- Clone
- 16-10A1 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- B7-1, B7, Ly-53
- Isotype
- Armenian Hamster IgG
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
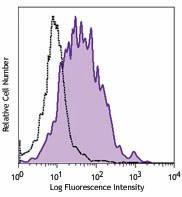
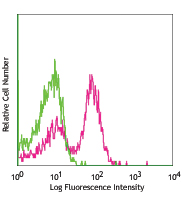
LPS-stimulated (day 3) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD80 (clone 16-10A1) PE/Cyanine7 (filled histogram) or Armenian hamster IgG PE/Cyanine7 isotype control (open histogram).
| Cat # | Size | Price | Save |
|---|---|---|---|
| 104733 | 25 µg | ¥25,520 | |
| 104734 | 100 µg | ¥64,240 |
CD80 is a 60 kD highly glycosylated protein. It is a member of the Ig superfamily and is also known as B7-1, B7, and Ly-53. CD80 is constitutively expressed on dendritic cells and monocytes/macrophages, and inducibly expressed on activated B and T cells. The ligation of CD28 on T cells with CD80 and CD86 (B7-2) on antigen presenting cells (such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells) elicits co-stimulation of T cells resulting in enhanced cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. CD80 appears to be expressed later in the immune response than CD86. CD80 can also bind to CD152, also known as CTLA-4, to deliver an inhibitory signal to T cells.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Reported Reactivity
- Dog
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Armenian Hamster
- Immunogen
- CHO cell line transfected with mouse B7 (CD80)
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with PE/Cyanine7 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤0.5 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunoprecipitation2, in vitro and in vivo blocking of CTLA-4 Ig to CD80 by blocking costimulation of T cells by activated B cells2-4, and immunohistochemical staining of acetone-fixed frozen sections1,4. The Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin < 0.01 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for functional assays (Cat. Nos. 104747-104752).
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Harlan DM, et al. 1994. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:3137. (IHC)
- Razi-Wolf Z, et al. 1992. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:4210. (Block, IP)
- Hathcock KS, et al. 1994. J. Exp. Med. 180:631. (Block)
- Herold KC, et al. 1997. J. Immunol. 158:984. (Block, IHC)
- Ma XT, et al. 2006. Cancer Res. 66:1169.
- Andoniou CE, et al. 2005. Nature Immunology 6:1011. (FC)
- Lawson BR, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:5366.
- Turnquist HR, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:7018.
- Misra RS, et al. 2010. J. Exp Med. 207:1775. PubMed
- del Rio ML, et al. 2011. Transpl. Int. 24:501. (FC) PubMed
- Philipsen L, et al. 2013. Mol Cell Proteomics. 12:2551. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_2563112 (BioLegend Cat. No. 104733)
AB_2563112 (BioLegend Cat. No. 104734)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Ig superfamily, 60 kD
- Distribution
-
Macrophages, activated B cells and T cells, dendritic cells
- Function
- T cell costimulation
- Ligand/Receptor
- CD28 (stimulatory), CD152(CTLA4) (inhibitory)
- Cell Type
- B cells, Dendritic cells, Macrophages, T cells, Tregs
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Costimulatory Molecules, Immunology, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules, Immune Checkpoint Receptors
- Antigen References
-
1. Barclay AN, et al. 1997. The Leukocyte Antigen FactsBook Academic Press.
2. Linsley PS, et al. 1991. J. Exp. Med. 174:561.
3. Salomon B, et al. 2001. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19:225. - Gene ID
- 12519 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD80 on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All CD80 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Biotin anti-mouse CD80
LPS-stimulated (3 days) BALB/c splenocytes were stained with... -
FITC anti-mouse CD80
LPS-stimulated (3 days) BALB/c splenocytes stained with 16-1... -
PE anti-mouse CD80
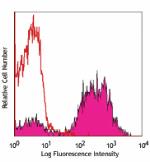
Thioglycolate-elicited Balb/c mouse peritoneal macrophages s... -
Purified anti-mouse CD80
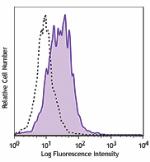
LPS-stimulated (3 days) BALB/c splenocytes stained with puri... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse CD80
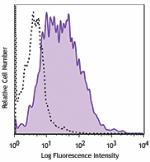
LPS-stimulated (3 days) BALB/c splenocytes were stained with... -
APC anti-mouse CD80
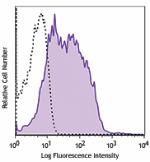
LPS-stimulated (3 days) BALB/c splenocytes were stained with... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD80
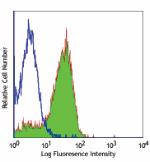
Thioglycolate-elicited Balb/c mouse peritoneal macrophages s... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD80
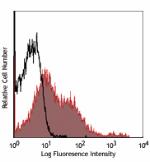
LPS-stimulated (day-3) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained wit... 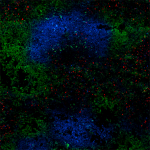
1 week 4T1 cells (mouse breast cancer cell line) induced BAL... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD80
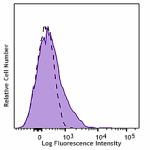
LPS-stimulated (day 3) BALB/c splenocytes were stained with ... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse CD80
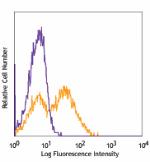
Anti-mouse IgM and CD40 (1C10) stimulated (4 days) C57BL/6 s... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse CD80
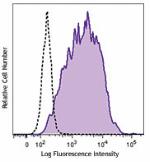
LPS-stimulated (day 3) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained wit... 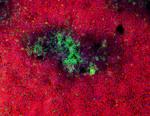
C57BL/6 mouse frozen thymus section was fixed with 4% parafo... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse CD80
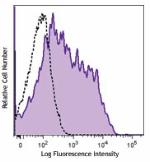
LPS-stimulated (day 3) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were staine... -
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse CD80
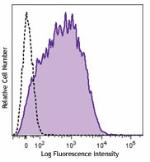
LPS-stimulated (day 3) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were staine... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD80
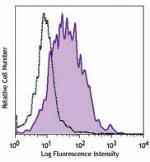
LPS-stimulated (day 3) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were staine... -
Purified anti-mouse CD80 (Maxpar® Ready)
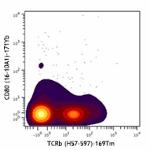
Mouse splenocytes were cultured with either media alone (top... 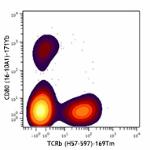
-
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD80
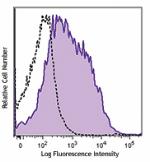
LPS-stimulated (day 3) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained wit... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse CD80
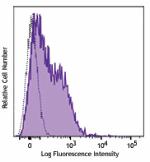
LPS-stimulated (3 days) C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained wit... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse CD80
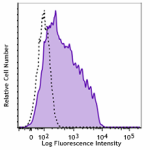
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stimulated with LPS for 3 day... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse CD80
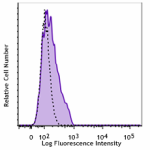
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stimulated with LPS for 3 day... -
TotalSeq™-A0849 anti-mouse CD80
-
TotalSeq™-C0849 anti-mouse CD80
-
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse CD80
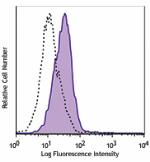
LPS-stimulated (3 days) BALB/c splenocytes stained with LEAF... -
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-mouse CD80
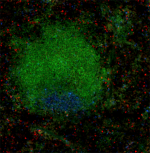
BALB/c mouse was subcutaneous injected with a million of 4T1... -
TotalSeq™-B0849 anti-mouse CD80 Antibody
-
PE/Fire™ 640 anti-mouse CD80
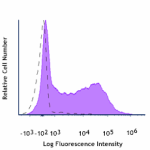
LPS-stimulated (day 3) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were staine... -
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-mouse CD80
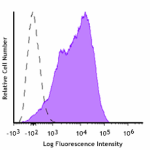
LPS-stimulated (day 3) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were staine... -
Spark Red™ 718 anti-mouse CD80 (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-mouse CD80 (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Spark PLUS B550™ anti-mouse CD80 Antibody

LPS stimulated (3 days) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stain... 
LPS stimulated (3 days) C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stai...














Follow Us