- Clone
- D7 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Sca-1
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
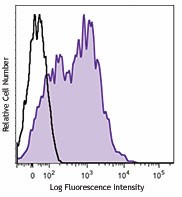
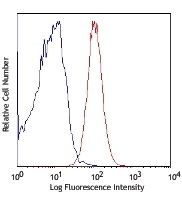
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with Ly-6A/E (clone D7) Brilliant Violet 421™ (filled histogram) or rat IgG2a, κ Brilliant Violet 421™ isotype control (open histogram). -

C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6A/E (clone D7) Brilliant Violet 421™ (filled histogram) or rat IgG2a, κ Brilliant Violet 421™ isotype control (open histogram). Data shown was gated on lymphoid cell population.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 108127 | 125 µL | 155€ | ||||
| 108128 | 50 µg | 206€ | ||||
Ly-6A/E, also known as Sca-1, is an 18 kD member of the Ly-6 multigene family. Ly6A/E is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked protein expressed on hematopoietic stem cells. In mice expressing the Ly-6.2 haplotype (e.g., AKR, C57BL, C57BR, DBA/2, SJL, SWR, and 129), Ly-6A/E is also expressed on peripheral B lymphocytes and thymic and peripheral T lymphocytes. Strains expressing the Ly-6.1 haplotype (e.g., BALB/c, CBA, C3H/He, DBA/1, and NZB) have low Ly-6A/E expression on resting peripheral lymphocytes. The expression of Ly-6A/E on lymphocytes is upregulated upon activation from both Ly6.1 and Ly6.2 haplotype mice. Ly-6A/E is thought to be involved in the regulation of both T and B cell responses.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- IL-2-dependent mouse T-cell line (CTL-L)
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA).
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with Brilliant Violet 421™ under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- µg sizes: 0.2 mg/mLµL sizes: lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For immunofluorescent staining using the µg size, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤0.25 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. For immunofluorescent staining using the µl size, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
Brilliant Violet 421™ excites at 405 nm and emits at 421 nm. The standard bandpass filter 450/50 nm is recommended for detection. Brilliant Violet 421™ is a trademark of Sirigen Group Ltd.
Learn more about Brilliant Violet™.
This product is subject to proprietary rights of Sirigen Inc. and is made and sold under license from Sirigen Inc. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer a non-transferable right to use the purchased product for research purposes only. This product may not be resold or incorporated in any manner into another product for resale. Any use for therapeutics or diagnostics is strictly prohibited. This product is covered by U.S. Patent(s), pending patent applications and foreign equivalents. - Excitation Laser
-
Violet Laser (405 nm)
- Application Notes
-
The D7 antibody has been reported to induce T cell activation and inhibit TCR-induced IL-2 production. Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: Western blotting1,2, immunoprecipitation1, in vitro lymphocyte activation3-6, induction of redirected lysis7, induction of T cell inhibitory signalling8, immunofluorescence9, and immunohistochemical staining of acetone-fixed frozen sections13 and Bouin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples9.
The two Sca-1 recognizing clones D7 and E13-161.7 have been shown to bind distinct epitopes due to the inability of D7 to block the binding of E13-161.7.14 -
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Ortega G, et al. 1986. J. Immunol. 137:3240. (WB, IP)
- Palfree RGE, et al. 1986. Immunogenetics 23:197. (WB)
- Codias EK, et al. 1990. J. Immunol. 144:2197.
- Malek TR, et al. 1986. J. Exp. Med. 164:709.
- Codias EK, et al. 1990. J. Immunol. 145:1407.
- Ivanov V, et al. 1994. J. Immunol. 153:2394.
- Karlhofer FM, et al. 1991. J. Immunol. 146:3662.
- Fleming T, et al. 1994. J. Immunol. 153:1955.
- van Bragt MPA, et al. 2005. Biol. Reprod. 73:634. (IF, IHC)
- Umland O, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:4147.
- Cridland SO, et al. 2009. Blood Cell. Mol. Dis. 45:149. (FC) PubMed
- Pronk CJ, et al. 2011. J. Exp Med. PubMed
- English A, et al. 2000. J. Immunol. 165:3763. (IHC)
- Bamezai A and Rock KL. 1995. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:4294.
- Wiesner DL, et al. 2015. PLoS Pathog. 11:1004701. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_10898327 (BioLegend Cat. No. 108127)
AB_2563064 (BioLegend Cat. No. 108128)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Ly-6 multigene family, 18 kD
- Distribution
-
Hematopoietic stem cells, activated T cells and B cells, subset of resting B cells and T cells
- Function
- Regulates B and T cell responses
- Cell Type
- B cells, Hematopoietic stem and progenitors, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, T cells
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Stem Cells
- Antigen References
-
1. Rock KL, et al. 1989. Immunol. Rev. 111:195.
2. Morrison SJ, et al. 1994. Immunity 1:661.
3. Spangrude GJ, et al. 1988. J. Immunol. 141:3697.
4. Malek T, et al. 1986. J. Exp. Med. 164:709. - Gene ID
- 110454 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Ly-6A/E on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
- What is the F/P ratio range of our BV421™ format antibody reagents?
-
It is lot-specific. On average it ranges between 2-4.
Other Formats
View All Ly-6A/E Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
APC anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with D7 APC -
Biotin anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with biotinylated D7, followed b... -
FITC anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
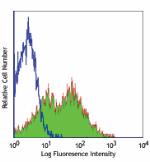
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with D7 FITC -
PE anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
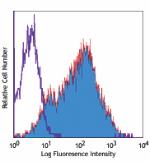
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with D7 PE -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
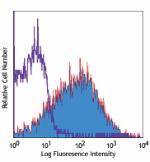
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with D7 PE/Cyanine5 -
Purified anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
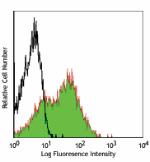
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with purified D7, followed by an... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
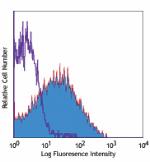
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with D7 PE/Cyanine7 -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
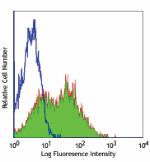
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with D7 Alexa Fluor® 488 -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
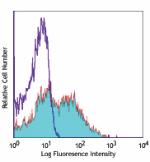
C57BL/6 mouse splenocyteS stained with D7 Alexa Fluor® 647 -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
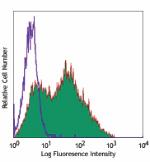
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with Pacific Blue™ D... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
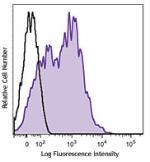
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with Ly-6A/E (clone D... 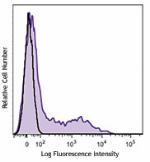
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6A/E (c... -
PerCP anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
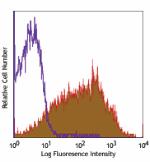
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with D7 PerCP -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
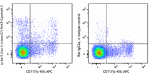
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow stained with Lineage FITC, CD117 (... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
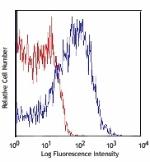
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with D7 APC/Cyanine7 -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
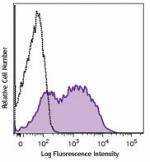
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with Ly-6A/E (clone D... 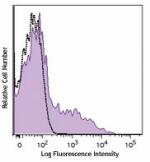
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6A/E (c... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
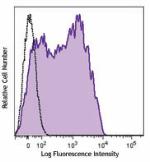
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with Ly-6A/E (clone D... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
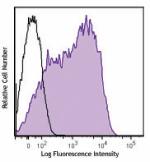
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with Ly-6A/E (clone D... -
Purified anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1) (Maxpar® Ready)
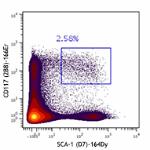
Mouse bone marrow cells stained with 164Dy anti-Sca-1 (D7) a... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
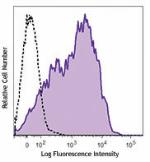
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with Ly-6A/E (clone D... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
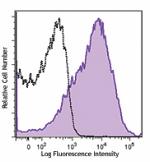
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with Ly-6A/E (clone D... 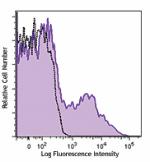
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6A/E (c... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
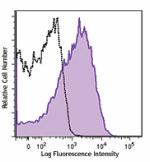
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with Ly-6A/E (clone D... 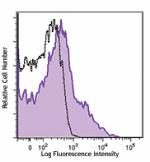
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6A/E (c... -
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
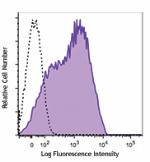
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with Ly-6A/E (clone D... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
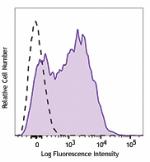
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with Ly-6A/E (clone D... -
TotalSeq™-A0130 anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
-
TotalSeq™-B0130 anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
-
TotalSeq™-C0130 anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
-
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)
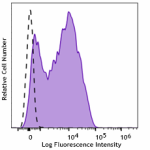
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse Ly-6A... -
Spark PLUS UV395™ anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse Ly-6A... -
PerCP/Fire™ 806 anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1) Antibody

C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse... -
Brilliant Violet 750™ anti-mouse Ly-6A/E (Sca-1)

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse Ly-6A...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 














Follow Us