mouse CD31
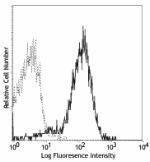
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with 390 PE -
Purified anti-mouse CD31

C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with 390 PE -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD31
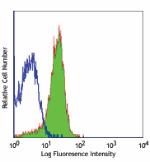
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 390 Alexa Fluor® 488 -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD31
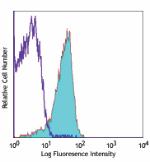
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 390 Alexa Fluor® 647 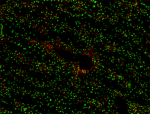
C57BL/6 mouse frozen liver section was fixed with 4% parafor... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD31
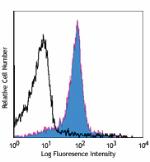
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 390 PE/Cyanine7 -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD31
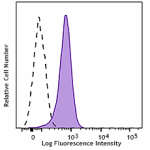
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD31 (clone 390)... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse CD31
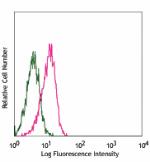
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 390 Pacific Blue&trad... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse CD31
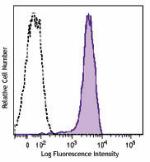
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD31 (clone 390)... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse CD31
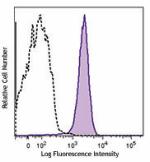
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD31 (clone 390)... -
Purified anti-mouse CD31 (Maxpar® Ready)

Mouse splenocytes stained with 165Ho-anti-CD31 (390) and 169... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD31
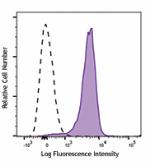
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD31 (clone 390)... -
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-mouse CD31
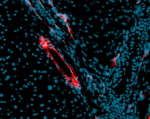
C57BL/6 mouse frozen liver section was fixed with 4% parafor... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse CD31
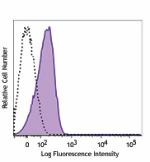
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD31 (clone 390)... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse CD31
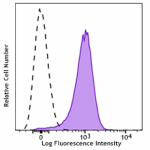
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD31 (clone 390) Brill... -
TotalSeq™-A0904 anti-mouse CD31
-
TotalSeq™-C0904 anti-mouse CD31
-
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse CD31
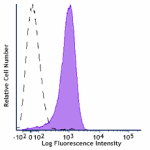
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD31 (clone 390)... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD31
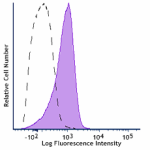
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD31 (clone 390)... -
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse CD31
-
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse CD31
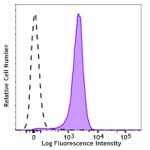
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD31 (clone 390)... -
Spark YG™ 570 anti-mouse CD31
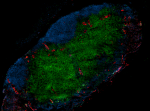
C57BL/6 mouse frozen lymph node section was fixed with 4% pa... -
TotalSeq™-B0904 anti-mouse CD31 Antibody

 Login / Register
Login / Register 














Follow Us