- Clone
- L161 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Workshop
- V T-CD01.18
- Other Names
- R7, M241, BDCA-1
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-

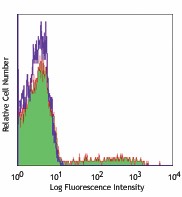
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with L161 PE -
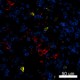
Confocal image of human lymph node sample acquired using the IBEX method of highly multiplexed antibody-based imaging: CD1c (red) in Cycle 3, CD8 (blue) in Cycle 4, and CD25 (yellow) in Cycle 4. Tissues were prepared using ~1% (vol/vol) formaldehyde and a detergent. Following fixation, samples are immersed in 30% (wt/vol) sucrose for cryoprotection. Images are courtesy of Drs. Andrea J. Radtke and Ronald N. Germain of the Center for Advanced Tissue Imaging (CAT-I) in the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID, NIH).
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 331505 | 25 tests | $146 | ||||
| 331506 | 100 tests | $317 | ||||
CD1c, also known as R7 or M241, is a 43 kD member of the five CD1 antigens (CD1a-e) in humans. The CD1 molecules are type I glycoprotein with structural similarities to MHC class I and are non-covalently associated with β2-microglobulin, belonging to the Ig superfamily. CD1c is expressed on cortical thymocytes, Langerhans cells, dendritic cells, and a subset of B cells. It has been reported that CD1c is also expressed on mature T cells in a tightly regulated manner. CD1c is involved in antigen-presentation of glycolipids. It may also act in T cells as an immune regulatory molecule.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Reported Reactivity
- African Green, Baboon, Cynomolgus, Rhesus
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA)
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with PE under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
SB - Reported in the literature, not verified in house - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunohistochemical staining on frozen tissue4, 5, formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded immunohistochemical staining6, and spatial biology (IBEX)7,8.
- Additional Product Notes
-
Iterative Bleaching Extended multi-pleXity (IBEX) is a fluorescent imaging technique capable of highly-multiplexed spatial analysis. The method relies on cyclical bleaching of panels of fluorescent antibodies in order to image and analyze many markers over multiple cycles of staining, imaging, and, bleaching. It is a community-developed open-access method developed by the Center for Advanced Tissue Imaging (CAT-I) in the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID, NIH).
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- del C Salamone M, et al. 2001. J Leukoc Biol. 70:567.
- de Fraissinette A, et al. 1988. Exp Hematol. 16:764.
- Li D, et al. 2012. J Exp Med. 209:109. PubMed
- Xu C, et al. 2010. Am J Hematol. 85:539 (IHC-F)
- Gerlini G, et al. 2001. J Invest Dermatol. 117:576 (IHC-F)
- Poposki J, et al. 2016. Clin Exp Allergy 45:384 (IHC-P) PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2020. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:33455-33465. (SB) PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2022. Nat Protoc. 17:378-401. (SB) PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_1088999 (BioLegend Cat. No. 331505)
AB_1088999 (BioLegend Cat. No. 331506)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- 43 kD, Ig superfamily, MHC I-like molecule, associates with β2-microglobulin
- Distribution
-
B cell subset, cortical thymocytes, dendritic cells, and Langerhans cells
- Function
- Presents lipid antigen to CD1c-restricted T cells
- Ligand/Receptor
- CD1c-restricted TCR
- Cell Type
- B cells, Dendritic cells, Langerhans cells, Thymocytes
- Biology Area
- Immunology
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Fainboim LM and del C. Salamone. 2002. J. Biol. Reg. Homeos. Ag. 16:125.
2. M. del Salamone C, et al. 2001. J. Leukocyte Biol. 70:567.
3. Zola H, et al. Eds. 2007. Leukocyte and Stromal Cell Molecules:The CD Markers. P42. - Gene ID
- 911 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD1c on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
- What type of PE do you use in your conjugates?
- We use R-PE in our conjugates.
- If an antibody clone has been previously successfully used in IBEX in one fluorescent format, will other antibody formats work as well?
-
It’s likely that other fluorophore conjugates to the same antibody clone will also be compatible with IBEX using the same sample fixation procedure. Ultimately a directly conjugated antibody’s utility in fluorescent imaging and IBEX may be specific to the sample and microscope being used in the experiment. Some antibody clone conjugates may perform better than others due to performance differences in non-specific binding, fluorophore brightness, and other biochemical properties unique to that conjugate.
- Will antibodies my lab is already using for fluorescent or chromogenic IHC work in IBEX?
-
Fundamentally, IBEX as a technique that works much in the same way as single antibody panels or single marker IF/IHC. If you’re already successfully using an antibody clone on a sample of interest, it is likely that clone will have utility in IBEX. It is expected some optimization and testing of different antibody fluorophore conjugates will be required to find a suitable format; however, legacy microscopy techniques like chromogenic IHC on fixed or frozen tissue is an excellent place to start looking for useful antibodies.
- Are other fluorophores compatible with IBEX?
-
Over 18 fluorescent formats have been screened for use in IBEX, however, it is likely that other fluorophores are able to be rapidly bleached in IBEX. If a fluorophore format is already suitable for your imaging platform it can be tested for compatibility in IBEX.
- The same antibody works in one tissue type but not another. What is happening?
-
Differences in tissue properties may impact both the ability of an antibody to bind its target specifically and impact the ability of a specific fluorophore conjugate to overcome the background fluorescent signal in a given tissue. Secondary stains, as well as testing multiple fluorescent conjugates of the same clone, may help to troubleshoot challenging targets or tissues. Using a reference control tissue may also give confidence in the specificity of your staining.
- How can I be sure the staining I’m seeing in my tissue is real?
-
In general, best practices for validating an antibody in traditional chromogenic or fluorescent IHC are applicable to IBEX. Please reference the Nature Methods review on antibody based multiplexed imaging for resources on validating antibodies for IBEX.
Other Formats
View All CD1c Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
PerCP anti-human CD1c
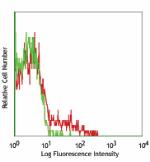
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with L161 PerCP -
Purified anti-human CD1c
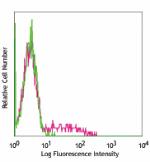
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with purified L16... -
Biotin anti-human CD1c
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with biotinylated... -
PE anti-human CD1c
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with L161 PE 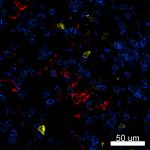
Confocal image of human lymph node sample acquired using the... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-human CD1c
Human T lymphoblastic leukemia cell line, Molt-4, stained wi... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-human CD1c
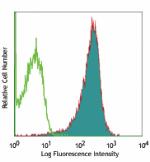
Human T lymphoblastic leukemia cell line, Molt-4, stained wi... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-human CD1c
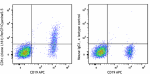
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 AP... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-human CD1c
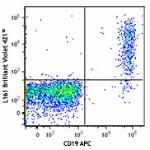
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 AP... 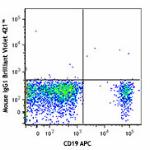
-
PE/Cyanine7 anti-human CD1c
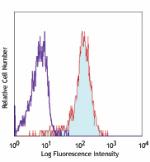
Human T lymphoblastic leukemia cell line Molt-4 stained with... -
FITC anti-human CD1c
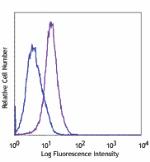
Human T lymphoblastic cell line, Molt-4, stained with L161 F... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-human CD1c
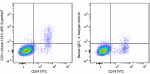
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes stained with CD19 FITC an... -
APC anti-human CD1c
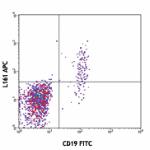
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 FI... 
-
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-human CD1c

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 AP... 
-
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-human CD1c

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 PE... 
-
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-human CD1c

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 AP... 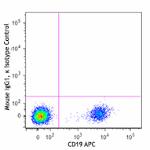
-
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-human CD1c

Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 FI... 
-
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-human CD1c
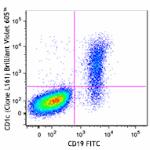
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 FI... 
-
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-human CD1c
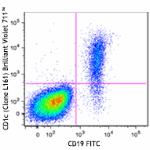
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 FI... 
-
TotalSeq™-A0160 anti-human CD1c
-
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-human CD1c
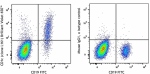
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 FI... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-human CD1c
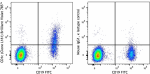
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 FI... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-human CD1c
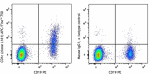
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with CD19 PE... -
TotalSeq™-C0160 anti-human CD1c
-
TotalSeq™-B0160 anti-human CD1c
-
TotalSeq™-D0160 anti-human CD1c
-
PE/Cyanine5 anti-human CD1c
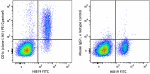
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with HIB19 F... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-human CD1c (Flexi-Fluor™)

 Login/Register
Login/Register 
















Follow Us