- Clone
- W15086B (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- fMet-Leu-Phe receptor 1, FMLP, FPR, fMLF-R
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
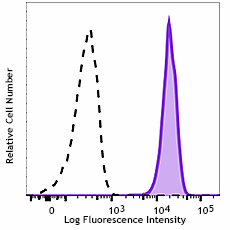
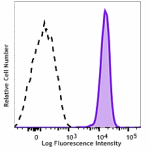
Human peripheral blood leukocytes were stained with PE anti-human FPR1 (clone W15086B) (filled histogram) or PE mouse IgG1, κ isotype control (open histogram); data shown is gated on the granulocyte population.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 391605 | 25 tests | $141 | ||||
| 391606 | 100 tests | $341 | ||||
FPR1 (Formyl Peptide Receptor 1), a G protein-coupled receptor consisting of seven transmembrane domains, is expressed on phagocytic cells and other cell types such as monocytes. FPR1 is a high affinity receptor for N-formyl-methionyl peptides (fMLP), which are powerful neutrophil chemotactic factors. Binding of fMLP to the receptor stimulates intracellular calcium mobilization and superoxide anion release. Endogenous peptide ligands for this receptor have also been identified. FPR1 mediates the response to invasion of the host by microbial pathogens and is important in host defense and inflammation.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Full length human FPR1 transfected cells
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA)
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with PE under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- RRID
-
AB_2721634 (BioLegend Cat. No. 391605)
AB_2721634 (BioLegend Cat. No. 391606)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Seven transmembrane domains, G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR)
- Distribution
-
Monocytes, Neutrophils
- Function
- Chemotaxis
- Ligand/Receptor
- N-formylated peptides, Ac9-25, FAM19A4, Annexin A1
- Cell Type
- Monocytes, Neutrophils, Eosinophils
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Antigen References
-
1. Boulay F, et al. 1990. Biochemistry 29:11123.
2. Ye RD, et al. 2009. Pharmacol. Rev. 61:119.
3. Prossnitz ER, et al. 1999. Biochemistry 38:2240.
4. Wang W, et al. 2015. Cell Mol. Immunol. 12:615. - Gene ID
- 2357 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about FPR1 on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
- What type of PE do you use in your conjugates?
- We use R-PE in our conjugates.
Other Formats
View All FPR1 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-human FPR1 | W15086B | FC |
| FITC anti-human FPR1 | W15086B | FC |
| PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-human FPR1 | W15086B | FC |
| PE anti-human FPR1 | W15086B | FC |
| APC anti-human FPR1 | W15086B | FC |
Customers Also Purchased
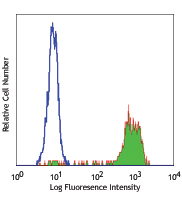

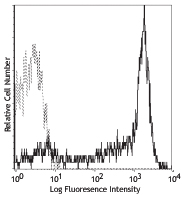
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-human FPR1
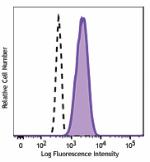
Human peripheral blood leukocytes were stained with purified... -
FITC anti-human FPR1
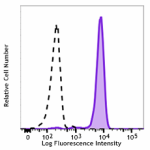
Human peripheral blood leukocytes were stained with FITC ant... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-human FPR1
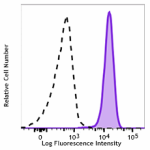
Human peripheral blood leukocytes were stained with PerCP/Cy... -
PE anti-human FPR1
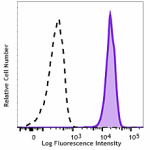
Human peripheral blood leukocytes were stained with PE anti-... -
APC anti-human FPR1
Human peripheral blood leukocytes were stained with APC anti...
 Login/Register
Login/Register 













Follow Us