- Clone
- W18224A (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- mLST8, mTOR Associated Protein, LST8 Homolog, Target Of Rapamycin Complex Subunit LST8, Mammalian Lethal With SEC13 Protein 8
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
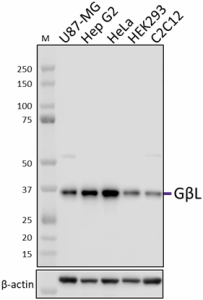
Whole cell extracts (15 µg protein) from the indicated cell lines were resolved by 4-12% Bis-Tris gel electrophoresis, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and probed with 1.0 µg/mL (1:500 dilution) of purified anti-GβL antibody (clone W18224A) overnight at 4°C. Proteins were visualized by chemiluminescence detection using HRP goat anti-rat IgG antibody (Cat. No. 405405) at a 1:3000 dilution. Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-β-actin antibody (Cat. No. 664804) was used as a loading control at a 1:10000 dilution (lower). Lane M: Molecular weight marker.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 939501 | 25 µg | $101 | ||||
| 939502 | 100 µg | $253 | ||||
In eukaryotic cells, the serine/threonine kinase mTOR plays a critical role in regulating cell proliferation and metabolism in response to nutrient availability, cellular energy status, growth factors, and stress. mTOR is found as a component of two functionally distinct oligomeric complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2. mTORC1 coordinates nutrient availability with cell growth and proliferation through phosphorylation of upstream regulators of proliferation and ribosomal biogenesis including 4E-BP1, p70 S6 Kinase 1, and p70 S6 Kinase 2. mTORC2 regulates proliferation and metabolism via phosphorylation of IG-1R, InsR, and Akt, and also plays a role in cytoskeletal architecture and reorganization through modification of Rac1. Both mTORC1 and mTORC2 can drive metabolic adaptation of tumors.
GβL, also referred to as mLST8, is a critical structural and scaffolding component of both mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling complexes. GβL increases mTOR kinase activity by stabilizing the mTOR active site through a direct interaction with the kinase domain. GβL association with mTORC2 is regulated through the action of the TRAF2 E3 ubiquitin ligase, which polyubiquitinates GβL and disrupts its interaction with the mTORC2 assembly factor SIN1. This modification results in a commensurate increase in formation of the mTORC1 complex, which lacks SIN1. Conversely, the deubiquitinating enzyme OTUD7B removes polyubiquintin chains from GβL, thereby promoting assembly of mTORC2.
Product Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- Full-length recombinant human GβL protein
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
WB - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by western blotting. For western blotting, the suggested use of this reagent is 0.5 - 1.0 µg/mL. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
This clone was tested for ICC using HeLa cells fixed with 4% PFA and permeabilized with either Triton X-100 or methanol. Both methods resulted in poor GßL staining.
This clone failed to immunoprecipitate GßL from whole cell extracts prepared from HeLa cells. - RRID
-
AB_2876768 (BioLegend Cat. No. 939501)
AB_2876768 (BioLegend Cat. No. 939502)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- GβL is a 326 amino acid protein with a predicted molecular weight of 36 kD.
- Distribution
-
Ubiquitously expressed/Cytosol
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Protein Synthesis
- Antigen References
-
- Yu XN, et al. 2020. Ann Surg Oncol. 27:1546-1557.
- Hwang Y, et al. 2019. Cancer Res. 79:3178-3184.
- Wang B, et al. 2017. Nature. 545:365-369.
- Kakumoto K, et al. 2015. PLoS One. 10:e0119015.
- Gene ID
- 64223 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about GbetaL on UniProt.org
Other Formats
View All GβL Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-GβL | W18224A | WB |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-GβL
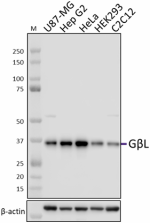
Whole cell extracts (15 µg protein) from the indicated cell ...
 Login/Register
Login/Register 







Follow Us