- Clone
- 429 (MVCAM.A) (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- VCAM-1, INCAM-110
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
_AF647_CD106_Antibody_1_FC_011108.jpg&Width=240&Height=300&altFmImage_path=&Compression=90&Crop=5)
-
_AF647_CD106_Antibody_1_FC_011108.jpg&Height=80&altFmImage_path=&Compression=90&Crop=5)
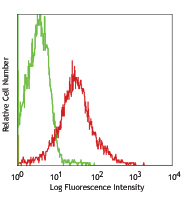
C57BL/6 bone marrow myeloid cells stained with 429 Alexa Fluor® 647 -
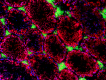
C57BL/6 mouse frozen testis section was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10 minutes at room temperature and blocked with 5% FBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Then the section was stained with 10 µg/mL of CD106 (clone 429 (MVCAM.A)) Alexa Fluor® 647 (green) and 10 µg/mL of CD117 (clone 2B8) Alexa Fluor® 594 (red) overnight at 4°C. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). The image was captured by 10X objective. -
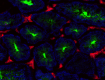
Dissected C57/B6 mouse testis was immersed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) overnight followed by 30% sucrose immersion overnight and frozen in OCT. Frozen section was blocked with 5% FBS and 5% mouse serum for 30 minutes at room temperature. Then the tissue section was stained with 5 µg/mL of anti-mouse CD147 (clone OX-114) Alexa Fluor® 594 (green) and CD106 (clone 429 (MVCAM.A)) Alexa Fluor® 647 (red) overnight at 4°C. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). The image was captured by 10X objective. -
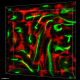
Formalin-fixed, 300 micron-thick mouse testis section was blocked, permeabilized and stained overnight with CD106 (clone 429, MCVAM.A) Alexa Fluor® 647 (red), and CD147 (clone OX-114) Alexa Fluor® 488 (green) both at 5 µg/mL, optically cleared, and analyzed at 225 µm imaging depth on a confocal microscope. Watch the video. -
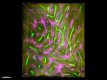
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (4%), 500 µm-thick mouse testis section was processed according to the Ce3D™ Tissue Clearing Kit protocol (Cat. No. 427701). The section was costained with anti-mouse CD147 Antibody (clone OX-114) Alexa Fluor® 488 at 5 µg/mL (green), anti-mouse CD117 (c-Kit) Antibody (clone 2B8) Alexa Fluor® 594 at 5 µg/mL (yellow), and anti-mouse CD106 Antibody (clone 429 (MVCAM.A)) Alexa Fluor® 647 at 5 µg/mL (magenta) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). The section was then optically cleared and mounted in a sample chamber. The image was captured with a 10X objective using Zeiss 780 confocal microscope and processed by Imaris image analysis software.
Watch the video.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 105711 | 25 µg | 101 CHF | ||||
| 105712 | 100 µg | 229 CHF | ||||
CD106 is a 110 kD glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked transmembrane protein, also known as VCAM-1 and INCAM-110. It is constitutively expressed on bone marrow stromal cells, myeloid progenitors, splenic dendritic cells, activated endothelial cells, as well as some lymphocytes. CD106 expression can be upregulated on endothelial cells by inflammatory cytokines. CD106 is involved in adhesion and acts as a counter-receptor for VLA-4 (α4/β1 integrin) and LPAM-1 (α4/β7 integrin). The 429 antibody has been reported to partially block VCAM-1-mediated binding.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- Mouse preadipose cell line PA6
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with Alexa Fluor® 647 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
IHC-F, 3D IHC - Verified - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤ 0.25 µg per 106 cells in 100 µL volume. For immunohistochemical staining on frozen tissue sections, the suggested use is 2.5 - 10 µg/mL. For 3D immunohistochemistry on formalin-fixed tissues, a concentration of 5.0 µg/mL is suggested. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for other applications.
* Alexa Fluor® 647 has a maximum emission of 668 nm when it is excited at 633nm / 635nm.
Alexa Fluor® and Pacific Blue™ are trademarks of Life Technologies Corporation.
View full statement regarding label licenses - Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunohistochemical staining2,3,5-7 of acetone-fixed frozen sections, blocking4,5,8 of ligand binding in vitro and in vivo, immunoprecipitation1 , and spacial biology (IBEX)11,12. The Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin < 0.01 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for functional assays (Cat. No. 105727 & 105728).
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Kinashi T, et al. 1995. J. Leukoc. Biol. 57:168. (IP)
- Koni PA, et al. 2001. J. Exp. Med. 193:741. (IHC)
- Ishiyama N, et al. 1998. Pathobiology 66:274. (IHC)
- Kinashi T, et al. 1994. Blood Cells 20:25. (Block)
- Baron JL, et al. 1994. J. Clin. Invest. 93:1700. (Block IHC)
- Buck CA, et al. 1996. Cell Adhes. Commun. 4:69. (IHC)
- Hata H, et al. 2004. J. Clin. Invest. 114:582. (IHC)
- Meunier MC, et al. 2005. Nature Medicine 11:1222. (Block) PubMed
- Monnier J, et al. 2012. J. Immunol. 189:956. PubMed
- Motohashi N, et al. 2013. J Cell Sci. 126:2678. PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2020. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117:33455-65. (SB) PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2022. Nat Protoc. 17:378-401. (SB) PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_493430 (BioLegend Cat. No. 105711)
AB_493429 (BioLegend Cat. No. 105712)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Ig superfamily, 47 kD
- Distribution
-
Bone marrow stromal cells, myeloid progenitors, splenic dendritic cells, activated endothelial cells
- Function
- Adhesion
- Ligand/Receptor
- VLA-4 (α4/β1 integrin) and LPAM-1 (α4/β7 integrin)
- Cell Type
- Dendritic cells, Endothelial cells, Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Adhesion, Cell Biology, Immunology, Neuroinflammation, Neuroscience, Stem Cells
- Molecular Family
- Adhesion Molecules, CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Barclay AN, et al. 1997. The Leukocyte Antigen FactsBook Academic Press.
2. Kinashi T, et al. 1995. J. Leukoc. Biol. 57:168.
3. Bevilacquea MP. 1993. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 11:767.
4. Koni PA, et al. 2001. J. Exp. Med. 193:741. - Gene ID
- 22329 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD106 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All CD106 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Biotin anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | FC |
| FITC anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | FC |
| LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | FC, IHC-F, IP |
| Purified anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | FC,IHC-F,IP |
| Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | FC,IHC-F,SB |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | FC,IHC-F,3D IHC |
| PE anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | FC |
| PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | FC |
| APC anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | FC |
| PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | FC |
| Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | FC |
| Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | IHC-F |
| TotalSeq™-A0226 anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | PG |
| Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | FC,IHC-F,IP |
| TotalSeq™-C0226 anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | PG |
| TotalSeq™-B0226 anti-mouse CD106 | 429 (MVCAM.A) | PG |
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Biotin anti-mouse CD106
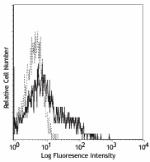
C57BL/6 bone marrow myeloid cells stained with 429 FITC -
FITC anti-mouse CD106

C57BL/6 bone marrow myeloid cells stained with 429 FITC -
LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse CD106

C57BL/6 bone marrow myeloid cells stained with 429 FITC -
Purified anti-mouse CD106
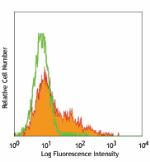
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow myeloid cells stained with 429 pur... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD106
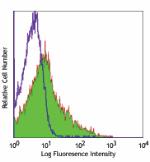
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells stained with 429 Alexa Fluor... 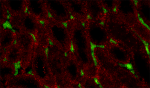
C57BL/6 mouse frozen testis section was fixed with 4% parafo... 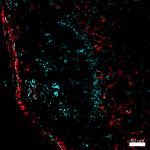
Mice were injected subcutaneously with sheep red blood cells... 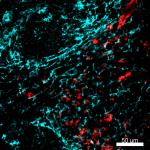
Mice were injected subcutaneously with sheep red blood cells... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD106
_AF647_CD106_Antibody_1_FC_011108.jpg&Width=150&altFmImage_path=&Crop=5)
C57BL/6 bone marrow myeloid cells stained with 429 Alexa Flu... 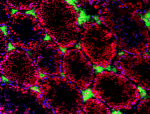
C57BL/6 mouse frozen testis section was fixed with 4% parafo... 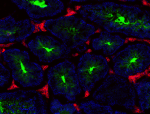
Dissected C57/B6 mouse testis was immersed in 4% paraformal... 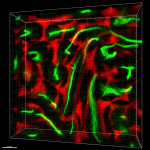
Formalin-fixed, 300 micron-thick mouse testis section was bl... 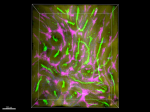
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (4%), 500 µm-thick mouse testis secti... -
PE anti-mouse CD106
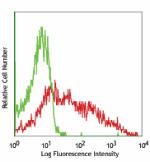
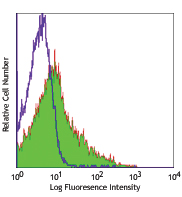
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with 429 PE (gated on myel... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD106
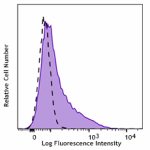
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells stained with CD106 (clone 42... -
APC anti-mouse CD106
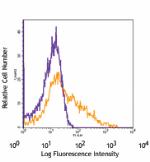
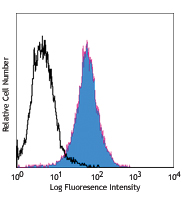
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells stained with 429 APC -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD106
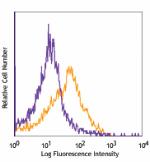
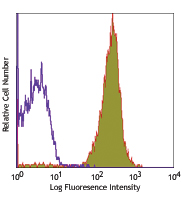
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with 429 PE/Cyanine7 -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse CD106

C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with 429 Pacific Blue&trad... 
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with rat IgG2a isotype con... -
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-mouse CD106
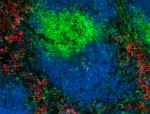
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... 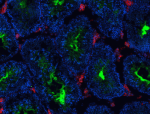
Dissected C57/B6 mouse testis was immersed in 4% paraformal... -
TotalSeq™-A0226 anti-mouse CD106
-
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse CD106

C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow myeloid cells stained with 429 pur... -
TotalSeq™-C0226 anti-mouse CD106
-
TotalSeq™-B0226 anti-mouse CD106
 Login / Register
Login / Register 













Follow Us