- Clone
- O91E9 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Transcription factor MafB, V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog B, MAF bZIP transcription factor B, KRML, MCTO, DURS3,
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG2b, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
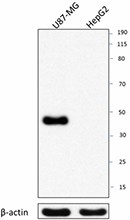
-

Total protein extracts (15 µg protein) from U87-MG and HepG2 (negative control) were resolved by 4-12% Bis-tris gel electrophoresis, transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with 1 µg/mL purified anti-MAFB (clone O91E9) antibody. Proteins were visualized using a goat anti-mouse-IgG secondary antibody conjugated to HRP and chemiluminescence detection. Purified anti-β-actin (clone Poly6221) antibody was used as a loading control.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 692302 | 25 µg | $106 | ||||
MAFB belongs to the Maf transcription factor family, the members of which contain basic leucine zipper (bZIP) domains that bind to DNA. These bZIP domains are located within the Maf recognition element (MARE) and regulate the transcription by binding to acidic domains within the target genes. MAFB plays roles in differentiation processes, including the differentiation of macrophage, pancreatic alpha and beta cells, podocytes in the renal glomerulus, and rhombomeres in the embryonic brain. MAFB is also central to embryonic thymus development, parathyroid gland development, the creation of hair cuticles, and urethral masculinization. In the hematopoietic system, MAFB is important for myeloid lineage commitment of hematopoietic stem cells. MAFB was recently reported to have features of oncogene. It was viewed as a sensitive and specific marker for poor prognosis in multiple myeloma patients. Silencing of MAFB inhibited migration and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. In liver cancer, MAFB promotes cancer cell proliferation by transcriptionally targeting Cyclin D1.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Recombinant human MAFB protein fragment produced in 293T cells.
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
WB - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by Western blotting. For Western blotting, the suggested use of this reagent is 0.25 - 2.0 µg per ml. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- RRID
-
AB_2632763 (BioLegend Cat. No. 692302)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- 323 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of 36 kD.
- Distribution
-
Nucleus
- Function
- Acts as a transcriptional activator or repressor. Plays a pivotal role in regulating lineage-specific hematopoiesis by repressing ETS1-mediated transcription of erythroid-specific genes in myeloid cells.
- Interaction
- Homodimer or heterodimer with other bHLH-Zip transcription factors. Binds DNA as a homodimer or a heterodimer. Forms homodimers and heterodimers with FOS, FOSB and FOSL2. Interacts with PAX6, ETS1 and LRP1.
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Transcription Factors
- Antigen References
-
1. Kataoka K, et al. 1994. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:700.
2. Eychene A, et al. 2008. Nat. Rev. Cancer 8:683.
3. Miyai M, et al. 2010. J. Dermatol. Sci. 57:178.
4. Suzuki K, et al. 2014. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111:16407.
5. Sarrazin S, et al. 2009. Cell. 138:300.
6. Vicente-Duenas C, et al. 2012. EMBO J. 31:3704.
7. Yang W, et al. 2015. BMC Cancer 15:461.
8. Yu H, et al. 2016. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 39:700. - Gene ID
- 9935 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about MAFB on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All MAFB Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-MAFB | O91E9 | WB |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-MAFB
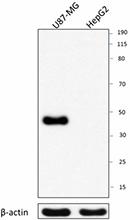
Total protein extracts (15 µg protein) from U87-MG and HepG2...

 Login/Register
Login/Register 







Follow Us