- Clone
- 1D7-B9-C8-F6 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2)
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG2b, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
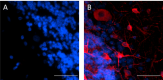
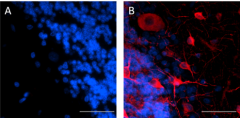
IHC staining of Purified anti-MAP2 (clone 1D7-B9-C8-F6) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human cerebellum tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Citrate Buffer, 10X (Cat. No. 420902), the tissue was incubated without (panel A) and with (panel B) 10 µg/mL of Purified anti-MAP2 (clone 1D7-B9-C8-F6) followed by incubation with Alexa Fluor® 647 goat anti-mouse IgG (Cat. No. 405322) for 1 hour at room temperature. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (Cat. No. 422801). Images were captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm -

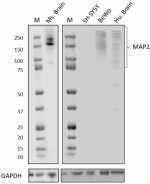
Whole cell extracts (15 µg total protein) from indicated cell lines and/or tissues were resolved by 4-12% Bis-Tris gel electrophoresis, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and probed with 1 µg/mL of Purified anti-MAP2 (clone 1D7-B9-C8-F6) overnight at 4°C. Proteins were visualized by chemiluminescence detection using HRP Goat anti-mouse IgG (Cat. No. 405306). Direct-Blot™ HRP anti-GAPDH (Cat. No. 607903) was used as a loading control at a 1:50000 Dilution. Western-Ready™ ECL Substrate Premium Kit (Cat. No. 426319) was used as a detection agent. Lane M: Molecular weight marker
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 631151 | 25 µg | $175 | ||||
| 631152 | 100 µg | $440 | ||||
Microtubules are 25 nm diameter protein rods found in most kinds of eukaryote cells. They are polymerized from a dimeric subunit made of one α subunit and one β tubulin subunit. Microtubules are associated with a family of proteins called microtubule associated proteins (MAPs), which includes the protein τ (tau) and a group of proteins referred to as MAP1, MAP2, MAP3, MAP4 and MAP5. MAP2 undergoes alternative splicing which results in four isoforms: MAP2A, MAP2B, MAP2C and MAP2D. MAP2A and MAP2B result in proteins with an apparent molecular weight of ~280 kD. MAP2C and MAP2D are smaller molecular weight proteins which correspond protein bands running at ~70-75 kD on SDS-PAGE gels. All these MAP2 isoforms share a C-terminal core sequence which includes either three or four microtubule binding domains, which are very similar to those found in the related microtubule binding protein τ (tau). MAP2 isoforms are expressed only in neuronal cells and specifically in the perikarya and dendrites of these cells. Antibodies to MAP2 are therefore excellent markers for neuronal cells, their perikarya and neuronal dendrites.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse, Human
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- Recombinant fragment of the N-terminus of human MAP2
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
IHC-P - Quality tested
WB - Verified - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded immunohistochemical staining. For immunohistochemistry, a concentration range of 1.0 - 10.0 µg/mL is suggested. For western blotting, the suggested use of this reagent is 0.25 - 1.0 µg/mL. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
This antibody (clone 1D7-B9-C8-F6) works with both Sodium Citrate H.I.E.R. (Cat. No. 928502) and Tris-EDTA pH 9.0 (10mM Tris, 1mM EDTA) antigen retrieval buffers, however, signal to noise ratio is higher using Sodium Citrate.
This antibody (clone 1D7-B9-C8-F6) is not suitable for immunocytochemistry. - RRID
-
AB_3097544 (BioLegend Cat. No. 631151)
AB_3097544 (BioLegend Cat. No. 631152)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- MAP2 is a 1,827 amino acid protein with a predicted molecular weight of 199.5 kD.
- Distribution
-
Cellular distribution: plasma membrane, cytoskeleton, nucleus, and cytosol
Tissue distribution: Predominantly in the nervous system - Function
- Microtubule assembly
- Interaction
- MAP2 interacts with microtubules. It has also been reported to interact with KNDC1 via KIND2.
- Cell Type
- Neural Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Microtubules
- Antigen References
-
- De Camilli P, et al. 1984. Neuroscience. 11:817-46.
- Bloom GS, et al. 1984. J Cell Biol. 98:320-30.
- Maschietto M, et al. 2013. Front Cell Neurosci. 25:7.
- La Via L,et al. 2013. Nucelic Acids Res. 41:617-31.
- Ji B, et al. 2014. Hum Mol Genet. 23:5683-705.
- Fu X, et al. 2013. J Neurosci. 33:709.
- Gene ID
- 4133 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about MAP2 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All MAP2 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-MAP2 | 1D7-B9-C8-F6 | IHC-P,WB |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
 Login/Register
Login/Register 







Follow Us