- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Annexin A5
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
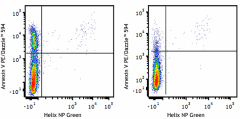
Human T leukemia cell line Jurkat, treated (left) or non-treated (right) with BioLegend's anti-human CD95 (EOS9.1) mAb (cat. 305704) for 4 hours at 37°C, then stained with Annexin V- PE/Dazzle™ 594 for 15 minutes at 37°C. Helix NP Green at 1.25µM final concentration (cat. 425303) was added before running sample.)
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 640955 | 25 tests | $136 | ||||
| 640956 | 100 tests | $347 | ||||
Annexin V (or Annexin A5) is a member of the annexin family of intracellular proteins that binds to phosphatidylserine (PS) in a calcium-dependent manner. PS is normally only found on the intracellular leaflet of the plasma membrane in healthy cells, but during early apoptosis, membrane asymmetry is lost and PS translocates to the external leaflet. Fluorochrome-labeled Annexin V can then be used to specifically target and identify apoptotic cells. Annexin V Binding Buffer (Cat. No. 422201) is recommended for use with Annexin V staining. Annexin V binding alone cannot differentiate between apoptotic cells and necrotic. Therefore, we recommend using our Helix NP™ Blue (Cat No. 425305), Helix NP™ Green (Cat No. 425303) or Helix NP™ NIR (Cat. No. 425301). Early apoptotic cells will exclude 7-AAD and PI, while late stage apoptotic cells and necrotic cells will stain positively, due to the passage of these dyes into the nucleus where they bind to DNA.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Reported Reactivity
- Other Species
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA)
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with PE/Dazzle™ 594 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this product is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per 100,000 - million cells in a 100 µl volume of Annexin V Binding Buffer (Cat No. 422201). It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
* PE/Dazzle™ 594 has a maximum excitation of 566 nm and a maximum emission of 610 nm. - Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Annexin V Staining
- Wash cells twice with cold BioLegend Cell Staining Buffer (Cat. No. 420201) and then resuspend cells in Annexin V Binding Buffer (Cat. No. 422201) at a concentration of 1x106 cells/mL.
- Transfer 100 µL of cell suspension in 5 mL test tube.
- Add 5 µL of fluorochrome conjugated Annexin V.
- Stain with a viability dye, such as PI (Cat. No. 421301), 7-AAD (Cat. Nos. 420403 & 420404), or Helix NP dyes (Cat. Nos. 425301, 425303, & 425305), if desired.
- Gently vortex the cells and incubate for 15 min at RT (25°C) in the dark.
- Add 400* µL of Annexin V Binding Buffer (Cat. No. 422201) to each tube. *For more concentrated samples, add a minimum of 200 µl of Annexin V Binding Buffer in this step.
- Analyze by flow cytometry.
For a better experience detecting apoptosis, we now recommend Apotracker™. Cell staining with Apotracker™ is Calcium independent. Thus, no special buffers are required, and the protocol can be shortened for single-step co-staining with other reagents.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Koopman G, et al. 1994. Blood 84:1415.
- Vermes I, et al. 1995. J. Immunol. Methods 184:39.
- Dachary-Prigent J, et al. 1993. Blood 81:2554.
- Sekine C, et al. 2009. Int Immunol. PubMed
- Grujic M, et al. 2010. J. Immunol. 185:1730. PubMed
- Hussain MS, et al. 2013. Hum Mol Genet. 22:5199. PubMed
- Feng Q, et al. 2014. PLoS One. 9:95927. PubMed
- Isobe T, et al. 2014. eLife. 3:1977. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
not an antibody (BioLegend Cat. No. 640955)
not an antibody (BioLegend Cat. No. 640956)
Antigen Details
- Biology Area
- Apoptosis/Tumor Suppressors/Cell Death, Cell Biology, Neuroscience
- Gene ID
- 308 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Annexin V on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- How is your Annexin made and what sequence does it cover?
-
It is made in E. coli, covering human aa Met1-Asp320.
- How does pH and staining temperature affect Annexin V-Phosphatidylserine binding?
-
Annexin-Phosphatidylserine binding is lost below pH 5.2 and with prolonged incubation over a temperature of 42°C.
- Why do I need to use Annexin V Binding Buffer?
-
Annexin V binding requires the presence of calcium in the solution. So, we provide Annexin V Binding Buffer (cat # 422201), which is optimized for the best performance of Annexin V staining.
- Can I use RPMI during Annexin V staining?
-
It is best to follow protocol as described on the product data sheet. Moreover, RPMI 1640 has a relatively high concentration of phosphate and low calcium ion concentration, which negatively impacts Annexin binding to its target phosphatidylserine (PS). Measurement of cell death by using Annexin V may also be significantly affected by time of incubation on ice, calcium concentration, and type of medium.
- Can I freeze Annexin V conjugates?
-
It should not be frozen as it will lead to loss of biological activity due to dimerization.
- Is Annexin V suitable for conjugation with the Maxpar® kit for CyTOF®?
-
Maxpar® Labeling kits require the protein to be partially reduced, so the metal chelate can be introduced through an SH group in the hinge region of the reduced antibody. Human Annexin V contains only one Cysteine which was reported to be chemically inactive. Thus, the Maxpar® labeling protocol would not work with Annexin V, unless a free –SH group can be introduced to Annexin V. For more information regarding SH-mediated conjugation of Annexin V please consult published papers such as this one.
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.

 Login/Register
Login/Register 















Follow Us