- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- 4',6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole, Dilactate
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
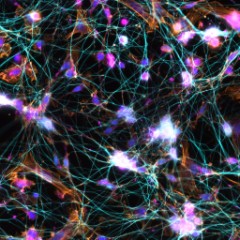
-
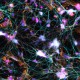
Methanol fixed superior cervical ganglion neurons were stained with anti-tubulin β3 (pink) and anti-TRIM46 (aqua), then stained with secondary antibodies, phalloidin (orange) and DAPI (blue). Image generously submitted to the 2017 Cell Life Imaging Competition by Ankita Patil from Drexel University. -
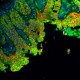
Frozen mouse intestine stained with purified anti-Ankyrin-B (green), E-Cadherin (red) and DAPI (blue) followed by anti-goat Alexa Fluor® 488 and anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor® 568. Image generously submitted to the 2017 Cell Life Imaging Competition by Kathleen Ignatoski from University of Michigan. -
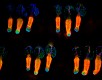
Whole mount mouse tail epidermis was stained with purified anti-Keratin 14 (green, clone Poly19053), purified anti-Keratin 15 (orange, clone Poly18339) and DAPI (blue). Image generously submitted to the 2017 Cell Life Imaging Competition by Kif Liakath. -
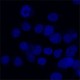
Human cervical cancer cell line, HeLa, was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with 300 nM DAPI. -
Human cervical cancer cell line, HeLa, was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with 300 nM DAPI.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 422801 | 10 mg | $101 | ||||
DAPI (4',6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole, Dilactate), a blue fluorescent nucleic acid stain, preferentially binds dsDNA and associates with the minor groove AT clusters. The molecular weight for DAPI is 457.5. Association of DAPI with dsDNA increases fluorescence approximately 20-fold, with an emission maximum of 460 nm. The increase in fluorescence is believed to be due to displacement of water molecules from the minor groove and DAPI. DAPI can also bind RNA and emits at a longer wavelength of 500 nm, with only a 20% increase in fluorescence.
DAPI is a popular nuclear stain for identification of cell cycle and specifically stains nuclei but not cytoplasm. The dilactate form is more water soluble compared to the dihydrochloride form.
DAPI can be excited by a UV laser, xenon, or a mercury-arc lamp.
Product Details
- Formulation
- Lyophilized
- Preparation
- To make 5 mg/ml (10.9 mM) solution, dissolve entire contents of vial in 2 ml of deionized water.
- Storage & Handling
- Store between 2°C and 8°C, protected from light. For long term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C.
- Application
-
ICFC, ICC
- Recommended Usage
-
This product can be used at 30 µM for flow cytometry and 300 nM for immunofluorescence. It is recommended to titrate the dye for optimal performance.
- Excitation Laser
-
Ultraviolet Laser (355 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Protocols for Counterstaining with DAPI:
Immunofluorescence Staining
Note: Cells may be fixed by method of choice, such as with 4% paraformaldehyde. DAPI staining is done after staining for other markers. Fixation and permeabilization of cells is not necessary to counterstain with DAPI.
1. Fix cells using method of choice.
2. Incubate the cells with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for 15 minutes.
3. Dilute the DAPI solution (we recommend to 300 nM) with PBS. Remove excess PBS from the slide and cover with DAPI solution, making sure the cells are completely covered.
4. Incubate for up to 5 minutes. Rinse the slide several times to remove all free DAPI. It is recommended to use a mounting medium with antifade reagent to reduce fluorescence quenching. The slide is ready to view under the microscope with appropriate filters.
Nuclear Staining for Flow Cytometry
Note: Cells may be fixed with 4% paraformadehyde or absolute ethanol.
1. Fix cells with absolute ethanol or 4% paraformaldehyde.
2. Centrifuge, discard the supernatant, and add 5 ml of PBS, allowing cells to rehydrate for 15 minutes.
3. Dilute the DAPI to 30 µM (recommended) in staining buffer (such as BioLegend's FOXP3 Perm Buffer, Cat. No. 421402).
4. Centrifuge cell suspension from step 3 above, discard supernatant, and add 1 ml of DAPI solution; then incubate at room temperature for 15 minutes.
5. Analyze by flow cytometry using an instrument with appropriate lasers. - Additional Product Notes
-
View more applications data for this product in our Scientific Poster Library.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) - Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Cell Cycle/DNA Replication, Neuroscience
- Antigen References
-
1. Langlois RG, et al. 1980. Chromosoma. 77:229.
2. Kubista M, et al. 1987. Biochemistry 26:4545. - Gene ID
- NA
 Login/Register
Login/Register 















Follow Us