
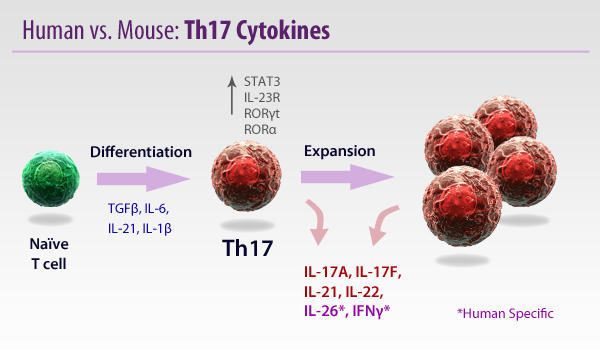
CD4+ T helper (Th) cells are critical mediators of host immune responses. Based on transcription factors and cytokine production, Mossman and Coffman delineated two main classes of helper cells: Th1 and Th2.
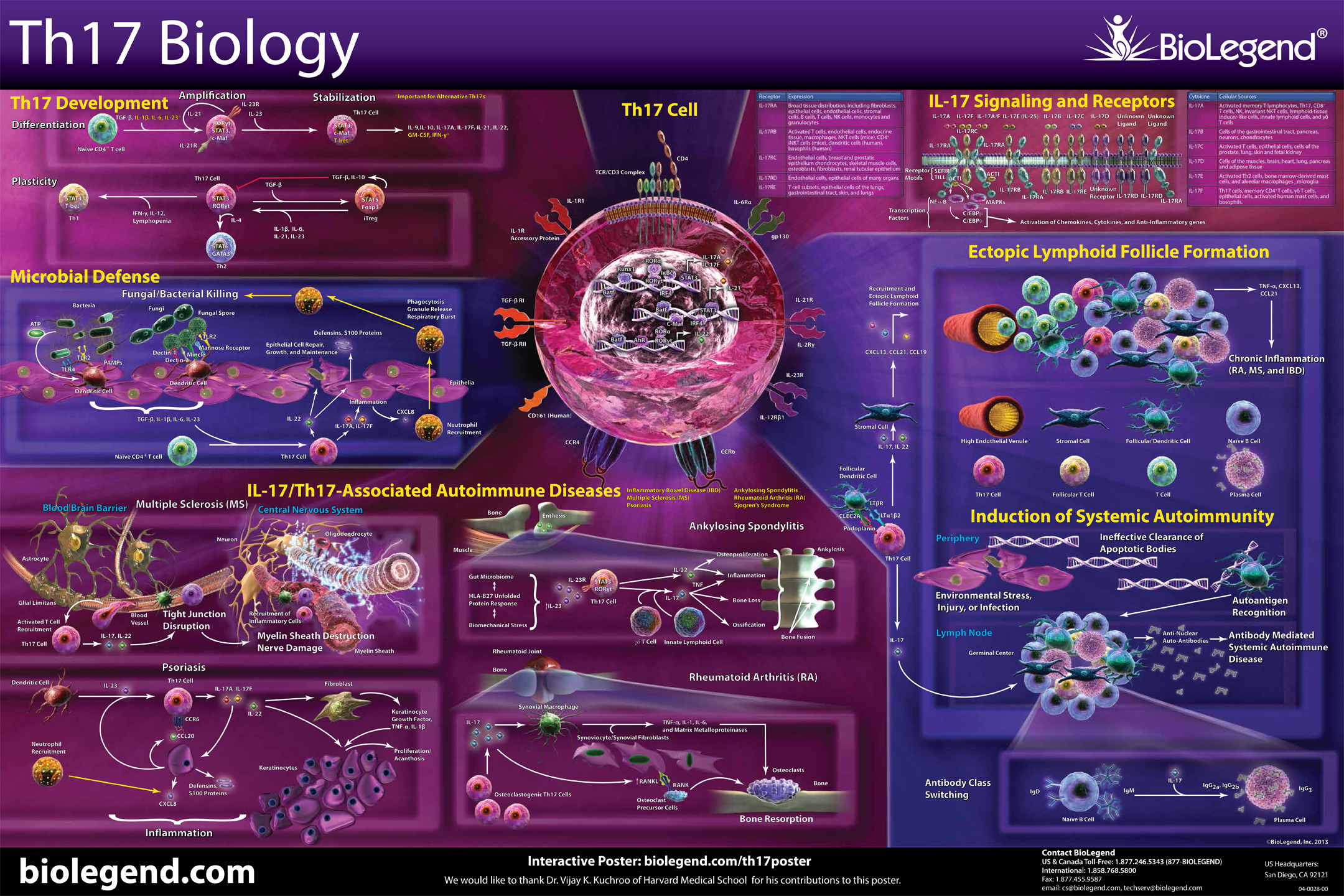
While investigating the role of IL-12, a Th1 promoting cytokine in a murine model of EAE, Cua et al. surprisingly found that elimination of IL-12 exacerbated disease. IL-12 is composed of p35 and p40 subunits. IL-23, an IL-12 family member, also utilizes p40, but is completed by the p19 subunit. Realizing this, Cua demonstrated the elimination of IL-23 specific p19, but not p35 (IL-12), protected the mice from disease onset. Thus, a third T Helper class was discovered and dubbed Th17 Cells.
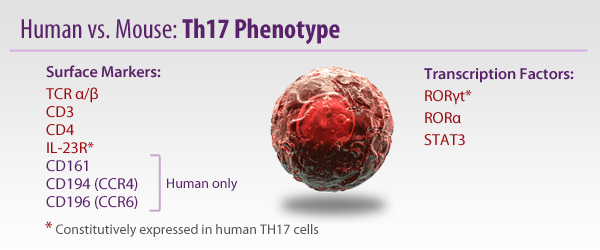
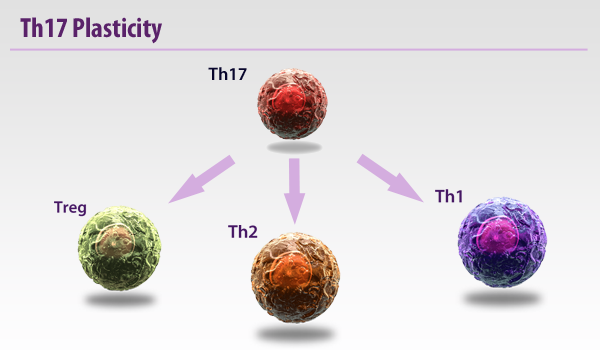
Whereas Th1s are involved with intracellular defense and Th2s are associated with antibody or humoral responses, Th17s have been found to be vital in extracellular pathogen defense. Th17s are intimately involved with the elimination of bacteria such as K. pneumoniae, B. fragilis, C. rodentium, E. coli, and some fungal species. Due to their prolific inflammatory ability, they have been implicated in some autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis. However, there are some reports that Th17s can maintain a protective effect, particularly in the gut.
References:
Annunziato F, et al. 2008. Int. Immunol. 20:1361.
Cua DJ, et al. 2003. Nature. 421:744.
Mosmann TR, et al. 1986. J. Immunol. 136:2348.
 Login/Register
Login/Register 






Follow Us