- Clone
- RB6-8C5 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Gr-1
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2b, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
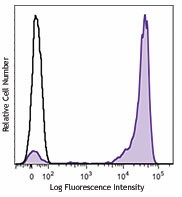
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G/Ly-6C (clone RB6-8C5) Brilliant Violet 421™ (filled histogram) or rat IgG2b, κ Brilliant Violet 421™ isotype control (open histogram). Data shown was gated on myeloid cell population.
Gr-1 is a 21-25 kD protein also known as Ly-6G/Ly-6C. This myeloid differentiation antigen is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked protein expressed on granulocytes and macrophages. In bone marrow, the expression levels of Gr-1 directly correlate with granulocyte differentiation and maturation; Gr-1 is also transiently expressed on bone marrow cells in the monocyte lineage. Immature Myeloid Gr-1+ cells play a role in the development of antitumor immunity.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- Raised against granulocytes of mouse origin
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA).
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with Brilliant Violet 421™ under optimal conditions.
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining using the µl size, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood. For flow cytometric staining using the µg size, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤ 0.25 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
Brilliant Violet 421™ excites at 405 nm and emits at 421 nm. The standard bandpass filter 450/50 nm is recommended for detection. Brilliant Violet 421™ is a trademark of Sirigen Group Ltd.
Learn more about Brilliant Violet™.
This product is subject to proprietary rights of Sirigen Inc. and is made and sold under license from Sirigen Inc. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer a non-transferable right to use the purchased product for research purposes only. This product may not be resold or incorporated in any manner into another product for resale. Any use for therapeutics or diagnostics is strictly prohibited. This product is covered by U.S. Patent(s), pending patent applications and foreign equivalents. - Excitation Laser
-
Violet Laser (405 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Clone RB6-8C5 binds with high affinity to mouse Ly-6G molecules and to a lower extent to Ly-6C19. Clone RB6-8C5 impairs the binding of anti-mouse Ly-6G clone 1A819. However, clone RB6-8C5 is able to stain in the presence of anti-mouse Ly-6C clone HK1.420.
The RB6-8C5 antibody has been used to identify peripheral blood neutrophils and deplete granulocytes in vivo. Additional reported applications (for relevant formats of this clone) include: in vitro complement-mediated cytotoxicity2, in vivo depletion3-5,9, immunoprecipitation1, immunohistochemical staining6 (including paraffin-embedded sections9,16,33-35, acetone-fixed frozen sections11 and zinc-fixed sections15), and Western blotting7. RB6-8C5 is not suitable for depletion of hepatic myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSCs)20.
Special Note: For in vivo studies or highly sensitive assays, we recommend Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Cat. No. 108436). -
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Fleming TJ, et al. 1993. J. Immunol. 151:2399. (IP)
- Brummer E, et al. 1984. J. Leukocyte Biol. 36:505. (CMCD)
- Stoppacciaro A, et al. 1993. J. Exp. Med. 178:151. (Deplete)
- Tumpey TM, et al. 1996. J. Virol. 70:898. (Deplete)
- Czuprynski CJ, et al. 1994. J. Immunol. 152:1836. (Deplete)
- Nitta H, et al. 1997. Cell Vision 4:73. (IHC)
- Jutila MA, et al. 1988. Eur. J. Immunol. 18:1819. (WB)
- Engwerda CR, et al. 2004. Am. J. Pathol. 165:2123.
- Brown CR, et al. 2004. Infect. Immun. 72:4956. (Deplete, IHC)
- Andoniou CE, et al. 2005. Nature Immunology 6:1011. (FC) PubMed
- Li M, et al. 2006. P. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 103:11736. (IHC)
- Dzhagalov I, et al. 2007. Blood 109:1620. (FC) PubMed
- Fazilleau N, et al. 2007. Nature Immunol. 8:753. (FC) PubMed
- Heuser M, et al. 2007. Blood 110:1639. (FC) PubMed
- Wang T, et al. 2007. Infect. Immun. 75:1144. (IHC)
- Bosio CM, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:4538. (IHC)
- Boehme SA, et al. 2009. Int. Immunol. 21:81. (IHC)
- Piao Y, et al. 2012. Neuro Oncol. 14:1379. PubMed
- Ribechini E, et al. 2009. Eur. J. Immunol. 39:3538.
- Ma C, et al. 2012. J. Leukoc. Biol. 92:1199.
- Li J, et al. 2012. Arthritis Rheum. 64:1098. PubMed
- Fan Q, et al. 2014. Cancer Res. 74:471. PubMed
- Korrer MJ, et al. 2014. PLoS One. 9:91370. PubMed
- Morshed M, et al. 2014. J Immunol. 192:5314. PubMed
- Collins C, et al. 2014. PNAS. 111:9899. PubMed
- Madireddi S, et al. 2014. J Exp Med. 211:1433. PubMed
- Bianchi G, et al. 2014. Cell Death Dis. 5:1135. PubMed
- Guo H, et al. 2014. J Leukoc Biol. 96:419. PubMed
- Roderick JE, et al. 2014. PNAS. 111:14436. PubMed
- Distel E, et al. 2014. Circ Res. 115:759. PubMed
- Iwai H, et al. 2015. Tuberculosis. 95:246. PubMed
- Charmsaz S, et al. 2015. PLoS One. 10:130692. PubMed
- Whiteland J, et al. 1994 J Histochem Cytochem 43:3 (IHC-P)
- Brown C, et al. 2003 J Immunology 171:2 (IHC-P)
- Obregon-Henao A, et al. PLoS One 8:11 (IHC-P)
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_10900232 (BioLegend Cat. No. 108433)
AB_2562903 (BioLegend Cat. No. 108445)
AB_2562219 (BioLegend Cat. No. 108434)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- 21-25 kD
- Distribution
-
Granulocytes, monocytes
- Cell Type
- Granulocytes, Monocytes, Neutrophils
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Antigen References
-
1. Fleming TJ, et al. 1993. J. Immunol. 151:2399.
2. Jutila MA, et al. 1988. Eur. J. Immunol. 18:1819.
3. Goni O, et al. 2002. Int. Immunol. 14:1125. - Gene ID
- 17067 View all products for this Gene ID 546644 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Ly-6G Ly-6C on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- What is the F/P ratio range of our BV421™ format antibody reagents?
-
It is lot-specific. On average it ranges between 2-4.
Other Formats
View All Ly-6G/Ly-6C Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
APC anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow stained with Ly-6G/Ly-6C APC (clon... -
Biotin anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow stained with biotinylated Ly-6G/Ly... -
FITC anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
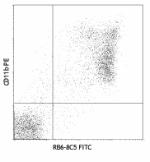
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow stained with Ly-6G/Ly-6C (clone RB... -
PE anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
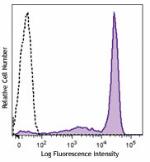
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G/Ly-6... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
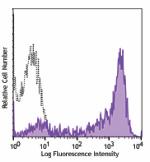
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow stained with Ly-6G/Ly-6C (clone RB... -
Purified anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
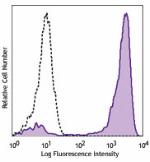
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with purified L... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
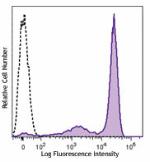
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G/Ly-6... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
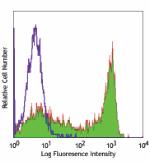
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow (gated on myeloid cell population)... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
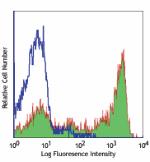
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow (gated on myeloid cell population)... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
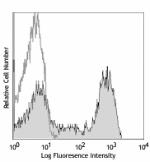
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow (gated on myeloid cell population)... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
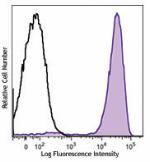
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G/Ly-6... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
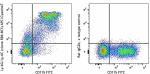
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow stained with CD11b FITC and Ly-6G/... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
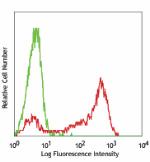
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow (gated on myeloid cell population)... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
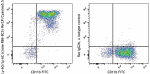
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow were stained with CD11b FITC and L... -
PerCP anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
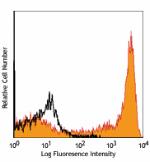
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow (gated on myeloid cell population)... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
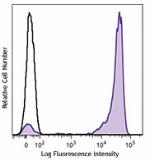
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G/Ly-6... -
Brilliant Violet 570™ anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
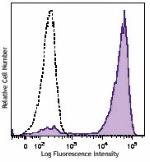
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G/Ly6C... -
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
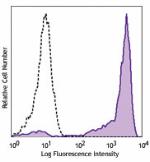
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with LEAF™ puri... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
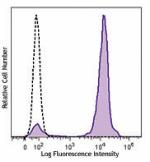
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G/Ly-6... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
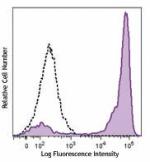
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G/Ly-6... -
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
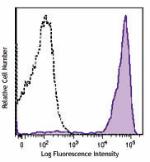
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G/Ly-6... -
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
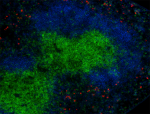
C57BL/6 mouse frozen lymph node section was fixed with 4% pa... 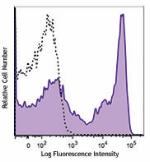
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G/Ly-6... -
Purified anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1) (Maxpar® Ready)
Mouse splenocytes stained with 141Pr anti-Ly-6G/C (RB6-8C5) ... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G/Ly-6... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)

C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with CD11b PE a... 
-
TotalSeq™-A0116 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
-
TotalSeq™-C0116 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
-
TotalSeq™-B0116 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
-
Spark Blue™ 550 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
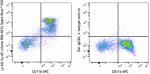
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow was stained with CD11b APC and Ly-... -
APC/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
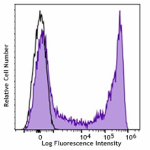
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G/Ly-6... -
Spark Violet™ 423 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (GR-1) Antibody
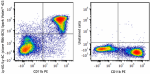
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse... -
Spark UV™ 387 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (GR-1)
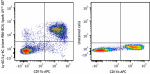
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse... -
Spark Violet™ 538 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow were stained with anti-mouse CD11b... -
Spark PLUS UV395™ anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1)

C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1) (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-mouse Ly-6G/Ly-6C (Gr-1) (Flexi-Fluor™)
 Login/Register
Login/Register 
















Follow Us