- Clone
- SMI 310 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Neurofilament heavy polypeptide, NF-H, 200 kD neurofilament protein, neurofilament triplet H protein
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
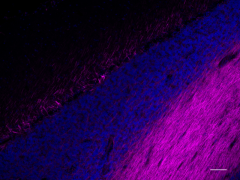
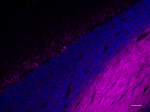
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosphorylated antibody (clone SMI 310) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human cerebellum tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Retrieve-All Antigen Unmasking System 3 (Cat. No. 927801), the tissue was incubated with the primary antibody at 10 µg/mL overnight at 4°C. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. The image was captured with a 10X objective. Scale bar: 100 µm -
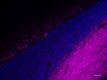
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosphorylated antibody (clone SMI 310) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human cerebellum tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Retrieve-All Antigen Unmasking System 3 (Cat. No. 927801), the tissue was incubated with the primary antibody at 10 µg/mL overnight at 4°C. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm -
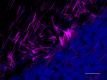
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosphorylated antibody (clone SMI 310) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded mouse cerebellum tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Retrieve-All Antigen Unmasking System 3 (Cat. No. 927801), the tissue was incubated with the primary antibody at 5 µg/mL overnight at 4°C. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. The image was captured with a 10X objective. Scale bar: 100 µm -
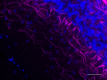
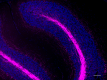
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosphorylated antibody (clone SMI 310) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded mouse brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Retrieve-All Antigen Unmasking System 3 (Cat. No. 927801), the tissue was incubated with the primary antibody at 5 µg/mL overnight at 4°C. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm -
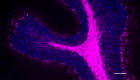
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosphorylated antibody (clone SMI 310) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded rat cerebellum tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Retrieve-All Antigen Unmasking System 3 (Cat. No. 927801), the tissue was incubated with the primary antibody at 5 µg/mL overnight at 4°C. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. The image was captured with a 10X objective. Scale bar: 100 µm -
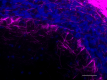
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosphorylated antibody (clone SMI 310) on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded rat brain tissue. Following antigen retrieval using Retrieve-All Antigen Unmasking System 3 (Cat. No. 927801), the tissue was incubated with the primary antibody at 5 µg/mL overnight at 4°C. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. The image was captured with a 40X objective. Scale bar: 50 µm
| Cat # | Size | Price | Save |
|---|---|---|---|
| 837709 | 25 µg | ¥34,980 | |
| 837710 | 100 µg | ¥71,060 |
Neurofilaments (NF) are approximately 10 nanometer intermediate filaments found in neurons. They are a major component of the neuronal cytoskeleton, and function primarily to provide structural support for the axon and regulate axon diameter. There are three major NF subunits, and the names given to these subunits are based upon the apparent molecular mass of the mammalian subunits on SDS-PAGE: the light or lowest (NF-L) runs at 68-70 kD; the medium or middle (NF-M) runs at about 145-160 kD; the heavy or highest (NF-H) runs at 200-220 kD. However, the actual molecular weight of these proteins is considerably lower due to the highly charged C-terminal regions of the molecules. The level of NF gene expression correlates with axonal diameter, which controls how fast electrical signals travel down the axon. Mutant mice with NF abnormalities have phenotypes resembling amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. NF immunostaining is common in diagnostic neuropathology. It is useful for differentiating neurons (positive for NF) from glia (negative for NF).
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with Alexa Fluor® 647 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
IHC-P - Quality tested
SB - Reported in the literature, not verified in house
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded immunohistochemical staining. For immunohistochemistry, a concentration range of 5.0 - 10 µg/ml is suggested. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
* Alexa Fluor® 647 has a maximum emission of 668 nm when it is excited at 633 nm / 635 nm.
Alexa Fluor® and Pacific Blue™ are trademarks of Life Technologies Corporation.
View full statement regarding label licenses - Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: Western blotting4, immunocytochemistry2, immunohistochemical staining of frozen tissue sections1,3, and spatial biology (IBEX)5,6.
Clone SMI 310 reacts with an extensively phosphorylated epitope of neurofilament H and, to a much lesser extent, neurofilament M in most mammalian species. Phosphatase treatment of samples abolishes reaction with SMI 310. A very extensive degree of hyperphosphorylation of neurofilaments seems to be necessary for its reactivity.
- Additional Product Notes
-
Iterative Bleaching Extended multi-pleXity (IBEX) is a fluorescent imaging technique capable of highly-multiplexed spatial analysis. The method relies on cyclical bleaching of panels of fluorescent antibodies in order to image and analyze many markers over multiple cycles of staining, imaging, and, bleaching. It is a community-developed open-access method developed by the Center for Advanced Tissue Imaging (CAT-I) in the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID, NIH).
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Dubourg O, et al. 2011. Acta Myol. 30(2):103. (IHC-F) PubMed
- Mizui T, et al. 2009. J Neurochem. 109(2):611. (ICC)
- Denlger-Crish C, et al. 2014. Front Neursci. 8:290. (IHC-F) PubMed
- Mulot SF, et al. 1994. FEBS Lett. 349(3):359. (WB)
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2020. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117:33455-65. (SB) PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2022. Nat Protoc. 17:378-401. (SB) PubMed
- RRID
-
AB_2734612 (BioLegend Cat. No. 837709)
AB_2734613 (BioLegend Cat. No. 837710)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- The medium or middle neurofilament (NF-M) runs at 145-160 kD, and the heavy or highest neurofilament (NF-H) runs at 200-220 kD.
- Distribution
-
Tissue distribution: CNS, peripheral nerves and glandular cells of the prostate.
Cellular distribution: Cytoskeleton, nucleus, cytosol, and mitochondrion. - Function
- Neurofilaments are the major components of the neuronal cytoskeleton. They provide axonal support and regulate axon diameter.
- Interaction
- Cell bodies and dendrites are generally unstained while other cells and tissues are unreactive, except for peripheral axons.
- Cell Type
- Mature Neurons
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers
- Molecular Family
- Intermediate Filaments, Phospho-Proteins
- Antigen References
-
- Siedler D, et al. 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 8:429.
- Gene ID
- 4744 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Neurofilament HM NF-H NF-M Phospho on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All Neurofilament H&M (NF-H/NF-M), Phospho Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosphorylated | SMI 310 | IHC-P,WB,IHC-F,ICC |
| Biotin anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosphorylated | SMI 310 | WB |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosphorylated | SMI 310 | IHC-P |
| Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosphorylated | SMI 310 | IHC-P |
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Purified anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosphorylated
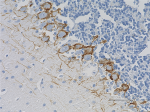
IHC staining of purified anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M... 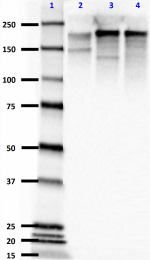
Western blot of purified anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M... -
Biotin anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosphorylated
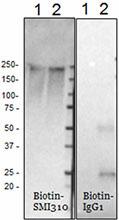
Western blot of anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosph... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosphorylated
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Neurofilament H & M (N... 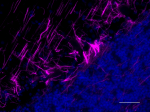
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Neurofilament H & M (N... 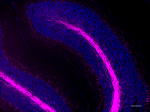
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Neurofilament H & M (N... 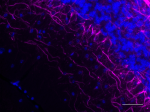
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Neurofilament H & M (N... 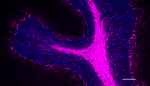
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Neurofilament H & M (N... 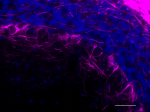
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-Neurofilament H & M (N... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-Neurofilament H & M (NF-H/NF-M), Phosphorylated
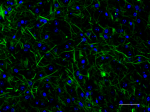
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-Neurofilament H & M (N... 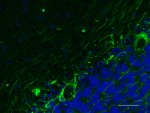
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-Neurofilament H & M (N... 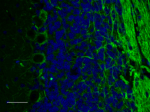
IHC staining of Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-Neurofilament H & M (N...












Follow Us